Abstract
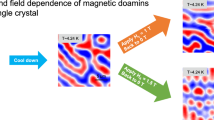
Magnetic phase transition in Fe49Rh51 was studied using wide-field Kerr microscopy. In zero magnetic field, temperature dependences of rotation of polarization plane on the sample surface are obtained. The analysis of the obtained data shows that the temperature of the AFM–FM phase transition is TN, heat = 323.5 K, and that of the reverse FM–AFM phase transition is TN, cool = 317 K. In a magnetic field of 0.5 T, the temperature hysteresis shifts to lower temperatures by 4 K. For the first time ever, the magnetic polar domains with a disordered labyrinthine shape are found on the sample surface.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
D. Sander, S. O. Valenzuela, D. Makarov, C. H. Marrows, E. E. Fullerton, P. Fischer, J. McCord, P. Vavassori, S. Mangin, and P. Pirro, “The 2017 magnetism roadmap,” J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 50, 363001 (2017).
A. Zakharov, “Crystal lattice parameter and structural distortions in Fe-Rh alloy at phase transitions,” Fiz. Met. Metalloved. 24, 84–90 (1967).
S. A. Nikitin, G. Myalikgulyev, A. M. Tishin, M. P. Annaorazov, K. A. Asatryan, and A. L. Tyurin, “The magnetocaloric effect in Fe49Rh51 compound,” Phys. Lett. A 148, 363–366 (1990).
A. M. Aliev, A. B. Batdalov, L. N. Khanov, A. P. Kamantsev, V. V. Koledov, A. V. Mashirov, V. G. Shavrov, R. M. Grechishkin, A. R. Kaul, and V. Sampath, “Reversible magnetocaloric effect in materials with first order phase transitions in cyclic magnetic fields: Fe48Rh52 and Sm0.6Sr0.4MnO3,” Appl. Phys. Lett. 109, 202407 (2016).
E. Stern-Taulats, A. Planes, P. Lloveras, M. Barrio, J.‑L. Tamarit, S. Pramanick, S. Majumdar, C. Frontera, and L. Mañosa, “Barocaloric and magnetocaloric effects in Fe49Rh51,” Phys. Rev. B 89, 214105 (2014).
S. Nikitin, G. Myalikgulyev, M. Annaorazov, A. L. Tyurin, R. W. Myndyev, and S. A. Akopyan, “Giant elastocaloric effect in FeRh alloy,” Phys. Lett. A 171, 234–236 (1992).
S. Foner, “Vibrating sample magnetometer,” Rev. Sci. Instrum. 27 (7), 548 (1956).
G. W. H. Hohne, W. F. Hemminger, and H. J. Flammersheim, Differential Scanning Calorimetry, 2nd ed. (Springer, Berlin, 2003).
A. Chirkova, F. Bittner, K. Nenkov, N. V. Baranov, L. Schultz, K. Nielsch, and T. G. Woodcock, “The effect of the microstructure on the antiferromagnetic to ferromagnetic transition in FeRh alloys,” Acta Mater. 131, 31–38 (2017).
A. S. Komlev, D. Y. Karpenkov, D. A. Kiselev, T. S. Ilina, A. Chirkova, R. R. Gimaev, T. Usami, T. Taniyama, V. I. Zverev, and N. S. Perov, “Ferromagnetic phase nucleation and its growth evolution in FeRh thin films,” J. Alloys Compd. 874, 159924 (2021).
V. I. Zverev, R. R. Gimaev, T. Miyanaga, A. A. Vaulin, A. F. Gubkin, B. B. Kovalev, A. M. dos Santos, E. Lovell, L. F. Cohen, and N. A. Zarkevich, “Peculiarities of the phase transformation dynamics in bulk FeRh based alloys from magnetic and structural measurements,” J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 522, 167560 (2021).
E. Mancini, F. Pressacco, M. Haertinger, E. E. Fullerton, T. Suzuki, G. Woltersdorf, and C. H. Back, “Magnetic phase transition in iron–rhodium thin films probed by ferromagnetic resonance,” J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 46, 245302 (2013).
A. Hubert and R. Schäfer, Magnetic Domains: The Analysis of Magnetic Microstructures (Springer, Berlin, 1998).
I. V. Soldatov and R. Schäfer, “Selective sensitivity in Kerr microscopy,” Rev. Sci. Instrum. 88, 073701 (2017).
A. A. Amirov, F. Cugini, A. P. Kamantsev, T. Gottschall, M. Solzi, A. M. Aliev, Yu. I. Spichkin, V. V. Koledov, and V. G. Shavrov, “Direct measurements of the magnetocaloric effect of Fe49Rh51 using the mirage effect,” J. Appl. Phys. 127, 233905 (2020).
F. Schmidt, W. Rave, and A. Hubert, “Enhancement of magneto-optical domain observation by digital image processing,” IEEE Trans. Magn. 21 (5), 1596–1598 (1985).
Funding
The work is supported by the mutual program of the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation and German Exchange Academic Service DAAD “Michael Lomonosov/Immanuel Kant” (Project no. 2295-21).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by O. Golovnya
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taaev, T.A., Amirov, A.A., Aliev, A.M. et al. Kerr Microscopy Study of Magnetic Phase Transition in Fe49Rh51. Phys. Metals Metallogr. 123, 402–406 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X22040123
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X22040123