Abstract
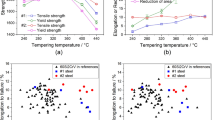
The results of structural studies of ferritic–martensitic steels EK181 (Fe–12Cr–W–V–Ta–B–C) and ChS139 (Fe–12Cr–Ni–Mo–W–Nb–V–B–N–C) after aging at temperatures of 450, 550, 650, and 700°C for a period of 1000–22 000 h are presented. Optical and electron microscopy are used in the study. The following common trends are revealed for both steels: aging for up to 19 000 h at 450 and 550°C is characterized by a low rate of decomposition of the supersaturated solid solution and by the preservation of the structural parameters of the studied steels at the initial level; aging at 650 and 700°C initiates, starting from an exposure time of 1000 h, the softening processes accompanied by the formation of a subgrain structure and coagulation of carbides. The precipitation of the Fe2(Mo, W) Laves phase after aging at a temperature of 650°C is a distinctive feature of the structure of steel ChS139 compared to steel EK181.









Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
R. Odette and S. Zinkle, Structural Alloys for Nuclear Energy Applications (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2019).
R. L. Klueh and A. T. Nelson, “Ferritic/martensitic steels for next-generation reactors,” J. Nuclear Mater. 371, 37–52 (2007).
M. V. Leont’eva-Smirnova, A. N. Agafonov, G. N. Ermolaev, A. G. Ioltukhovskii, E. M. Mozhanov, L. I. Reviznikov, V. V. Tsvelev, V. M. Chernov, T. M. Bulanova, V. N. Golovanov, Z. O. Ostrovskii, V. K. Shamardin, A. I. Blokhin, M. B. Ivanov, E. V. Kozlov, Yu. R. Kolobov, and B. K. Kardashev, “Microstructure and mechanical properties of low-activated ferritic-martensitic steel EK-181 (RUSFER-EK-181),” Perspektivnye Materialy, No. 6, 40–52 (2006).
N. S. Nikolaeva, M. V. Leont’eva-Smirnova, E. M. Mozhanov, T. A. Churyumova, P. V. Kotov, E. V. Tsvetkova, A. V. Mitroshenkov, and K. V. Prokhorenkov, “Optimization of technology for heat treatment of pipes made of ferritic-martensitic steels EK181, ChS139,” VANT. Ser.: Materialovedenie i Novye Materialy, No. 2, 45–58 (2013).
V. V. Sagaradze, T. N. Kochetkova, N. V. Kataeva, K. A. Kozlov, V. A. Zavalishin, N. F. Vil’danova, V. S. Ageev, M. V. Leont’eva-Smirnova, and A. A. Nikitina, “Structure and creep of russian reactor steels with a bcc structure,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 118, No. 5, 494–506 (2017).
V. M. Chernov, M. V. Leont’eva-Smirnova, E. M. Mozhanov, N. S. Nikolaeva, A. N. Tyumentsev, N. A. Polekhina, I. Yu. Litovchenko, and E. G. Astafurova, “Thermal stability of the microstructure of 12% chromium ferritic–martensitic steels after long-term aging at high temperatures,” Tech. Phys. 61, 209–214 (2016).
X. Xiao, G. Liu, B. Hu, J. Wang, and W. Ma, “Microstructure stability of V and Ta microalloyed 12% Cr reduced activation ferrite/martensite steel during long-term aging at 650°C,” J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 31, No. 3, 311–319 (2015).
X. Hu, L. Huang, W. Yan, W. Wang, W. Sha, Y. Shan, and K. Yan, “Evolution of microstructure and changes of mechanical properties of CLAM steel after long-term aging,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 586, 253–258 (2013).
H. Ghassemi-Armaki, R. P. Chen, K. Maruyama, M. Yoshizawa, and M. Igarashi, “Static recovery of tempered lath martensite microstructures during long-term aging in 9–12% Cr heat resistant steels,” Mater. Lett. 63, 2423–2425 (2009).
K. Shiba, H. Tanigawa, T. Hirose, H. Sakasegawa, and S. Jitsukawa, “Long-term properties of reduced activation ferritic/martensitic steels for fusion reactor blanket system,” Fusion Eng. Des. 86, 2895–2899 (2011).
P. Hu, W. Yan, W. Sha, W. Wang, Y. Shan, and K. Yan, “Microstructure evolution of a 10Cr heat-resistant steel during high temperature creep,” J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 27, No. 4, 344–351 (2011).
Y. Xu, Y. Nie, M. Wang, W. Li, and X. Jin, “The effect of microstructure evolution on the mechanical properties of martensite ferritic steel during long-term aging,” Acta Mater. 131, 110–122 (2017).
K. A. Lanskaya, High-Chromium Heat Resistant Steels (Metallurgiya, Moscow, 1976) [in Russian].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by O. Kadkin
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nikolaeva, N.S., Leont’eva-Smirnova, M.V. & Mozhanov, E.M. Effect of Thermal Aging for up to 22 Thousand Hours on the Structural and Phase State of Ferritic–Martensitic Steels EK181 and ChS139. Phys. Metals Metallogr. 123, 489–499 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X22050118
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X22050118