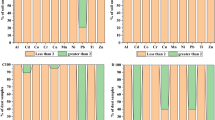
Abstract
Soil and road dust are important receptors of heavy metals in the environment. Meanwhile, heavy metal could transfer to the atmosphere through resuspension. Due to the serious consequences and atmospheric haze in Jing-Jin-Ji area, it’s important to evaluate the pollution level, particle size distribution and sources of heavy metals. For heavy metals in soil samples, similar concentrations to the background values and no obvious pollution or low-level pollution was presented. Higher concentration of Cu (78.9 mg/kg) and Zn (261 mg/kg) were found in road dust. The source appointment results showed that Mn, Co, Cr, Ni, Zn and Pb in soils and Cr, Co and Mn in road dust were mainly from the natural sources, while traffic source contributed to most of Cu, Zn and Pb in road dust. Different particle size distribution patterns were found in soils and road dusts, and the finest particles presented the highest heavy metal concentrations.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen H, Teng Y, Lu S, Wang Y, Wang J (2015) Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China. Sci Total Environ 512–513:143–153
Chen H, Teng Y, Lu S, Wang Y, Wu J, Wang J (2016) Source apportionment and health risk assessment of trace metals in surface soils of Beijing metropolitan, China. Chemosphere 144:1002–1011
De Silva S, Ball AS, Huynh T, Reichman SM (2016) Metal accumulation in roadside soil in Melbourne, Australia: effect of road age, traffic density and vehicular speed. Environ Pollut 208:102–109
Gao J, Wang K, Wang Y, Liu S, Zhu C, Hao J, Liu H, Hua S, Tian H (2018) Temporal-spatial characteristics and source appointment of PM2.5 as well as its associated chemical species in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region of China. Environ Pollut 233:714–724
Gong C, Ma L, Cheng H, Liu Y, Xu D, Li B, Liu F, Ren Y, Liu Z, Zhao C, Yang K, Nie H, Lang C (2014) Characterization of the particle size fraction associated heavy metals in tropical arable soils from Hainan Island, China. J Geochem Explor 139:109–114
Kamani H, Ashrafi SD, Isazadeh S, Jaafari J, Hoseini M, Mostafapour FK, Bazrafshan E, Nazmara S, Mahvi AH (2015) Heavy metal contamination in street dusts with various land uses in Zahedan, Iran. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 94:382–386
Lanzerstorfer C (2018) Heavy metals in the finest size fractions of road-deposited sediments. Environ Pollut 239:522–531
Lee CS, Li X, Shi W, Cheung SC, Thornton I (2006) Metal contamination in urban, suburban, and country park soils of Hong Kong: a study based on GIS and multivariate statistics. Sci Total Environ 356:45–61
Liu Y, Sun J, Zhao M, Ni Y, Wang W, Fan Z (2022) Seasonal variation and contamination risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediment of an estuary alluvial island in eastern China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 108:337–343
Luo X, Yu S, Zhu Y, Li X (2012) Trace metal contamination in urban soils of China. Sci Total Environ 421–422:17–30
Padoan E, Romè C, Ajmone-Marsan F (2017) Bioaccessibility and size distribution of metals in road dust and roadside soils along a peri-urban transect. Sci Total Environ 601–602:89–98
Pan L, Ma J, Wang X, Hou H (2016) Heavy metals in soils from a typical county in Shanxi Province, China: levels, sources and spatial distribution. Chemosphere 148:248–254
Pan H, Lu X, Lei K (2017) A comprehensive analysis of heavy metals in urban road dust of Xi’an, China: contamination, source apportionment and spatial distribution. Sci Total Environ 609:1361–1369
Qian J, Shana X, Wang Z, Tu Q (1996) Distribution and plant availability of heavy metals in different particle-size fractions of soil. Sci Total Environ 187:131–141
Shao Y, Yang G, Luo M, Xu D, Tazoe H, Yamada M, Ma L (2021) Background and fingerprint characteristics of anthropogenic 236U and 137Cs in soil and road dust samples collected from Beijing and Zhangjiakou, China. Chemosphere 263:127909
Škrbić BD, Buljovčić M, Jovanović G, Antić I (2018) Seasonal, spatial variations and risk assessment of heavy elements in street dust from Novi Sad. Serbia Chemosphere 205:452–462
Tian X, Chai G, Xie Q, Fan M, Qin S, Fan C, Gong Y, Liu J, Li G (2022) Risk identification of heavy metals in agricultural soils from a typically high Cd geological background area in upper reaches of the Yangtze River. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03417-y. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol
Vallverdu-Coll N, Mateo R, Mougeot F, Ortiz-Santaliestra ME (2019) Immunotoxic effects of lead on birds. Sci Total Environ 689:505–515
Vardhan K, Kumar PS, Panda RC (2019) A review on heavy metal pollution, toxicity and remedial measures: Current trends and future perspectives. J Mol Liq 290:111197
Wang B, Xia D, Yu Y, Chen H, Jia J (2018) Source apportionment of soil-contamination in Baotou City (North China) based on a combined magnetic and geochemical approach. Sci Total Environ 642:95–104
Wei X, Gao B, Wang P, Zhou H, Lu J (2015) Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in street dusts from different functional areas in Beijing, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 112:186–192
Yang Q, Li Z, Lu X, Duan Q, Huang L, Bi J (2018) A review of soil heavy metal pollution from industrial and agricultural regions in China: pollution and risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 642:690–700
Yu Y, Li Y, Li B, Shen Z, Stenstrom MK (2016) Metal enrichment and lead isotope analysis for source apportionment in the urban dust and rural surface soil. Environ Pollut 216:764–772
Yu S, Liu W, Xu Y, Yi K, Zhou M, Tao S, Liu W (2019) Characteristics and oxidative potential of atmospheric PM2.5 in Beijing: sources apportionment and seasonal vatiation. Sci Total Environ 650:277–287
Zhang R, Zhang Z, Wu J, Wang L (2022) Spatial characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in the soil-vegetation system of a red mud slag yard, SW China. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-022-03493-8. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol
Zhao H, Li X, Wang X, Tian D (2010) Grain size distribution of road-deposited sediment and its contribution to heavy metal pollution in urban runoff in Beijing, China. J Hazard Mater 183:203–210
Acknowledgements
This work was financially support by Key Deployment Projects of CAS (ZDRW-CN-2018-1), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Numbers: 111875266, U1832212, 91643206, U1932103) and Institute of High Energy Physics Foundation, Chinese Academy of Sciences (E0546BU20B).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, Y., Yang, G., Luo, M. et al. Multiple Evaluation of Typical Heavy Metals Pollution in Surface Soil and Road Dust from Beijing and Hebei Province, China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 109, 317–322 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-022-03537-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-022-03537-z