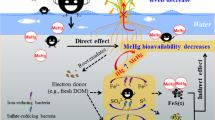
Abstract
Mercury (Hg) bioaccumulation in Hg-polluted farmlands poses high health risk for humans and wildlife, and remediation work is urgently needed. Here, we first summarize some specific findings related to the environmental process of Hg in Hg-polluted farmlands, and distinguish the main achievements and deficiencies of available remediation strategies in recent studies. Results demonstrate that farmland is a sensitive area with vibrant Hg biogeochemistry. Current remediation methods are relatively hysteretic whether in mechanism understanding or field application, and deficient for large-scale Hg-polluted farmlands in view of safety, efficiency, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness. New perspectives including environment-friendly functional materials, assisted phytoremediation and agronomic regulations are worthy of further study as their key roles in reducing Hg exposure risk and protecting agricultural sustainability.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeysinghe KS, Qiu GL, Goodale E, Anderson CWN, Bishop K, Evers DC, Goodale MW, Hintelmann H, Liu SJ, Mammides C, Quan RC, Wang J, Wu PP, Xu XH, Yang XD, Feng XB (2017) Mercury flow through an Asian rice-based food web. Environ Pollut 229:219–228
Chen R, Zhang CB, Zhao YL, Huang YC, Liu ZQ (2018) Foliar application with nano-silicon reduced cadmium accumulation in grains by inhibiting cadmium translocation in rice plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25(3):2361–2368
Dash HR, Das S (2015) Bioremediation of inorganic mercury through volatilization and biosorption by transgenic Bacillus cereus BW-03(pPW-05). Int Biodeter Biodegr 103:179–185
Evangelou MW, Ebel M, Schaeffer A (2007) Chelate assisted phytoextraction of heavy metals from soil. Effect, mechanism, toxicity, and fate of chelating agents. Chemosphere 68(6):989–1003
Franchi E, Rolli E, Marasco R, Agazzi G, Borin S, Cosmina P, Pedron F, Rosellini I, Barbafieri M, Petruzzelli G (2017) Phytoremediation of a multi contaminated soil: mercury and arsenic phytoextraction assisted by mobilizing agent and plant growth promoting bacteria. J Soil Sediment 17(5):1224–1236
Francois F, Lombard C, Guigner JM, Soreau P, Brian-Jaisson F, Martino G, Vandervennet M, Garcia D, Molinier AL, Pignol D, Peduzzi J, Zirah S, Rebuffat S (2012) Isolation and characterization of environmental bacteria capable of extracellular biosorption of mercury. Appl Environ Microb 78(4):1097–1106
Gong YY, Liu YY, Xiong Z, Kaback D, Zhao DY (2012) Immobilization of mercury in field soil and sediment using carboxymethyl cellulose stabilized iron sulfide nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 23(29):294007
Gong YY, Zhao DY, Wang QL (2018) An overview of field-scale studies on remediation of soil contaminated with heavy metals and metalloids: technical progress over the last decade. Water Res 147:440–460
Gong YY, Huang Y, Wang MX, Liu FF, Zhang T (2019) Application of iron-based materials for remediation of mercury in water and soil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 102:721–729
Haque S, Zeyaullah M, Nabi G, Srivastava PS, Ali A (2010) Transgenic tobacco plant expressing environmental E. coli merA gene for enhanced volatilization of ionic mercury. J Microbiol Biotechnol 20(5):917–924
He M, Tian L, Braaten HFV, Wu QR, Luo J, Cai LM, Meng JH, Lin Y (2019) Mercury-organic matter interactions in soils and sediments: angel or devil? B Environ Contam Tox 102(5):621–627
Huang Y, Wang L, Wang W, Li T, He Z, Yang X (2019) Current status of agricultural soil pollution by heavy metals in China: a meta-analysis. Sci Total Environ 651(Pt 2):3034–3042
Kocman D, Horvat M, Pirrone N, Cinnirella S (2013) Contribution of contaminated sites to the global mercury budget. Environ Res 125:160–170
Krisnayanti BD, Anderson CWN, Utomo WH, Feng XB, Handayanto E, Mudarisna N, Ikram H, Khususiah (2012) Assessment of environmental mercury discharge at a four-year-old artisanal gold mining area on Lombok Island, Indonesia. J Environ Monitor 14(10):2598–2607
Kumari S, Jamwal R, Mishra N, Singh DK (2020) Recent developments in environmental mercury bioremediation and its toxicity: a review. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 13:100283
Li P, Feng X, Qiu G (2010) Methylmercury exposure and health effects from rice and fish consumption: a review. Int J Environ Res Public Health 7(6):2666–2691
Li X, Zhang J, Gong Y, Yang S, Ye M, Yu X, Ma J (2020a) Status of mercury accumulation in agricultural soils across China (1976–2016). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 197:110564
Li R, Wu H, Ding J, Li N, Fu WM, Gan LJ, Li Y (2020b) Transgenic merA and merB expression reduces mercury contamination in vegetables and grains grown in mercury-contaminated soil. Plant Cell Rep 39(10):1369–1380
Liu Z, Tran KQ (2021) A review on disposal and utilization of phytoremediation plants containing heavy metals. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 226:112821
Liu LW, Li W, Song WP, Guo MX (2018) Remediation techniques for heavy metal-contaminated soils: principles and applicability. Sci Total Environ 633:206–219
Liu Z, Chen B, Wang LA, Urbanovich O, Nagorskaya L, Li X, Tang L (2020) A review on phytoremediation of mercury contaminated soils. J Hazard Mater 400:123138
Liu YW, Liu GL, Wang ZW, Guo YY, Yin YG, Zhang XS, Cai Y, Jiang GB (2021) Understanding foliar accumulation of atmospheric Hg in terrestrial vegetation: Progress and challenges. Crit Rev Env Sci Tec
Makarova AS, Nikulina E, Fedotov P (2021) Induced phytoextraction of mercury. Sep Purif Rev 51:174–194
Marrugo-Negrete J, Durango-Hernandez J, Pinedo-Hernandez J, Olivero-Verbel J, Diez S (2015) Phytoremediation of mercury-contaminated soils by Jatropha curcas. Chemosphere 127:58–63
Mello IS, Targanski S, Pietro-Souza W, Frutuoso Stachack FF, Terezo AJ, Soares MA (2020) Endophytic bacteria stimulate mercury phytoremediation by modulating its bioaccumulation and volatilization. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 202:110818
Natasha, Shahid M, Khalid S, Bibi I, Bundschuh J, Khan Niazi N, Dumat C (2020) A critical review of mercury speciation, bioavailability, toxicity and detoxification in soil-plant environment: Ecotoxicology and health risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 711:134749
Nowack B, Schulin R, Robinson BH (2006) Critical assessment of chelant-enhanced metal phytoextraction. Environ Sci Technol 40(17):5225–5232
O’Brien PL, DeSutter TM, Casey FXM, Khan E, Wick AF (2018) Thermal remediation alters soil properties: a review. J Environ Manage 206:826–835
O’Connor D, Peng TY, Li GH, Wang SX, Duan L, Mulder J, Cornelissen G, Cheng ZL, Yang SM, Hou DY (2018) Sulfur-modified rice husk biochar: a green method for the remediation of mercury contaminated soil. Sci Total Environ 621:819–826
Ottesen RT, Birke M, Finne TE, Locutura M, Reimann C, Tarvainen T, Team GP (2013) Mercury in European agricultural and grazing land soils. Appl Geochem 33:1–12
Parks JM, Johs A, Podar M, Bridou R, Hurt RA, Smith SD, Tomanicek SJ, Qian Y, Brown SD, Brandt CC, Palumbo AV, Smith JC, Wall JD, Elias DA, Liang LY (2013) The genetic basis for bacterial bercury bethylation. Science 339:1332–1335
Pogrzeba M, Ciszek D, Galimska-Stypa R, Nowak B, Sas-Nowosielska A (2016) Ecological strategy for soil contaminated with mercury. Plant Soil 409(1):371–387
Qian XL, Wu YG, Zhou HY, Xu XH, Xu ZD, Shang LH, Qiu GL (2018) Total mercury and methylmercury accumulation in wild plants grown at wastelands composed of mine tailings: Insights into potential candidates for phytoremediation. Environ Pollut 239:757–767
Qiu GL, Feng XB, Wang SF, Shang LH (2005) Mercury and methylmercury in riparian soil, sediments, mine-waste calcines, and moss from abandoned Hg mines in east Guizhou province, southwestern China. Appl Geochem 20(3):627–638
Rothenberg SE, Feng XB, Zhou WJ, Tu M, Jin BW, You JM (2012) Environment and genotype controls on mercury accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivated along a contamination gradient in Guizhou, China. Sci Total Environ 426(2):272–280
Rothenberg SE, Anders M, Ajami NJ, Petrosino JF, Balogh E (2016) Water management impacts rice methylmercury and the soil microbiome. Sci Total Environ 572:608–617
Sahinkaya E, Uçar D, Kaksonen AH (2017) Bioprecipitation of metals and metalloids. Springer, In Sustainable heavy metal remediation, pp 199–231
Sas-Nowosielska A, Galimska-Stypa R, Kucharski R, Zielonka U, Malkowski E, Gray L (2008) Remediation aspect of microbial changes of plant rhizosphere in mercury contaminated soil. Environ Monit Assess 137(1–3):101–109
Semenov MV, Krasnov GS, Semenov VM, Ksenofontova N, Zinyakova NB, van Bruggen A (2021) Does fresh farmyard manure introduce surviving microbes into soil or activate soil-borne microbiota? J Environ Manage 294:113018
Shen ZM, Zhang JD, Qu LY, Dong ZQ, Zheng SS, Wang WH (2009) A modified EK method with an I-/I-2 lixiviant assisted and approaching cathodes to remedy mercury contaminated field soils. Environ Geol 57(6):1399–1407
Sun T, Ma M, Du H, Wang X, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Wang D (2019) Effect of different rotation systems on mercury methylation in paddy fields. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 182:109403
Sun WJ, Cheng K, Sun KY, Ma XM (2021) Microbially mediated remediation of contaminated sediments by heavy metals: a critical review. Curr Pollut Rep 7(2):201–212
Tang WL, Dang F, Evans D, Zhong H, Xiao L (2017) Understanding reduced inorganic mercury accumulation in rice following selenium application: selenium application routes, speciation and doses. Chemosphere 169:369–376
Tang ZY, Fan FL, Deng SP, Wang DY (2020) Mercury in rice paddy fields and how does some agricultural activities affect the translocation and transformation of mercury: a critical review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 202:110950
Tian X (2021) Effects of straw, cow dung and its composting products on soil DOM characteristics and bio-mercury enrichment in paddy. (in Chinese with Eglish abstract). Guizhou university
Tiodar ED, Vacar CL, Podar D (2021) Phytoremediation and microorganisms-assisted phytoremediation of mercury-contaminated soils: challenges and perspectives. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(5):2435
United Nations Environment Programme (2018) Global Mercury Assessment 2018. Switzerland, Geneva
Vinceti M, Filippini T, Wise LA (2018) Environmental selenium and human health: an update. Curr Environ Health Rep 5(4):464–485
Virkutyt J, Sillanpaa M, Latostenmaa P (2002) Electrokinetic soil remediation-critical overview. Sci Total Environ 289(1–3):97–121
Wang ZB, He TR (2019) Effect of different selenization remediation agents on remediation of mercury pollution in paddyfields. (Chinese with English abstract). China Environ Sci 39(10):4254–4261
Wang YD, Stauffer C, Keller C, Greger M (2005) Changes in Hg fractionation in soil induced by willow. Plant Soil 275(1):67–75
Wang JX, Feng XB, Anderson CW, Xing Y, Shang LH (2012) Remediation of mercury contaminated sites: a review. J Hazard Mater 221–222:1–18
Wang T, Sun HW, Mao HJ, Zhang YF, Wang CP, Zhang ZY, Wang BL, Sun L (2014) The immobilization of heavy metals in soil by bioaugmentation of a UV-mutant Bacillus subtilis 38 assisted by NovoGro biostimulation and changes of soil microbial community. J Hazard Mater 278:483–490
Wang SQ, Zhong TY, Chen DM, Zhang XY (2016) Spatial distribution of mercury (Hg) concentration in agricultural soil and its risk assessment on food safety in China. Sustainability 8(8):795
Wang XN, Zhang DY, Pan XL, Lee DJ, Al-Misned FA, Mortuza MG, Gadd GM (2017a) Aerobic and anaerobic biosynthesis of nano-selenium for remediation of mercury contaminated soil. Chemosphere 170:266–273
Wang JX, Xia JC, Feng XB (2017b) Screening of chelating ligands to enhance mercury accumulation from historically mercury-contaminated soils for phytoextraction. J Environ Manage 186(Pt 2):233–239
Wang YM, Yang RX, Zheng JY, Shen ZG, Xu XM (2019a) Exogenous foliar application of fulvic acid alleviate cadmium toxicity in lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 167:10–19
Wang JX, Xing Y, Xie YY, Meng Y, Xia JC, Feng XB (2019b) The use of calcium carbonate-enriched clay minerals and diammonium phosphate as novel immobilization agents for mercury remediation: Spectral investigations and field applications. Sci Total Environ 646:1615–1623
Wang YN, O’Connor D, Shen ZT, Lo IMC, Tsang DCW, Pehkonen S, Pu SY, Hou DY (2019c) Green synthesis of nanoparticles for the remediation of contaminated waters and soils: constituents, synthesizing methods, and influencing factors. J Clean Prod 226:540–549
Wang JX, Shaheen SM, Anderson CWN, Xing Y, Liu SR, Xia JC, Feng XB, Rinklebe J (2020a) Nanoactivated carbon reduces mercury mobility and uptake by Oryza sativa L.: mechanistic investigation using spectroscopic and microscopic techniques. Environ Sci Technol 54(5):2698–2706
Wang Y, He TR, Yin DL, Han YX, Zhou X, Zhang G, Tian X (2020b) Modified clay mineral: a method for the remediation of the mercury-polluted paddy soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 204:111121
Wang YJ, Zhang Y, Ok YS, Jiang T, Liu P, Shu R, Wang DY, Cao XD, Zhong H (2021) Biochar-impacted sulfur cycling affects methylmercury phytoavailability in soils under different redox conditions. J Hazard Mater 407
Xia JC, Wang JX, Zhang LM, Anderson CWN, Wang X, Zhang H, Dai ZH, Feng XB (2020) Screening of native low mercury accumulation crops in a mercury - polluted mining region: agricultural planning to manage mercury risk in farming communities. J Clean Prod 262:121324
Xing Y, Wang JX, Xia JC, Liu ZM, Zhang YH, Du Y, Wei WL (2019) A pilot study on using biochars as sustainable amendments to inhibit rice uptake of Hg from a historically polluted soil in a Karst region of China. Ecotox Environ Safe 170:18–24
Xu J, Bravo AG, Lagerkvist A, Bertilsson S, Sjoblom R, Kumpiene J (2015) Sources and remediation techniques for mercury contaminated soil. Environ Int 74:42–53
Xu XH, Yan M, Liang LC, Lu QH, Han JL, Liu L, Feng XB, Guo JY, Wang YJ, Qiu GL (2019) Impacts of selenium supplementation on soil mercury speciation, and inorganic mercury and methylmercury uptake in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ Pollut 249:647–654
Yang Q, Wang YJ, Zhong H (2021) Remediation of mercury-contaminated soils and sediments using biochar: a critical review. Biochar 3:1–13
Ye SJ, Zeng GM, Wu HP, Zhang C, Dai J, Liang J, Yu JF, Ren XY, Yi H, Cheng M, Zhang C (2017) Biological technologies for the remediation of co-contaminated soil. Crit Rev Biotechnol 37(8):1062–1076
Yin DL, He TR, Zeng LX, Chen J (2016) Exploration of amendments and agronomic measures on the remediation of methylmercury-polluted rice in a mercury mining area. Water Air Soil Poll 227(9):333
Yin DL, He TR, Yin RS, Zeng LX (2018) Effects of soil properties on production and bioaccumulation of methylmercury in rice paddies at a mercury mining area, China. J Environ Sci 68:194–205
Zeb A, Li S, Wu J, Lian J, Liu W, Sun Y (2020) Insights into the mechanisms underlying the remediation potential of earthworms in contaminated soil: a critical review of research progress and prospects. Sci Total Environ 740:140145
Zhang SQ, Wang MX, Liu J, Tian SY, Yang XL, Xiao GQ, Xu GM, Jiang T, Wang DY (2022), Biochar affects methylmercury production and bioaccumulation in paddy soils: insights from soil-derived dissolved organic matter. J Environ Sci
Zhao XL, Wang DY (2010) Mercury in some chemical fertilizers and the effect of calcium superphosphate on mercury uptake by corn seedlings (Zea mays L.). J Environ Sci 22(8):1184–1188
Zhao T, Yu Z, Zhang J, Qu L, Li P (2018) Low-thermal remediation of mercury-contaminated soil and cultivation of treated soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25(24):24135–24142
Zhao AQ, Gao LY, Chen BQ, Feng L (2019) Phytoremediation potential of Miscanthus sinensis for mercury-polluted sites and its impacts on soil microbial community. Environ Sci Pollut R 26(34):34818–34829
Zhao L, Meng B, Feng XB (2020) Mercury methylation in rice paddy and accumulation in rice plant: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 195:110462
Zhou X (2021) Application of pennisetum americanum and soil conditioning technology in the safe use and remediation of mercury contaminated farmland.(in Chinese with English abstract). Guizhou university
Zhou YT, Aamir M, Liu K, Yang FX, Liu WP (2018) Status of mercury accumulation in agricultural soil across China: spatial distribution, temporal trend, influencing factor and risk assessment. Environ Pollut 240:116–124
Zhu HK, Zhong H, Fu FJ, Zeng Z (2015) Incorporation of decomposed crop straw affects potential phytoavailability of mercury in a mining-contaminated farming soil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 95(2):254–259
Acknowledgements
This work was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U1612442, 42007305, 41763017, 22166009), Science and Technology Project of Guizhou Province (QKHJC[2020]1Y187; QKHZC[2020]4Y031) and Fund for Newly-enrolled Talent of Guizhou University (Guidarenjihezi (2019)64). We would also thank Professor Yongmin Wang for grammar corrections.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. Funding for open access charge: Universidade de Santiago de Compostela/CISUG. All data generated or analysed during this study is included in this published article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, D., Zhou, X., He, T. et al. Remediation of Mercury-Polluted Farmland Soils: A Review. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 109, 661–670 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-022-03544-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-022-03544-0