Abstract
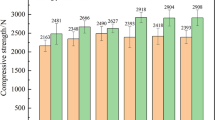
The hydrogen-rich reduction of ilmenite concentrates has a significant effect on the reduction of the carbon footprint of the titanium slag production process. This study investigates the hydrogen-rich reduction of Panzhihua ilmenite concentrate pellets. The pellets were roasted at 500, 700, 900, and 1100 °C and used as the raw material for the reduction process. The effects of the pellet roasting temperature, magnetite concentrate content of the pellets, reduction temperature, and reducing gas composition on the reduction process were experimentally studied. The results showed that the average reduction rate is affected by the phase and dense structure of the pellet, reduction temperature, and hydrogen content. Further, the reduction process can be accelerated by increasing the H2 content and reduction temperature. The high compressive strength of the pellet, owing to its dense inner structure, is not conducive for the reduction process. Moreover, studies show that the H2/CO ratio has negligible effects on the reduction mechanism. The reaction mechanism of the pellet reduction process is three-dimensional diffusion. Furthermore, the effect of the pellet phase on the hydrogen-rich reduction process has been discussed.
Graphical Abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes JE, Peter W, Blue CA (2009) Evaluation of low cost titanium alloy products. Mater Sci Forum 618–619:165–168. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.618-619.165
Liu W, Lü L, Yue H, Liang B, Li C (2017) Combined production of synthetic rutile in the sulfate TiO2 process. J Alloys Compd 705:572–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.02.195
Chen G, Jiang Q, Li K, He A, Peng J, Omran M, Chen J (2020) Simultaneous removal of Cr(III) and V(V) and enhanced synthesis of high-grade rutile TiO2 based on sodium carbonate decomposition. J Hazard Mater 388:122039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122039
Yang H, Fan X, Sun Z, Guo L, Zhan M (2011) Recent developments in plastic forming technology of titanium alloys. Sci China Technol Sci 54(2):490–501. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-010-4206-y
Theissmann R, Kluwig M, Koch T (2014) A reproducible number-based sizing method for pigment-grade titanium dioxide. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 5:1815–1822. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.5.192
Xibo L, Zhiqiang C (2015) Study on upgrading the quality grade of ilmenite concentrate. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium 36 (01):16–20+63
Yuan Z, Wang X, Xu C, Li W, Kwauk M (2006) A new process for comprehensive utilization of complex titania ore. Miner Eng 19(9):975–978. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2005.10.002
Zhu K, Wei Q, Li H, Ren X (2022) Recovery of titanium from ilmenite HCl leachate using a hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 10(6):2125–2135. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.1c07204
Samal S (2016) Synthesis and characterization of titanium slag from ilmenite by thermal plasma processing. JOM 68(9):2349–2358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-016-1817-1
Han FX, Sang XL, Xu JX (2013) Balance of raw input and energy of titanium slag smelting in closed high power direct current electric arc furnace. Adv Mater Res 734–737:1516–1521. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.734-737.1516
Dang J, Zhang G-h, Chou K-c (2015) Kinetics and mechanism of hydrogen reduction of ilmenite powders. J Alloys Compd 619:443–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.09.057
Lv W, Lv X, Xiang J, Hu K, Zhao S, Dang J, Han K, Song B (2019) Effect of preoxidation on the reduction of ilmenite concentrate powder by hydrogen. Int J Hydrogen Energy 44(8):4031–4040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.12.139
Gou H-P, Zhang G-H, Chou K-C (2015) Influence of pre-oxidation on carbothermic reduction process of ilmenite concentrate. ISIJ Int 55(5):928–933. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.55.928
Lei Y, Li Y, Peng J, Guo S, Li W, Zhang L, Wan R (2011) Carbothermic reduction of panzhihua oxidized ilmenite in a microwave field. ISIJ Int 51(3):337–343. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.51.337
Samanta S, Mukherjee S, Dey R (2014) Oxidation behaviour and phase characterization of titaniferous magnetite ore of eastern India. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China 24(9):2976–2985. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(14)63434-8
Chen D, Zhao L, Liu Y, Qi T, Wang J, Wang L (2013) A novel process for recovery of iron, titanium, and vanadium from titanomagnetite concentrates: NaOH molten salt roasting and water leaching processes. J Hazard Mater 244–245:588–595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.10.052
Tang J, Chu M-s, Li F, Feng C, Liu Z-g, Zhou Y-s (2020) Development and progress on hydrogen metallurgy. Int J Miner Metall Mater 27(6):713–723. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-020-2021-4
Yao W, Chi-hui G, Xi-jie C, Li-qiong J, Xiao-na G, Rui-shan C, Mao-sheng Z, Ze-yu C, Hao-dong W (2021) Carbon peak and carbon neutrality in China: goals, implementation path and prospects. China Geol 4:720–746. https://doi.org/10.31035/cg2021083
Zuo H-b, Wang C, Dong J-j, Jiao K-x, Xu R-s (2015) Reduction kinetics of iron oxide pellets with H2 and CO mixtures. Int J Miner Metall Mater 22(7):688–696. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-015-1123-x
Pinegar HK, Moats MS, Sohn HY (2011) Process simulation and economic feasibility analysis for a hydrogen-based novel suspension ironmaking technology. Steel Res Int 82 (8):951–963. https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.201000288
Dang J, Zhang G-h, Hu X-j, Chou K-c (2013) Non-isothermal reduction kinetics of titanomagnetite by hydrogen. Int J Miner Metall Mater 20(12):1134–1140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-013-0846-9
Si X-g, Lu X-g, Li C-w, Li C-h, Ding W-z (2012) Phase transformation and reduction kinetics during the hydrogen reduction of ilmenite concentrate. Int J Miner Metall Mater 19(5):384–390. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-012-0568-4
Lu C-y, Zou X-l, Lu X-g, Xie X-l, Zheng K, Xiao W, Cheng H-w, Li G-s (2016) Reductive kinetics of Panzhihua ilmenite with hydrogen. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China 26(12):3266–3273. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(16)64460-6
Wang Y, Yuan Z, Matsuura H, Tsukihashi F (2009) Reduction extraction kinetics of titania and iron from an ilmenite by H2-Ar gas mixtures. ISIJ Int 49(2):164–170. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.49.164
de Vries ML, Grey IE (2006) Influence of pressure on the kinetics of synthetic llmenite reduction in hydrogen. Metall Mater Trans B 37(2):199–208. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02693149
Lv W, Zhou G, Chen F, Liu Z, Tang J, Chu M, Lv X (2022) A novel process for preparing high-strength pellets of ilmenite concentrate. J Sustain Metall 8(1):551–565. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-022-00508-w
Choi K, Jeon HS, Lee S, Kim Y, Park H (2022) Gaseous reduction behavior of primary ilmenite at temperatures between 1273 K and 1473 K. Metall Mater Trans B 53(1):334–341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-021-02370-9
Sun H, Wang J, Han Y, She X, Xue Q (2013) Reduction mechanism of titanomagnetite concentrate by hydrogen. Int J Miner Process 125:122–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2013.08.006
Lv W, Lv X, Zhang Y, Li S, Tang K, Song B (2017) Isothermal oxidation kinetics of ilmenite concentrate powder from Panzhihua in air. Powder Technol 320:239–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2017.07.058
Zhao S-q, Lv X-d, Yan Z-m, Lv X-w, Lv W, Bai C-g (2021) Effect of pre-oxidation degree on gaseous reduction of pre-oxidized ilmenite concentrate by CO. J Iron Steel Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-021-00623-0
Lu F, Wen L, Zhao Y, Zhong H, Xu J, Zhang S, Yang Z (2019) The competitive adsorption behavior of CO and H2 molecules on FeO surface in the reduction process. Int J Hydrogen Energy 44(13):6427–6436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.01.173
Hancock JD, Sharp JH (1972) Method of comparing solid-state kinetic data and its application to the decomposition of kaolinite, brucite, and BaCO3. J Am Ceram Soc 55(2):74–77. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1972.tb11213.x
Khawam A, Flanagan DR (2006) Solid-state kinetic models: basics and mathematical fundamentals. J Phys Chem B 110(35):17315–17328. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp062746a
Ding C, Lv X, Li G, Bai C, Xuan S, Tang K, Lv X (2018) Isothermal reduction of powdery 2CaO·Fe2O3 and CaO·Fe2O3 under H2 atmosphere. Int J Hydrogen Energy 43(1):24–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.11.075
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52104325).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report there are no competing interests to declare.
Additional information
The contributing editor for this article was Sharif Jahanshahi.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, F., Lv, W., Zhou, G. et al. Investigation of the Hydrogen-Rich Reduction of Panzhihua Ilmenite Concentrate Pellets. J. Sustain. Metall. 8, 1130–1139 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-022-00555-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-022-00555-3