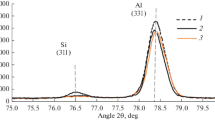
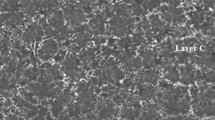
Abstract
The microstructure, the grain structure, and the elemental composition of the Al–11.8Si–0.6Mg–0.4Mn–0.6Fe–0.8Ni–1.7Cu alloy (wt %) fabricated at melt cooling rates of 102 and 105 K/s have been investigated by scanning electron microscopy, electron backscattered diffraction, and electron-probe microanalysis. An increase in the cooling rate of the melt from 102 to 105 K/s refines the structural constituents of the alloy (grain sizes, intermetallic particle sizes, silicon particle sizes) by two orders of magnitude. The foil formed at a melt cooling rate of 105 K/s has a layered microstructure in the cross-section. High-rate solidification provides a constant concentration of elements in the layers. The formation of nanoinclusions in the foil layer adjacent to the mold has been explained. The composition of submicron (up to 200 nm) compounds localized at the boundaries of eutectic grains in the layer at the freely solidified side has been identified.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
A. T. Volochko, “Modification of eutectic and primary silicon particles in silumins. Development prospects,” Lit’e i Metallurgiya, No. 4 (81), 38–45 (2015).
C. Jiqiang, L. Chao, W. Feng, Z. Hongjin, and R. Renguo, “Effect of micro alloying end tensile deformation on the internal structures of eutectic Si phase in Al–Si alloy,” J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, No. 3, 4682–4691 (2020).
E. I. Marukovich and V. Yu. Stetsenko, Modification of Alloys (Belarus. Navuka, Minsk, 2009) [in Russian].
H. Shaodong, D. Yanchao, A. Annie, Y. Fautrelle, R. Moreau, Z. Ren, K. Deng, C. Li, and X. Li, “Effect of a magnetic field on macro segregation of the primary silicon phase in hypereutectic Al–Si alloy during directional solidification,” J. Alloys Compd. 722, 108–115 (2017).
M. Li, N. Omura, Y. Murakami, I. Matsui, and S. Tada, “A comparative study of the primary phase formation in Al–7 wt. % Si and Al–17 wt. % Si alloys solidified by electromagnetic stirring processing,” Mater. Today Commun. 24, 101146 (2020).
E. I. Marukovich and V. Yu. Stetsenko, “The main problems of casting silumins. Solutions,” Lit’e i Metallurgiya, No. 3 (84), 28–30 (2016).
A. M. Khalil, I. S. Loginova, A. N. Solonin, and A. O. Mosleh, “Controlling liquation behavior and solidification cracks by continuous laser melting process of AA–7075 aluminum alloy,” Mater. Lett. 277, 128364 (2020).
S. C. Yoon, S-J. Hong, S. Hong, and H. S. Kim, “Mechanical properties of equal channel angular pressed powder extrudates of a rapidly solidified hypereutectic Al–20 wt % Si alloy,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 449–451, 966–970 (2007).
H. Jones, “Formation of phases and microstructures by rapid solidification processing: an update,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 179, 14180(1–7) (1994).
O. V. Gusakova, V. G. Shepelevich, D. V. Aleksandrov, and I. O. Starodumov, “Features of the structure formation in Al–12.2Si–0.2Fe alloys under rapid solidification from the melt,” Rasplavy, No. 2, 138–148 (2020).
Z. Chen, Y. Lei, and H. Zhang, “Structure and properties of nanostructured A357 alloy produced by melt spinning compared with direct chill ingot,” J. Alloys Compd. 509, 7473–7477 (2011).
L. Hengcheng, T. Yunyi, S. Xiaojing, L. Guangjin, H. Yiyun, U. S. Dixit, and P. Pavel, “Dispersoid particles precipitated during the solute ionizing course of Al–12 wt % Si–4 wt % Cu–1.2 wt % Mn alloy and their influence on high temperature strength,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 699, 201–209 (2017).
D. Tianshun, C. Chunxiang, L. Shuangjin, Y. Lijun, and S. Jibing., “Influence of rapid solidification of Cu–P intermediate alloy on wear resistance of Al–Si alloy,” Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 37, No. 4, 0686–0689 (2008).
S. Liua, X. Zhanga, H-L. Peng, X. Han, H.-Y. Yanga, T.-T. Li, L. Zhu, S. Zhang, F. Qiua, Z.-H. Ba, S.‑M. Chen, W. Zhou, and Q-C. Jianga, “In situ nanocrystals manipulate solidification behavior and microstructures of hypereutectic Al–Si alloys by Zr-based amorphous alloys,” J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, No. 3, 4644–4654 (2020).
T. Gao, Z.-Q. Li, Y.-X. Zhang, and X.-F. Liu, “Evolution behavior of c-Al3.5FeSi in Mg melt and a separation method of Fe from Al–Si–Fe alloys,” Acta Metall. Sin. (Eng. Lett.) 31, 48–54 (2018).
I. Johansen and H. J. Roven, “Mechanical properties of a rapidly solidified A1–Si–Ni–Mn alloy,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 179/180, 605–608 (1994).
Z. Zhang, H. Tezuka, E. Kobayashi, and T. Sato, “Effects of the Mn/Fe ratio and cooling rate on the modification of Fe intermetallic compounds in cast A356 based alloy with different Fe contents,” Mater. Trans. 54, No. 8, 1484–1490 (2001).
O. Gusakova, V. Shepelevich, D. V. Alexandrov, and I. O. Starodumov, “Formation of the microstructure of rapidly solidied hypoeutectic Al–Si alloy,” Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 229, 417–425 (2020).
V. G. Shepelevich, O. V. Gusakova, and S. V. Gusakova, “Structural and phase state of Al–Si–Fe–Mn alloys during high-speed solidification,” Proc. of the MNTK Conf. “Materials, Equipment and Resource-Saving Technologies” April 21–23, 2021 (Mogilev, 2021), pp. 160–161.
V. G. Shepelevich, O. V. Gusakova, D. V. Aleksandrov, and I. O. Starodumov, “Influence of the melt cooling rate on the microstructure of the Al–Si–Mn alloy,” Proc. of the 5th ISPC “Applied Problems of Optics, Informatics, Radiophysics and Condensed Matter Physics” May 15–17, 2019 (Minsk, 2019), pp. 273–275.
A. S. Kalinichenko and Yu. K. Krivosheev, “Determination of the depth of melt supercooling and the nature of structure formation during quenching from a liquid state,” Lit’e i Metallurgiya, No. 3, 60–65 (2001).
W. Wang and H. -H. Qiu, “Interfacial thermal conductance in rapid contact solidification process,” Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer. 45, 2043–2053 (2002).
M. A. Martorano and J. D. T. Capocchi, “Heat transfer coefficient at the metal-mould interface in the unidirectional solidification of Cu–8% Sn alloys,” Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 43, 2541–2552 (2000).
P. S. We and F. B. Yeh, “Heat transfer coefficient in rapid solidification of a liquid layer on a substrate,” J. Heat Transfer 122, 792–799 (2000).
P. K. Galenko and D. M. Kherlakh, “Diffusionless crystal growth in a eutectic system during rapid solidification,” J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 103, 150–158 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by T. Gapontseva
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gusakova, O.V., Gusakova, S.V. & Shepelevich, V.G. Melt Cooling Rate Effect on the Microstrucutre of Al–Si Alloy Doped with Mg, Mn, Fe, Ni, and Cu. Phys. Metals Metallogr. 123, 500–506 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X22050039
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X22050039