Abstract
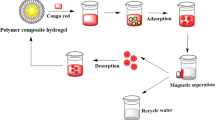
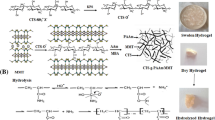
In this study, we have developed a simple technique to prepare cationic chitosan hydrogel with interconnected porous structure using freeze–thaw process and the obtained hydrogel was named FCS hydrogel. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) imaging discovered that the synthesized hydrogel demonstrated interconnected porous structure in the scope of 5–20 μm. We also showed that the FCS hydrogel exhibits pH responsiveness behavior, and demonstrated reversible swelling and de-swelling behaviors maintaining their mechanical stability. We demonstrate that the FCS hydrogel swelling capacity decreased at alkaline pH and rose with a decline in pH value. Besides, the FCS hydrogel presented specific surface area of 78.25 ± 8.75 m2 g−1, due to the cryogenic treatment of glutaraldehyde cross-linked chitosan hydrogel could increase the surface area and permeability of composite hydrogel and then strongly increasing the adsorption capacity. Subsequently, the FCS monolithic hydrogel tested dyes removal, which provides a high removal efficiency towards anionic dyes including congo red (CR) and sodium fluorescein (SFL) dyes. Significantly, we show that the FCS hydrogel could be regenerated and reused as an adsorbent for wastewater treatment without significant loss of pollutants removal efficiency over a number of adsorption and washing cycles. This study offers a promising environmental friendly and sustainable interconnected porous hydrogel for anionic dye removal from wastewater.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao J, Yin J, Zhong J et al (2019) Facile preparation of a self-assembled artemia cyst shell–TiO2–MoS2 porous composite structure with highly efficient catalytic reduction of nitro compounds for wastewater treatment. Nanotechnology 31:85603
Wang C, Yin J, Han S et al (2019) Preparation of palladium nanoparticles decorated polyethyleneimine/polycaprolactone composite fibers constructed by electrospinning with highly efficient and recyclable catalytic performances. Catalysts 9:559
Binaeian E, Zadvarzi SB, Yuan D (2020) Anionic dye uptake via composite using chitosan-polyacrylamide hydrogel as matrix containing TiO2 nanoparticles; comprehensive adsorption studies. Int J Biol Macromol 162:150–162
Islam MA (2020) Synthesis of manganite (γ− MnOOH) for the adsorptive degradation of methylene blue (MB) and orange green (OG) from aqueous solution. Cell 1818:482533
Kapoor RT, Danish M, Singh RS et al (2021) Exploiting microbial biomass in treating azo dyes contaminated wastewater: mechanism of degradation and factors affecting microbial efficiency. J Water Process Eng 43:102255
Demirbas A (2009) Agricultural based activated carbons for the removal of dyes from aqueous solutions: a review. J Hazard Mater 167:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.12.114
Gupta VK, Suhas (2009) Application of low-cost adsorbents for dye removal a review. J Environ Manage 90:2313–2342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2008.11.017
Vashi H, Iorhemen OT, Tay JH (2017) Aerobic granulation: a recent development on the biological treatment of pulp and paper wastewater. Environ Technol Innov 9:265–274
An B, Choi J (2019) An experimental application of four types of chitosan bead for removal of cationic and anionic pollutants. Water Air Soil Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4365-9
Mezohegyi G, van der Zee FP, Font J et al (2012) Towards advanced aqueous dye removal processes: a short review on the versatile role of activated carbon. J Environ Manage 102:148–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.02.021
Halbus AF, Athab ZH, Hussein FH (2021) Review on preparation and characterization of activated carbon from low cost waste materials. Egypt J Chem 64:7255–7268
Hussein FH, Halbus AF, Lafta AJ, Athab ZH (2015) Preparation and characterization of activated carbon from iraqi khestawy date palm. J Chem. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/295748
Zahraa HA (2015) Production and characterization of activated carbon from iraqi palm fiber. Asian J Chem 27:3658–3662
Halbus AF, Athab ZH, Hussein FH (2013) Adsorption of disperse blue dye on Iraqi date palm seeds activated carbon. Int J Chem Sci 11:1219–1233
Ren J, Wang X, Zhao L et al (2021) Effective removal of dyes from aqueous solutions by a gelatin hydrogel. J Polym Environ 29:3497–3508
Sinha V, Chakma S (2019) Advances in the preparation of hydrogel for wastewater treatment: a concise review. J Environ Chem Eng 7:103295
Hou N, Wang R, Geng R et al (2019) Facile preparation of self-assembled hydrogels constructed from poly-cyclodextrin and poly-adamantane as highly selective adsorbents for wastewater treatment. Soft Matter 15:6097–6106
Loo S-L, Vásquez L, Athanassiou A, Fragouli D (2021) Polymeric hydrogels—a promising platform in enhancing water security for a sustainable future. Adv Mater Inter 8:2100580. https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.202100580
Weerasundara L, Gabriele B, Figoli A et al (2020) Hydrogels: novel materials for contaminant removal in water—a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 51:1–45. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2020.1776055
Kaith BS, Singh A, Sharma AK, Sud D (2021) Hydrogels: synthesis, classification, properties and potential applications—a brief review. J Polym Environ 29:3827–3841
Yu Y, Cheng Y, Tong J et al (2021) Recent advances in thermo-sensitive hydrogels for drug delivery. J Mater Chem B 9:2979–2992
Qi X, Tong X, Pan W et al (2021) Recent advances in polysaccharide-based adsorbents for wastewater treatment. J Clean Prod 315:128221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128221
Hassanzadeh P, Gharbani P, Derakhshanfard F, Maher BM (2021) Preparation and characterization of PVDF/gC 3 N 4/chitosan polymeric membrane for the removal of direct blue 14 dye. J Polym Environ. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-218812/v1
Younes I, Rinaudo M (2015) Chitin and chitosan preparation from marine sources. Structure, properties and applications. Mar Drugs 13:1133–1174
Ostrowska-Czubenko J, Gierszewska M, Pieróg M (2015) pH-responsive hydrogel membranes based on modified chitosan: water transport and kinetics of swelling. J Polym Res 22:1–12
Galan J, Trilleras J, Zapata PA et al (2021) Optimization of chitosan glutaraldehyde-crosslinked beads for reactive blue 4 anionic dye removal using a Surface response methodology. Life 11:85
Chang X, Chen D, Jiao X (2008) Chitosan-based aerogels with high adsorption performance. J Phys Chem B 112:7721–7725
Bratskaya S, Privar Y, Nesterov D et al (2019) Chitosan gels and cryogels cross-linked with diglycidyl ethers of ethylene glycol and polyethylene glycol in acidic media. Biomacromol 20:1635–1643. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.8b01817
Yang C, Shi X, Qi L et al (2021) Electrical writing induced covalent cross-linking on hydrogel for multidimensional structural information storage. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13:36538–36547. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c09548
Pérez-Calderón J, Santos MV, Zaritzky N (2020) Synthesis, characterization and application of cross-linked chitosan/oxalic acid hydrogels to improve azo dye (Reactive Red 195) adsorption. React Funct Polym 155:104699
Mathew AP, Laborie M-PG, Oksman K (2009) Cross-linked chitosan/chitin crystal nanocomposites with improved permeation selectivity and pH stability. Biomacromol 10:1627–1632. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm9002199
Kayan GÖ, Kayan A (2021) Composite of natural polymers and their adsorbent properties on the dyes and heavy metal ions. J Polym Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-021-02154-x
Reghioua A, Barkat D, Jawad AH et al (2021) Magnetic chitosan-glutaraldehyde/zinc oxide/Fe 3 O 4 nanocomposite: optimization and adsorptive mechanism of remazol brilliant blue r dye removal. J Polym Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20673-5
Tu H, Yu Y, Chen J et al (2017) Highly cost-effective and high-strength hydrogels as dye adsorbents from natural polymers: chitosan and cellulose. Polym Chem 8:2913–2921
Mahmoodi H, Fattahi M, Motevassel M (2021) Graphene oxide–chitosan hydrogel for adsorptive removal of diclofenac from aqueous solution: preparation, characterization, kinetic and thermodynamic modelling. RSC Adv 11:36289–36304
Alves DCS, Goncalves JO, Coseglio BB et al (2019) Adsorption of phenol onto chitosan hydrogel scaffold modified with carbon nanotubes. J Environ Chem Eng 7:103460
Alves DC, Healy B, Yu T, Breslin CB (2021) Graphene-based materials immobilized within chitosan: applications as adsorbents for the removal of aquatic pollutants. Materials (Basel) 14:3655
Niu Z, Liu L, Zhang L, Chen X (2014) Porous graphene materials for water remediation. Small 10:3434–3441
da Silva Alves DC, Healy B, Pinto LA et al (2021) Recent developments in chitosan-based adsorbents for the removal of pollutants from aqueous environments. Molecules 26:594
Chatterjee S, Chatterjee T, Lim S-R, Woo SH (2011) Effect of the addition mode of carbon nanotubes for the production of chitosan hydrogel core–shell beads on adsorption of Congo red from aqueous solution. Bioresour Technol 102:4402–4409
Annabi N, Nichol JW, Zhong X et al (2010) Controlling the porosity and microarchitecture of hydrogels for tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part B Rev 16:371–383. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.TEB.2009.0639
Xue C, Wilson LD (2021) An overview of the design of chitosan-based fiber composite materials. J Compos Sci 5:160
Sun S, Tang Y, Fu Q et al (2012) Preparation of agarose/chitosan composite supermacroporous monolithic cryogels for affinity purification of glycoproteins. J Sep Sci 35:893–900
Ho M-H, Kuo P-Y, Hsieh H-J et al (2004) Preparation of porous scaffolds by using freeze-extraction and freeze-gelation methods. Biomaterials 25:129–138
Quirk RA, France RM, Shakesheff KM, Howdle SM (2004) Supercritical fluid technologies and tissue engineering scaffolds. Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci 8:313–321
Deville S, Saiz E, Nalla RK, Tomsia AP (2006) Freezing as a path to build complex composites. Science 311:515–518
Sornkamnerd S, Okajima MK, Kaneko T (2017) Tough and porous hydrogels prepared by simple lyophilization of LC gels. ACS Omega 2:5304–5314
Hwang Y, Sangaj N, Varghese S (2010) Interconnected macroporous poly (ethylene glycol) cryogels as a cell scaffold for cartilage tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part A 16:3033–3041
Ding Y, Song C, Gong W et al (2021) Robust, sustainable, hierarchical multi-porous cellulose beads via pre-crosslinking strategy for efficient dye adsorption. Cellulose 28:7227–7241
Luo W, Bai Z, Zhu Y (2018) Fast removal of Co (ii) from aqueous solution using porous carboxymethyl chitosan beads and its adsorption mechanism. RSC Adv 8:13370–13387
Azlan K, Saime WNW, Liew LAI (2009) Chitosan and chemically modified chitosan beads for acid dyes sorption. J Environ Sci 21:296–302
Pivarčiová L, Rosskopfová O, Galamboš M et al (2016) Sorption of pertechnetate anions on chitosan. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 308:93–98
Dui J, Zhu G, Zhou S (2013) Facile and economical synthesis of large hollow ferrites and their applications in adsorption for As (V) and Cr (VI). ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:10081–10089
Zhang Y, Yan W, Sun Z et al (2015) Fabrication of porous zeolite/chitosan monoliths and their applications for drug release and metal ions adsorption. Carbohydr Polym 117:657–665
Song W, Xu J, Gao L et al (2021) Preparation of freeze-dried porous chitosan microspheres for the removal of hexavalent chromium. Appl Sci 11:4217
Kizilay MY, Okay O (2003) Effect of initial monomer concentration on spatial inhomogeneity in poly (acrylamide) gels. Macromolecules 36:6856–6862
Nematidil N, Sadeghi M, Nezami S, Sadeghi H (2019) Synthesis and characterization of schiff-base based chitosan-g-glutaraldehyde/NaMMTNPs-APTES for removal Pb2+ and Hg2+ ions. Carbohydr Polym 222:114971
Ostrowska-Czubenko J, Gierszewska-Drużyńska M (2009) Effect of ionic crosslinking on the water state in hydrogel chitosan membranes. Carbohydr Polym 77:590–598
Roberts GAF, Taylor KE (1989) Chitosan gels, 3. The formation of gels by reaction of chitosan with glutaraldehyde. Die Makromol Chemie Macromol Chem Phys 190:951–960
Raju L, SCL AR, Prakash NKU, Rajkumar E (2021) Chitosan-terephthaldehyde hydrogels effect of concentration of cross-linker on structural, swelling, thermal and antimicrobial properties. Materialia 16:101082
Leduc J-F, Leduc R, Cabana H (2014) Phosphate adsorption onto chitosan-based hydrogel microspheres. Adsorpt Sci Technol 32:557–569
Saïed N, Aïder M (2014) Zeta potential and turbidimetry analyzes for the evaluation of chitosan/phytic acid complex formation. J food Res 3:71
Boardman SJ, Lad R, Green DC, Thornton PD (2017) Chitosan hydrogels for targeted dye and protein adsorption. J Appl Polym Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.44846
Lone S, Yoon DH, Lee H, Cheong IW (2019) Gelatin–chitosan hydrogel particles for efficient removal of Hg (II) from wastewater. Environ Sci Water Res Technol 5:83–90
Park H, Park K, Kim D (2006) Preparation and swelling behavior of chitosan-based superporous hydrogels for gastric retention application. J Biomed Mater Res Part A 76:144–150
Ullah F, Othman MBH, Javed F et al (2015) Classification, processing and application of hydrogels: a review. Mater Sci Eng C 57:414–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.07.053
Wu M, Chen W, Mao Q et al (2019) Facile synthesis of chitosan/gelatin filled with graphene bead adsorbent for orange II removal. Chem Eng Res Des 144:35–46
Domard A (1987) Determination of N-acetyl content in chitosan samples by cd measurements. Int J Biol Macromol 9:333–336
Hameed BH, El-Khaiary MI (2008) Malachite green adsorption by rattan sawdust: isotherm, kinetic and mechanism modeling. J Hazard Mater 159:574–579
Zhao R, Zheng H, Zhong Z et al (2021) Efficient removal of diclofenac from surface water by the functionalized multilayer magnetic adsorbent: kinetics and mechanism. Sci Total Environ 760:144307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144307
Wong S, Ghafar NA, Ngadi N et al (2020) Effective removal of anionic textile dyes using adsorbent synthesized from coffee waste. Sci Rep 10:1–13
Khraisheh MAM, Al-Ghouti MA, Allen SJ, Ahmad MNM (2004) The effect of pH, temperature, and molecular size on the removal of dyes from textile effluent using manganese oxides-modified diatomite. Water Environ Res 76:2655–2663
Hosseinzadeh H, Ramin S (2018) Effective removal of copper from aqueous solutions by modified magnetic chitosan/graphene oxide nanocomposites. Int J Biol Macromol 113:859–868
Yang S, Zhao F, Sang Q et al (2021) Investigation of 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane modifying attapulgite for congo red removal: mechanisms and site energy distribution. Powder Technol 383:74–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2021.01.046
Kıvanç MR, Ozay O, Ozay H (2020) Ilgin P (2020) Removal of anionic dyes from aqueous media by using a novel high positively charged hydrogel with high capacity. J Dispers Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2020.1847658
Puchana-Rosero MJ, Adebayo MA, Lima EC et al (2016) Microwave-assisted activated carbon obtained from the sludge of tannery-treatment effluent plant for removal of leather dyes. Coll Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 504:105–115
Pan M, Lin X, Xie J, Huang X (2017) Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies for phosphate adsorption on aluminum hydroxide modified palygorskite nano-composites. RSC Adv 7:4492–4500
Zhou C, Wu Q, Lei T, Negulescu II (2014) Adsorption kinetic and equilibrium studies for methylene blue dye by partially hydrolyzed polyacrylamide/cellulose nanocrystal nanocomposite hydrogels. Chem Eng J 251:17–24
Chiou MS, Li HY (2003) Adsorption behavior of reactive dye in aqueous solution on chemical cross-linked chitosan beads. Chemosphere 50:1095–1105
Acknowledgements
The authors express their gratitude to the College of Science, University of Babylon in Iraq for supporting this research. Z.H.A. and A.F.H. would like to express their acknowledgment to the University of Hull.
Funding
This study was supported by the University of Babylon, Environmental Research and Studies Center and College of Science, Iraq.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Athab, Z.H., Halbus, A.F., Abbas, A.S. et al. Enhanced Macroporous Cationic Chitosan Hydrogel by Freezing and Thawing Method with Superadsorption Capacity for Anionic Dyes. J Polym Environ 30, 3815–3831 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-022-02462-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-022-02462-w