Abstract
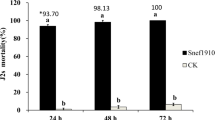
Root-knot nematodes (Meloidogyne spp.) are notorious plant-parasitic nematodes that affect agricultural crops. These obligate soil-dwelling parasites typically maneuver the host plant physiology by forming specialized feeding cells resulting in heavy yield losses. Scant management tools are available to effectively combat this pest. In an exploratory attempt of identifying new fungal biocontrol agent(s) for M. incognita from India, a Paecilomyces tenuis isolate from rhizosphere soil was found to incur > 90% mortality of the infective second-stage juveniles (J2s) at 24 h post-exposure to the fungal filtrate with about 87% parasitization. The fungal filtrate also significantly reduced the egg hatching and host-root penetration of M. incognita under in vitro and in vivo conditions revealing its effectiveness in curbing nematode pathogenicity with positive effects on plant growth. Chromatographic analyses revealed the presence of Huperzine A (433.56 mg L−1) in the P. tenuis isolate. Besides, the isolate possessed acetylcholinesterase inhibition attribute with an IC50 of 2.85 ± 0.12 mg mL−1 of the fungal filtrate. Further, GC-MS analysis revealed the production of other nematicidal compounds by the fungus including acetic acid. To conceptualize the mode of nematicidal action, RNA-Seq was done post-treatment of the M. incognita J2s and model worm Caenorhabditis elegans with fungal filtrate and pure Huperzine A. The transcriptomic profile unraveled the molecular intricacies underlying the nematicidal action affecting several biological pathways and developmental checkpoints of the nematode. Thus, the P. tenuis isolate offers significant potential to be used as a biocontrol agent against M. incognita along with its commercial use for Huperzine A production.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw reads were deposited in the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) database under the BioProject no. PRJNA800591; study accession no. SRP356762; Biosample accession nos. SAMN25258043 and SAMN25258042; and SRA accession nos. SRR17756040–SRR17756055.
References
Abd-Elgawad MM, Askary TH (2018) Fungal and bacterial nematicides in integrated nematode management strategies. Egypt J Biol Pest Control 28:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41938-018-0080-x
Adhikari M, Kim S, Kim HS, Lee HB, Lee YS (2016) Sixteen new records of ascomycetes from crop field soil in Korea. Korea J Mycol 44:271–288. https://doi.org/10.4489/KJM.2016.44.4.271
Ainge GD, Lorimer SD, Gerard PJ, Ruf LD (2002) Insecticidal activity of huperzine A from the New Zealand clubmoss, Lycopodium varium. J Agric Food Chem 50:491–494. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0106087
Aramburu J, Ortells MC, Tejedor S, Buxadé M, López-Rodríguez C (2014) Transcriptional regulation of the stress response by mTOR. Sci Signal 7:re2–re2. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.2005326
Atanasova L, Le Crom S, Gruber S, Coulpier F, Seidl-Seiboth V, Kubicek CP, Druzhinina IS (2013) Comparative transcriptomics reveals different strategies of Trichoderma mycoparasitism. BMC Genom 14:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-14-121
Baazeem A, Alorabi M, Manikandan P, Alotaibi SS, Almanea A, Abdel-Hadi A, Vijayaraghavan P, Raj SRF, Kim YO, Kim HJ (2021) Paecilomyces formosus MD12, a biocontrol agent to treat Meloidogyne incognita on brinjal in green house. J Fungi 7:632. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7348.1989.tb06792.x
Bailey F, Gray NF (1989) The comparison of isolation techniques for nematophagous fungi from soil. Ann Appl Biol 114:125–132. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7348.1989.tb06792.x
Barnes DE, Watabe E, Ono K, Kwak E, Kuroyanagi H, Ono S (2018) Tropomyosin isoforms differentially affect muscle contractility in the head and body regions of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. J Mol Cell Biol 29:1075–1088. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E17-03-0152
Baron NC, de Souza Pollo A, Rigobelo EC (2020) Purpureocillium lilacinum and Metarhizium marquandii as plant growth-promoting fungi. PeerJ 8:e9005. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.9005
Bilal S, Khan AL, Shahzad R, Asaf S, Kang SM, Lee IJ (2017) Endophytic Paecilomyces formosus LHL10 augments Glycine max L. adaptation to Ni-contamination through affecting endogenous phytohormones and oxidative stress. Front Plant Sci 8:870. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00870
Bilal S, Shahzad R, Khan AL, Kang S-M, Imran QM, Al-Harrasi A, Yun B-W, Lee I-J (2018) Endophytic microbial consortia of phytohormones-producing fungus Paecilomyces formosus LHL10 and bacteria Sphingomonas sp. LK11 to Glycine max L. regulates physio-hormonal changes to attenuate aluminum and zinc stresses. Front Plant Sci 9:1273. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01273
Byrd DW Jr, Kirkpatrick T, Barker K (1983) An improved technique for clearing and staining plant tissues for detection of nematodes. J Nematol 15:142–143
Chan YL, Cai D, Taylor PW, Chan MT, Yeh KW (2010) Adverse effect of the chitinolytic enzyme PjCHI-1 in transgenic tomato on egg mass production and embryonic development of Meloidogyne incognita. Plant Pathol 59:922–930. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3059.2010.02314.x
Chen S, Zhou Y, Chen Y, Gu J (2018) Fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 34:i884–i890. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty560
Coleman BR, Ratcliffe RH, Oguntayo SA, Shi X, Doctor BP, Gordon RK, Nambiar MP (2008) [+]-Huperzine A treatment protects against N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced seizure/status epilepticus in rats. Chem Biol Interact 175:387–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2008.05.023
Conesa A, Götz S (2008) Blast2GO: a comprehensive suite for functional analysis in plant genomics. Int J Plant Genomics 2008:619832. https://doi.org/10.1155/2008/619832
Contina JB, Dandurand LM, Knudsen GR (2017) Use of GFP-tagged Trichoderma harzianum as a tool to study the biological control of the potato cyst nematode Globodera pallida. Appl Soil Ecol 115:31–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2017.03.010
Dahlin P, Eder R, Consoli E, Krauss J, Kiewnick S (2019) Integrated control of Meloidogyne incognita in tomatoes using fluopyram and Purpureocillium lilacinum strain 251. Crop Prot 124:104874. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2019.104874
Dash M, Dutta TK, Phani V, Papolu PK, Shivakumara TN, Rao U (2017) RNAi-mediated disruption of neuropeptide genes, nlp-3 and nlp-12, cause multiple behavioral defects in Meloidogyne incognita. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 490:933–940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.06.143
Davies JT, Ireson JE, Allen GR (2005) The impact of gorse thrips, ryegrass competition, and simulated grazing on gorse seedling performance in a controlled environment. Biol Control 32:280–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2004.10.007
De Voer G, Peters D, Taschner PE (2008) Caenorhabditis elegans as a model for lysosomal storage disorders. Biochem Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1782:433–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2008.04.003
Den Belder E, Boekestein A, Van Esch JWJ, Thiel F (1993) Low temperature scanning electron microscopy in fungus-nematode interaction. Scanning 15:37–42. https://doi.org/10.1002/sca.4950150106
Djian C, Pijarowski L, Ponchet M, Arpin N, Favre-Bonvin J (1991) Acetic acid: a selective nematicidal metabolite from culture filtrates of paecilomyces lilacinus (Thom) samson and Trichoderma longibrachiatum Rifai. Nematologica 37:101–112. https://doi.org/10.1163/187529291X00105
Dong LH, Fan SW, Ling QZ, Huang BB, Wei ZJ (2014) Identification of huperzine A-producing endophytic fungi isolated from Huperzia serrata. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30:1011–1017. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-013-1519-6
Douda O, Manasova M, Zouhar M, Hnatek J, Stejskal V (2021) Field validation of the effect of soil fumigation of ethanedinitrile (EDN) on the mortality of Meloidogyne hapla and carrot yield parameters. Agronomy 11:208. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11020208
Du B, Xu Y, Dong H, Li Y, Wang J (2020) Phanerochaete chrysosporium strain B-22, a nematophagous fungus parasitizing Meloidogyne incognita. PLoS ONE 15:e0216688. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0216688
Ehwaeti ME, Phillips MS, Trudgill DL (1998) Dynamics of damage to tomato by Meloidogyne incognita. Fundam Appl Nematol 21:627–635
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V Jr, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-2952(61)90145-9
Faske TR, Hurd K (2015) Sensitivity of Meloidogyne incognita and Rotylenchulus reniformis to fluopyram. J Nematol 47:316–321
Fawcett EM, Hoyt JM, Johnson JK, Miller DL (2015) Hypoxia disrupts proteostasis in C. elegans. Aging Cell 14:92–101. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12301
Flatt T, Heyland A (2011) Mechanisms of life history evolution: the genetics and physiology of life history traits and trade-offs. OUP Oxford. https://doi.org/10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199568765.001.0001
Forghani F, Hajihassani A (2020) Recent advances in the development of environmentally benign treatments to control root-knot nematodes. Front Plant Sci 11:1125. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.01125
Frazier T, Shakes D, Hota U, Boyd L (2004) Caenorhabditis elegans UBC-2 functions with the anaphase-promoting complex but also has other activities. J Cell Sci 117:5427–5435. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.01417
Furukawa S, Yang L, Sameshima H (2014) Galantamine, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, reduces brain damage induced by hypoxia-ischemia in newborn rats. Int J Dev Neurosci 37:52–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2014.06.011
Glass NL, Donaldson GC (1995) Development of primer sets designed for use with the PCR to amplify conserved genes from filamentous ascomycetes. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:1323–1330. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.61.4.1323-1330.1995
Hada A, Dutta TK, Singh N, Singh B, Rai V, Singh NK, Rao U (2020) A genome-wide association study in Indian wild rice accessions for resistance to the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne graminicola. PLoS ONE 15:e0239085. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0239085
Hada A, Singh D, Satyanarayana KKVV, Chatterjee M, Phani V, Rao U (2021) Effect of fluensulfone on different functional genes of root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita. J Nematol 53:e2021. https://doi.org/10.21307/jofnem-2021-073
Han YF, Zhang YW, Liang JD, Liang ZQ (2007) A novel Paecilomyces species isolated from soil in China. Mycotaxon 102:51–56. https://doi.org/10.5248/114.25
Hesp K, Smant G, Kammenga JE (2015) Caenorhabditis elegans DAF-16/FOXO transcription factor and its mammalian homologs associate with age-related disease. Exp Gerontol 72:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2015.09.006
Hough A, Thomason IJ (1975) Effects of aldicarb on the behavior of Heterodera schachtii and Meloidogyne javanica. J Nematol 7:221–229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11515-015-1343-5
Hsia EY, Gui Y, Zheng X (2015) Regulation of Hedgehog signaling by ubiquitination. Front Biol 10:203–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11515-015-1343-5
Johnson CD, Rand JB, Herman RK, Stern BD, Russell RL (1988) The acetylcholinesterase genes of C. elegans: identification of a third gene (ace-3) and mosaic mapping of a synthetic lethal phenotype. Neuron 1:165–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/0896-6273(88)90201-2
Jones JT, Haegeman A, Danchin EG, Gaur HS, Helder J, Jones MG, Kikuchi T, Manzanilla-López R, Palomares-Rius JE, Wesemael WM (2013) Top 10 plant-parasitic nematodes in molecular plant pathology. Mol Plant Pathol 14:946–961. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12057
Kearn J, Ludlow E, Dillon J, O’Connor V, Holden-Dye L (2014) Fluensulfone is a nematicide with a mode of action distinct from anticholinesterases and macrocyclic lactones. Pestic Biochem Physiol 109:44–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2014.01.004
Keith SA, Maddux SK, Zhong Y, Chinchankar MN, Ferguson AA, Ghazi A, Fisher AL (2016) Graded proteasome dysfunction in Caenorhabditis elegans activates an adaptive response involving the conserved SKN-1 and ELT-2 transcription factors and the autophagy-lysosome pathway. PLoS Genet 12:e1005823. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1005823
Khan AL, Hamayun M, Kang SM, Kim YH, Jung HY, Lee J-H, Lee IJ (2012) Endophytic fungal association via gibberellins and indole acetic acid can improve plant growth under abiotic stress: an example of Paecilomyces formosus LHL10. BMC Microbiol 12:3. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-12-3
Kim ES, Kim MS, Moon A (2004) TGF-β-induced upregulation of MMP-2 and MMP-9 depends on p38 MAPK, but not ERK signaling in MCF10A human breast epithelial cells. Int J Oncol 25:1375–1382. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.25.5.1375
Kim D, Paggi JM, Park C, Bennett C, Salzberg SL (2019) Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype. Nat Biotechnol 37:907–915. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-019-0201-4
Lahm GP, Desaeger J, Smith BK, Pahutski TF, Rivera MA, Meloro T, Kucharczyk R, Lett RM, Daly A, Smith BT (2017) The discovery of fluazaindolizine: a new product for the control of plant parasitic nematodes. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 27:1572–1575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2017.02.029
Lai Y, Liu K, Zhang X, Zhang X, Li K, Wang N, Shu C, Wu Y, Wang C, Bushley KE, Xiang M, Liu X (2014) Comparative genomics and transcriptomics analyses reveal divergent lifestyle features of nematode endoparasitic fungus Hirsutella minnesotensis. Genome Biol Evol 6:3077–3093. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evu241
Laing R, Bartley DJ, Morrison AA, Rezansoff A, Martinelli A, Laing ST, Gilleard JS (2015) The cytochrome P450 family in the parasitic nematode Haemonchus contortus. Int J Parasitol 45:243–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpara.2014.12.001
Le TTM, Hoang ATH, Le TTB, Vo TTB, Van Quyen DV, Chu HH (2019) Isolation of endophytic fungi and screening of Huperzine A-producing fungus from Huperzia serrata in Vietnam. Sci Rep 9:16152. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-52481-2
Le TTM, Hoang ATH, Nguyen NP, Le TTB, Trinh HTT, Vo TTB, Van Quyen DV (2020) A novel huperzine A-producing endophytic fungus Fusarium sp. Rsp5.2 isolated from Huperzia serrate. Biotechnol Lett 42:987–995. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-020-02836-x
Li J, Zou C, Xu J, Ji X, Niu X, Yang J, Huang X, Zhang K-Q (2015) Molecular mechanisms of nematode-nematophagous microbe interactions: basis for biological control of plant-parasitic nematodes. Ann Rev Phytopath 53:67–95. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-phyto-080614-120336
Li XQ, Xu K, Liu XM, Zhang PA (2020) Systematic review on secondary metabolites of Paecilomyces species: chemical diversity and biological activity. Planta Med 86:805–821. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-1196-1906
Lin EH, Kao YR, Lin CA, Kuo TY, Yang SP, Hsu C-F, Chou T-Y, Ho C-C, Wu C-W (2016a) Hedgehog pathway maintains cell survival under stress conditions, and drives drug resistance in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 7:24179–24193. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.8253
Lin XW, Tang L, Yang J, Xu WH (2016b) HIF-1 regulates insect lifespan extension by inhibiting c-Myc-TFAM signaling and mitochondrial biogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1863:2594–2603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.07.007
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Love MI, Huber W, Anders S (2014) Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 15:550. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8
Maule AG, Mousley A, Marks NJ, Day TA, Thompson DP, Geary TG, Halton DW (2002) Neuropeptide signaling systems-potential drug targets for parasite and pest control. Curr Top Med Chem 2:733–758. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568026023393697
Mehboob M, Lang M (2021) Structure, function, and pathology of protein O-glucosyltransferases. Cell Death Dis 12:71. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-03314-y
Mishra J, Bhardwaj A, Pal M, Rajput R, Misra K (2018) High performance thin layer chromatography hyphenated with electrospray mass spectrometry for evaluation of nucleobases in two traditional Chinese medicinal mushrooms: a metabolomic approach. J Liq Chromatogr Relat 41:910–918. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826076.2018.1539672
Mitkowski NA, Abawi GS (2003) Root-knot nematodes. Plant Health Instr. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHI-I-2003-0917-01
Mkandawire TT, Grencis RK, Berriman M, Duque-Correa MA (2022) Hatching of parasitic nematode eggs: a crucial step determining infection. Trends Parasitol 38:174–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pt.2021.08.008
Moreira DC, Oliveira MME, Borba CM (2018) Human Pathogenic Paecilomyces from Food. Microorg 6:64. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms6030064
Moreno-Gavíra A, Diánez F, Sánchez-Montesinos B, Santos M (2020) Paecilomyces variotii as a plant-growth promoter in horticulture. Agronomy 10:597. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10040597
Moriya Y, Itoh M, Okuda S, Yoshizawa AC, Kanehisa M (2007) KAAS: an automatic genome annotation and pathway reconstruction server. Nucleic Acids Res 35:W182–W185. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm321
Morris JZ, Tissenbaum HA, Ruvkun G (1996) A phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase family member regulating longevity and diapause in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 382:536–539. https://doi.org/10.1038/382536a0
Morton O, Hirsch P, Kerry B (2004) Infection of plant-parasitic nematodes by nematophagous fungi-a review of the application of molecular biology to understand infection processes and to improve biological control. J Nematol 6:161–170. https://doi.org/10.1163/1568541041218004
Ntalli N, Ratajczak M, Oplos C, Menkissoglu-Spiroudi U, Adamski Z (2016) Acetic acid, 2-undecanone, and (e)-2-decenal ultrastructural malformations on Meloidogyne incognita. J Nematol 48:248–260. https://doi.org/10.21307/jofnem-2017-033
Pandit R, Patel R, Patel N, Bhatt V, Joshi C, Singh PK, Kunjadia A (2017) RNA-Seq reveals the molecular mechanism of trapping and killing of root-knot nematodes by nematode-trapping fungi. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 33:65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-017-2232-7
Papolu PK, Gantasala NP, Kamaraju D, Banakar P, Sreevathsa R, Rao U (2013) Utility of host delivered RNAi of two FMRF amide like peptides, flp-14 and flp-18, for the management of root knot nematode. Meloidogyne Incognita Plos One 8:e80603. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0080603
Pastor FJ, Guarro J (2006) Clinical manifestations, treatment and outcome of Paecilomyces lilacinus infections. Clin Microbiol Infect 12:948–960. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-0691.2006.01481.x
Pertea M, Pertea GM, Antonescu CM, Chang TC, Mendell JT, Salzberg SL (2016) StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat Biotechnol 33:290–295. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3122
Perveen Z, Shahzad SA (2013) comparative study of the efficacy of Paecilomyces species against root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita. Pak J Nematol 31:125–131
Phani V, Shivakumara TN, Davies KG, Rao U (2017) Meloidogyne incognita fatty acid-and retinol-binding protein (Mi-FAR-1) affects nematode infection of plant roots and the attachment of Pasteuria penetrans endospores. Front Microbiol 8:2122. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.02122
Phani V, Somvanshi VS, Shukla RN, Davies KG, Rao U (2018) A transcriptomic snapshot of early molecular communication between Pasteuria penetrans and Meloidogyne incognita. BMC Genom 19:850. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-018-5230-8
Phani V, Khan MR, Dutta TK (2021) Plant-parasitic nematodes as a potential threat to protected agriculture: current status and management options. Crop Prot 144:105573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2021.105573
Piotte C, Arthaud L, Abad P, Rosso MN (1999) Molecular cloning of an acetylcholinesterase gene from the plant parasitic nematodes, Meloidogyne incognita and Meloidogyne javanica. Mol Biochem Parasitol 99:247–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0166-6851(99)00033-x
Powell-Coffman JA (2010) Hypoxia signaling and resistance in C. elegans. Trends Endocrinol Metab 21:435–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2010.02.006
Rand JB (2007) Acetylcholine. WormBook. https://doi.org/10.1895/wormbook.1.131.1
Sang X, Yang M, Su J (2020) Research on endophytic fungi for producing huperzine A on a large-scale. Crit Rev Microbiol 6:654–664. https://doi.org/10.1080/1040841X.2020.1819771
Sedgwick B, Riches K, Bageghni SA, O’Regan DJ, Porter KE, Turner NA (2014) Investigating inherent functional differences between human cardiac fibroblasts cultured from nondiabetic and Type 2 diabetic donors. Cardiovasc Pathol 23:204–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carpath.2014.03.004
Shu S, Zhao X, Wang W, Zhang G, Cosoveanu A, Ahn Y, Wang M (2014) Identification of a novel endophytic fungus from Huperzia serrata which produces huperzine A. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30:3101–3109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-014-1737-6
Siddiqui IA, Shaukat SS (2004) Systemic resistance in tomato induced by biocontrol bacteria against the root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne javanica is independent of salicylic acid production. J Phytopathol 152:48–54. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1439-0434.2003.00800.x
Silva SD, Carneiro RM, Faria M, Souza DA, Monnerat RG, Lopes RB (2017) Evaluation of Pochonia chlamydosporia and Purpureocillium lilacinum for suppression of Meloidogyne enterolobii on tomato and banana. J Nematol 49:77–85. https://doi.org/10.21307/jofnem-2017-047
Silva-García O, Valdez-Alarcón JJ, Baizabal-Aguirre VM (2014) The Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway controls the inflammatory response in infections caused by pathogenic bacteria. Med Inflamm 2014:310183. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/310183
Sladowska M, Turek M, Kim MJ, Drabikowski K, Mussulini BHM (2021) Proteasome activity contributes to pro-survival response upon mild mitochondrial stress in Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS Biol 19:e3001302. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3001302
Slomczynska U, South MS, Bunkers G, Edgecomb D, Wyse-Pester D, Selness S, Ding Y, Christiansen J, Ediger K, Miller W (2014) Tioxazafen: a new broadspectrum seed treatment nematicide. In: Maienfisch P, Stevenson TM (eds) ACS symposium series, discovery and synthesis of crop protection products, vol 1204. Monsanto Corporation, Chesterfield, pp 129–147. https://doi.org/10.1021/bk-2015-1204.ch010
Sornakili A, Thankappan S, Sridharan AP, Nithya P, Uthandi S (2020) Antagonistic fungal endophytes and their metabolite-mediated interactions against phytopathogens in rice. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 112:101525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmpp.2020.101525
Steiner B, Aquino VR, Paz AA, Silla LM, Zavascki A, Goldani LZ (2013) Paecilomyces variotii as an emergent pathogenic agent of pneumonia. Case Rep Infect Dis 2013:273848. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/273848
Su J, Yang M (2015) Huperzine A production by Paecilomyces tenuis YS-13, an endophytic fungus isolated from Huperzia serrata. Nat Prod Res 29:1035–1041. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2014.980245
Tang XC, He XC, Bai DL (1999) Huperzine A: a novel acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. Drugs Fut 24:647–664. https://doi.org/10.1358/dof.1999.024.06.545143
Tanguy M, Véron L, Stempor P, Ahringer J, Sarkies P, Miska EA (2017) An alternative STAT signaling pathway acts in viral immunity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mbio 8:e00924-e1017. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00924-17
Thein MC, McCormack G, Winter AD, Johnstone IL, Shoemaker CB, Page AP (2003) Caenorhabditis elegans exoskeleton collagen COL-19: an adult-specific marker for collagen modification and assembly, and the analysis of organismal morphology. Dev Dynam 226:523–539. https://doi.org/10.1002/dvdy.10259
Tian WN, Braunstein LD, Pang J, Stuhlmeier KM, Xi QC, Tian X, Stanton RC (1998) Importance of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity for cell growth. J Biol Chem 273:10609–10617. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.17.10609
Tiganomilani MS, Carneiro RG, Defaria MR, Frazão HS, McCoy CW (1995) Isozyme characterization and pathogenicity of Paecilomyces fumosoroseus and P. lilacinus to Diabrotica speciosa (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) and Meloidogyne javanica (Nematoda: Tylenchidae). Biol Control 5:378–382. https://doi.org/10.1006/bcon.1995.1044
Tsang WY, Lemire BD (2003) The role of mitochondria in the life of the nematode, Caenorhabditis elegans. Biochim Biophys Acta 1638:91–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4439(03)00079-6
Turner LD, Conrad D (2015) Retrospective case-series of Paecilomyces lilacinus ocular mycoses in Queensland. Aust BMC Res Notes 8:627. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-015-1591-0
Wang R, Tang XC (2005) Neuroprotective effects of huperzine A. Neurosignals 14:71–82. https://doi.org/10.1159/000085387
Wang C, Lower S, Williamson VM (2009) Application of Pluronic gel to the study of root-knot nematode behavior. Nematology 11:453–464. https://doi.org/10.1163/156854109X447024
Wang Y, Zeng QG, Zhang ZB, Yan RM, Wang LY, Zhu D (2015) Isolation and characterization of endophytic huperzine A-producing fungi from Huperzia serrata. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 38:1267–1278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-010-0905-4
Wen-Xia H, Zhong-Wen H, Min J, Han Z, Wei-Ze L, Li-Bin Y, Fei L, Lu H, Ning Z, Xiao-Feng L (2020) Five novel and highly efficient endophytic fungi isolated from Huperzia serrata expressing huperzine A for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104:9159–9177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10894-4
Whitehead AG, Hemming JRA (1965) comparison of some quantitative methods of extracting small vermiform nematodes from soil. Ann Appl Biol 55:25–38. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7348.1965.tb07864.x
Wu Q, Gu Y (2006) Quantification of huperzine A in Huperzia serrata by HPLC-UV and identification of the major constituents in its alkaloid extracts by HPLC-DAD-MS-MS. J Pharm Biomed 40:993–998. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2005.07.047
Yang WN, Han H, Hu XD, Feng GF, Qian YH (2013) The effects of perindopril on cognitive impairment induced by d-galactose and aluminum trichloride via inhibition of acetylcholinesterase activity and oxidative stress. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 114:31–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2013.10.027
Yarden Y, Sliwkowski MX (2001) Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:127–137. https://doi.org/10.1038/35052073
Zangara A (2003) The psychopharmacology of huperzine A: an alkaloid with cognitive enhancing and neuroprotective properties of interest in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 75:675–686. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0091-3057(03)00111-4
Zelík P, Lukešová A, Voloshko LN, Štys D, Kopecký J (2009) Screening for acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity in cyanobacteria of the genus Nostoc. Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 24:531–536. https://doi.org/10.1080/14756360802234836
Zhang RW, Tang XC, Han YY, Sang GW, Zhang YD (1991) Drug evaluation of huperzine A in the treatment of senile memory disorders. Acta Pharmacol Sin 12:250–252
Zhang ZB, Zeng QG, Yan RM, Wang Y, Zou ZR, Zhu D (2011) Endophytic fungus Cladosporium cladosporioides LF70 from Huperzia serrata produces Huperzine A. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27:479–486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-010-0476-6
Zhang FF, Wang MZ, Zheng YX, Liu HY, Zhang XQ, Wu SS (2015) Isolation and characterization of endophytic Huperzine A-producing fungi from Phlegmariurus phlegmaria. Microbiology 84:701–709. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261715050185
Zhu D, Wang J, Zeng Q, Zhang Z, Yan R (2010) A novel endophytic Huperzine A–producing fungus, Shiraia sp. Slf14, isolated from Huperzia serrata. J Appl Microbiol 109:1469–1478. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2010.04777.x
Acknowledgements
The authors sincerely acknowledge Dr. Jayarama D. Bhat, D. Sc., Formerly Professor of Botany, Goa University, Goa, India, for his constructive comments and suggestions during the manuscript preparation and final drafting. We also acknowledge Mr. Purshotam and Mr. Vivek for helping in culture maintenance.
Funding
This work was supported by the Genomics Assisted Crop Improvement and Management project under World Bank and Indian Council of Agricultural Research sponsored National Agricultural Higher Education Project-Centre for Advanced Agricultural Science and Technology (NAHEP-CAAST) project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation and data collection were performed by RK, NJ, AH, JY, MC, CGB, JM, VSR and GC; analyses were performed by UR, VP, RK, RB, JG, AK and VSS; the first draft of the manuscript was written by RK, VP, NJ, VSS and UR; final drafting and critical revision of the manuscript were done by UR, VP and VSS. All authors commented on the previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Communicated by Aurelio Ciancio.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kassam, R., Jaiswal, N., Hada, A. et al. Evaluation of Paecilomyces tenuis producing Huperzine A for the management of root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita (Nematoda: Meloidogynidae). J Pest Sci 96, 723–743 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-022-01521-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-022-01521-4