Abstract
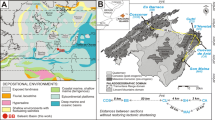
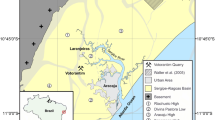
The < 900-m-thick Paleogene carbonates of the Maltese Islands and offshore wells comprise 16 facies grouped into 7 carbonate facies associations (TA, TB, TC, TD1, TD2, TE1 and TE2). Previous works misclassified facies as belonging to a carbonate ramp, which derailed hydrocarbon exploration. This study confirms that the 200-km-wide, flat-topped, Malta isolated carbonate platform consists of coarse-grained, platform margin sediments surrounding the muddy, shallow marine interior that was tectonically segmented by half graben during foreland extension. Dating by correlation to benthic foraminiferal zones reveals two > 15 Ma-long depositional hiatuses that bound the Eocene carbonates. Cyclic sediments are capped by Eocene gypsum beds and Oligocene palaeosols and were controlled by third-order sea level cycles. About 700 m of inner platform sediments accumulated from the Eocene (TA and TB) to the early Chattian (TC) until an abrupt and ubiquitous change to platform margin facies dominated by coralline red algae and subordinate corals (TD1). The succeeding transgressive rhodalgal biostrome (TD2) aggraded > 40 m and prograded into underfilled half graben, later capped by mobile dunes of large benthic foraminifera (TE1). Deeper water oligophotic to aphotic biota (TE2) draped over the platform by the late Chattian. Increased foreland subsidence and the spread of coarse-grained platform margin sediments signals the beginning of the drowning succession reflecting environmental stress, the decline of coral reef builders, reduced sedimentation rate and increased dispersal rates, culminating in hardgrounds along the drowning surface that terminated carbonate platform sedimentation by the end of the Chattian.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguirre J, Riding R, Braga J (2000) Diversity of coralline red algae: origination and extinction patterns from the Early Cretaceous to the Pleistocene. Paleobiology 26(4):651–667
Allen P, Allen J (2005) Basin Analysis. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Hoboken, p 451
Antonelli M, Franciosi R, Pezzi G, Querci A, Ronco GP, Vezzani F (1988) Palaeogeographic evolution and structural setting of the northern side of the Sicily Channel. Mem Soc Geol Ital 41:141–157
Argnani A (1990) The strait of Sicily rift zone: foreland deformation related to the evolution of a back-arc basin. J Geodyn 12:311–331
Bathurst RG (1975) Carbonate sediments and their diagenesis. Developments in Sedimentology, vol 12. Elsevier, Amsterdam, p 658
Beavington-Penney SJ (2004) Analysis of the effects of abrasion on the test of Palaeonummulites venosus: implications for the origin of nummulithoclastic sediments. Palaios 19:143–155
Beavington-Penney SJ, Wright VP, Racey A (2005) Sediment production and dispersal on foraminifera-dominated early Tertiary ramps: the Eocene El Garia Formation, Tunisia. Sedimentology 52:537–569
Beavington-Penney S, Wright V, Racey A (2006) The middle Eocene Seeb Formation of Oman: an investigation of acyclicity, stratigraphic completeness, and accummulation rates in shallow marine carbonate settings. J Sediment Res 76:1137–1161
Bennett S (1980) Palaeoenvironmental studies in Maltese mid-Tertiary carbonates. Unpublished PhD thesis, University of London
Bernoulli D, Jenkyns HC (1974) Alpine, Mediterranean, and Central Atlantic Mesozoic facies in relation to the early evolution of the Tethys. In: Modern and Ancient geosynclinal sedimentation, vol 19. SEPM Special publication, Tuls: pp 129–160
Bishop W, Debono G (1996) The hydrocarbon geology of southern offshore Malta and surrounding regions. J Pet Geol 19(2):129–160
Bismuth H, Bonnefous J (1981) The biostratigraphy of carbonate deposits of the middle and upper Eocene in northeatern offshore Tunisia. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 36:191–211
Bosellini A (2004) The western passive margin of Adria and its carbonate platforms. In: Special Volume of the Italian Geological Society for the IGC, pp 32, 79–92
Bosellini F (2006) Biotic changes and their control on Oligocene-Miocene reefs: a case study from the Apulia Platform margin (southern Italy). Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 241:393–409
Bosence D (1983a) Description and classification of rhodoliths (rhodoids, rhodolites). In: Peryt T (ed) Coated grains. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 217–224
Bosence D (1983b) The occurence and ecology of recent rhodoliths—a review. In: Peryt TM (ed) Coated grains. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 225–242
Bosence D (2005) A genetic classification of carbonate platforms based on their basinal and tectonic settings in the Cenozoic. Sed Geol 175:49–72
Bosworth W, El-Hawat A, Helgeson D, Burke K (2008) Cyrenaican “shock absorber” and associated inversion strain shadow in the collision zone of northeast Africa. Geology 36:695–698
BouDagher-Fadel M (2008) Evolution and geological significance of larger benthic foraminifera (Vols. Developments in Paleontology and Stratigraphy, 21). Elsevier, Amsterdam
Boulila S, Galbrun B, Miller K, Pekar S, Browning J, Laskar J, Wright J (2011) On the origin of Cenozoic and Mesozoic “third-order” eustatic sequences. Earth Sci Rev 109:94–112
Brandano M, Virgilio F, Tomassetti L, Pedley M, Matteucci R (2008) Facies analysis and palaeoenvironmental interpretation of the Late Oligocene Attard Member (Lower Coralline Limestone Formation), Malta. Sedimentology 56:1138–1158
Brown I, Osborne M, Gardner J (eds) (2018) Abstracts of ‘Eastern Mediterranean—An emerging major petroleum province’. Geol. Soc. (Petroleum Group), London
Burchette TP, Wright VP (1992) Carbonate ramp depostional systems. Sed Geol 79:3–57
Burgess P, Winefield P, Minzoni M, Elders C (2013) Methods for identification of isolated carbonate buildups from seismic reflection data. AAPG Bull 97:1071–1098
Buxton MW, Pedley HM (1989) A standardised model for Tethyan Tertiary carbonate ramps. J Geol Soc 146:746–748
Cahuzac B, Poignant A (1997) Essai de biozonation de l’Oligo-Miocene dans les bassins européens à l’aide des grands formaninfères néritiques. Bulletin De La Societé Géologique De France 168(2):155–169
Chaix C, Saint-Martin J-P (1994) Les associations coralliennes oligo-miocènes de Malte, un résumé de l'histoire paléobiogéographique de la Méditerranée. In: Interim Colloquium R.C.M.N.S (abstract book), 12. Marseille
Challis G (1979) Miocene echinoid biofacies of the Maltese Islands. Annales Géol. Pays Hellén. Tome hors série fasc. 1 VIth International Congress on Mediterranean Neogene, Athens, pp 253–262
Continental Shelf Department (2017) Malta petroleum exploration opportunities. OPM, Malta
Dart CJ, Bosence DW, McClay KR (1993) Stratigraphy and structure of the Maltese graben system. J Geol Soc 150:1153–1166
Davies C (1976) Accretion sets in the Lower Coralline Limestone of the Maltese Islands. J Sediment Petrol 46(2):414–417
Debono G, Xerri S, Bishop WF (2000) Continental, sabkha and open marine Liassic-Triassic sequence offers new exploration plays in Malta. EAGE conference on geology and petroleum geology. Malta, St Julians, pp 1–4
Dewey JF, Helman ML, Turco E, Hutton DH, Knott SD (1989) Kinematics of the western Mediterranean. In: Coward MP, Dietrich D, Park RG (eds) Alpine Tectonics, vol 45. Geological Society of London Special Publication, pp 265–283
Dorobek S (2008) Tectonic and depositional controls on syn-rift carbonate platform sedimentation. In: Lukasik J, Simo J (eds) Controls on carbonate platform and reef development. SEPM Special Publication No. 89, pp 57–81
Dunham RJ (1962) Classification of carbonate rocks according to depositional texture. In: Ham WE (ed) Classification of Carbonate Rocks, vol 1. Memoirs of the American Association of Petroleum Geologists, Tulsa, pp 108–121
Eberli G, Ginsburg R (1987) Segmentation and coalescence of Cenozoic carbonate platforms, northwestern Great Bahama Bank. Geology 15:75–79
Eberli G, Anselmetti F, Betzler C, Van Konijnenburg J-H, Bernoulli D (2004) Carbonate platform to basin transitions on seismic data and in outcrops: Great Bahama Bank and the Maiella Platform margin, Italy. In: Eberli G, Masaferro J, Sarg J (eds) Seismic imaging of carbonate reservoirs and systems, vol 81. AAPG Memoir pp 207–250
Embry A, Klovan JE (1971) A late Devonian reef tract on the northeastern Bank Island, Northwest Territories. Bull Can Petrol Geol 19:730–781
Felix R (1973) Oligo-Miocene stratigraphy of Malta and Gozo. Wageningen, Veeman
Finetti I (1982) Structure, stratigraphy and evolution of Central Mediterranean. Bollettino Di Geofisica Teorica Ed Applicata XXIV(96):247–315
Flügel E (2010) Microfacies of carbonate rocks. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Gallais F, Gutscher M-A, Graindorge D, Chamot-Rooke N, Klaeschen D (2011) A Miocene tectonic inversion in the Ionian Sea (Central Mediterranean): evidence from multichannel seismic data. J Geophys Res 116:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011JB008505
Gatt P (2005) Syntectonic deposition of an Oligo-Miocene phosphorite conglomerate bed in Malta. Central Mediterr Nat 4(2):109–118
Gatt P (2012) Carbonate facies, depositional sequences and tectonostratigraphy of the Paleogene Malta Platform. University of Durham, UK: PhD thesis (available online)
Gatt P (2019) Evaporite dissolution sinkholes in the Dwejra Depression, Malta. Eur Geol 48:53–57
Gatt P (2021) Embayment morphometrics, granulometry and carbonate mineralogy of sandy beaches in the Maltese Islands. Mar Geol 432:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MARGEO.2020.106394
Gatt P, Gluyas J (2012) Climatic controls on facies in Palaeogene Mediterranean subtropical carbonate platforms. Pet Geosci 18:355–367. https://doi.org/10.1144/1354-079311-032
Gatt P, Tucker M, Davies R (2009) Drowning of the Malta carbonate platform: facies and sequence stratigraphy of the Lower Coralline Limestone (U. Oligocene). In: Pascucci V, Andreucci S (eds) Sedimentary environments of Mediterranean Islands. International Association of Sedimentologists Abstracts, Alghero, p 181
Geel T (2000) Recognition of startigraphic sequences in carbonate platform and slope deposits: empirical models based on microfacies analysis of Paleogene deposits in sotheastern Spain. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 155:211–238
Gerdes K, Winefield P, Simmons M, Van Oosterhout C (2010) The influence of basin architecture and eustacy on the evolution of Tethyan Mesozoic and Cenozoic carbonate sequences. In: van Buchem F, Gerdes K, Esteban M (eds) Mesozoic and Cenozoic Carbonate Systems of the Mediterranean and the Middle East: Stratigraphic and diagenetic reference models, vol 329. Geological Society, Special Publications, London, pp 9–41
Gili E, Hedi Negra M, Skelton P (2003) North African cretaceous carbonate platform systems. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht
Goldhammer R, Elmore R (1984) Paleosols capping regressive carbonate cycles in the Pennsylvanian Black Prince Limestone, Arizona. J Sediment Petrol 54:1124–1137
Goldhammer RK, Dunn PA, Hardie LA (1990) Depostional cycles, composite sea-level changes, cyclic stacking patterns, and the hierarchy of stratigraphic forcing: Examples from Alpine Triassic platform carbonates. Geol Soc Am Bull 102:535–562
Gradstein F, Ogg J, Smith A (2004) A Geological time scale. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Grasso M, Lentini F (1982) Sedimentary and tectonic evolution of the Eastern Hyblean Plateau (SE Sicily) during the Late Cretaceous to Quaternary time. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 39:261–280
Grasso M, Mazzoldi G, Torelli L (1993) Structural and stratigraphic framework of the Tunisian Shelf surrounding the Islands of Lampione and Lampedusa (Pelagian sea). In: Max MD, Colantoni P (eds) International Scientific meeting, University of Urbino, vol 58. UNESCO reports in marine science, pp 65–70
Gruszczynski M, Marshall JD, Goldring R, Coleman ML, Małkowski K, Gaździcka E et al (2008) Hiatal surfaces from the Miocene Globigerina Limestone Formation of Malta: Biostratigraphy, sedimentology, trace fossils and early diagenesis. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 270:239–251
Halfar J, Godinez-Orta L, Mutti M, ValdezHolguin J, Borges J (2004) Nutrient and temperature controls on modern carbonate production: an example from the Gulf of California, Mexico. Geology 32:213–216
Hallock P, Glenn E (1986) Larger foraminifera: a tool for paleoenvironmental analysis of cenozoic carbonate depositional facies. Palaios 1:55–64
Hallock P, Hansen H (1979) Depth adapatation in Amphistegina: change in lamellar thickness. Bull Geol Soc Denmark 27:99–104
Hallock P, Pomar L (2008a) Cenozoic evolution of larger benthic foraminifers: paleoceanographic evidence for changing habitats. In: Proceedings of the 11th international coral reef symposium. Ft.Lauderdale, Florida
Hallock P, Pomar L (2008b) Cenozoic photic reef and carbonate ramp habitats: a new look using paleoceanographic evidence. In: Proceedings of the 11th international coral reef symposium. Ft. Lauderdale, Florida
Hallock P, Schlager W (1986) Nutrient excess and demise of Coral Reefs and Carbonate Platforms. Palaios 1:389–398
Han Q, Liu D (2014) Macroalgae blooms and their effects on seagrass ecosystems. J Ocean Univ China 13:791–798
Handford C, Loucks R (1993) Carbonate depositional sequences and systems tracts—responses of carbonate platforms to relative sea-level changes. In: Loucks R, Sarg J (eds) Carbonate sequence stratigraphy, vol 57. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Memoir, pp 3–41
Haq BU, Hardenbol J, Vail PR (1987) Chronology of fluctuating sea levels since the Triassic. Science 235:1156–1167
Illies JH (1981) Graben formation—the Maltese Islands—a case history. Tectonophysics 73:151–168
Isern A, Anselmetti F, Blum P (2005) A Neogene carbonate platform, slope, and shelf edifice shaped by sea level and ocean currents, Marion Plateau (northeast Australia). AAPG Mem 81:291–307
Jones R, McGurk D (2018) Re-imaging a carbonate build-up trend: Modern processing techniques uplifting old data. Eastern Mediterranean Workshop (6–7 December). EAGE, St Julian's, Malta, p 4
Jongsma D, van Hinte JE, Woodside JM (1985) Geologic structure and neotectonics of the North African continental margin south of Sicily. Mar Pet Geol 2:156–179
Jorry S, Davaud E, Caline B (2003) Controls on the distribution of Nummulite facies: a case study from the Late Ypresian El Garia Formation (Kesra plateau, central Tunisia). J Pet Geol 26:283–306
Kiessling W, Golonka J (2003) Patterns of Phanerozoic carbonate platform sedimentation. Lethaia 36:195–225
Klappa C (1978) Biolithogenesis of Microcodium: elucidation. In: Wright V, Tucker M (eds) Blackwell Scientific Publications
Klett T (2001) Total petroleum petroleum systems of the Pelagian Province, Tunisia, Libya, Italy and Malta- the bou Dabbous Tertiary and Jurassic-Cretaceous composite. U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin 2202-D
Knoerich AC, Mutti M (2003) Controls of facies and sediment composition on the diagenetic pathway of shallow-water Heterozoan carbonates: the Oligocene of the Maltese Islands. Int Earth Sci Rev (geologische Rundschau) 92:494–510
Kominz MA, Pekar SF (2001) Oligoceneeustasy from two-dimensional sequence stratigraphic backstripping. Geol Soc Am Bull 113:291–304
Knoerich AC, Mutti M (2006) Missing aragonitic biota and diagenetic evolution of Heterozoan Carbonates: a case study from the Oligo-Miocene of the Central Mediterranean. J Sediment Res 76:871–888
Leeder M, Gawthorpe R (1987) Sedimentary models for extensional tile-block/half graben basins. Geol Soc Spec Publ 28:139–152
Lipparini L, Scrocca D, Marsili P, Morandi S (2009) Offshore Malta licence in the Central Mediterranean Sea offers hope of hydrocarbon potential. First Break 27:105–116
Marlow L, Kornpihl K, Kendall C (2011) 2-D Basin modeling study of petroleum systems in the Levantine Basin, Eastern Mediterranean. GeoArabia 16:17–42
McCormick and Jones (2021) On the efficacy and limitations of isolated carbonate platforms as “oceanic dipsticks” to reconstruct subsidence histories, a case study from the Paleogene to Neogene strata on Grand Cayman and Cayman Brac, BWI. Mar Geol 436:106470
McKenzie J (1981) Holocene dolomitization of calcium carbonate sediments from the coastal sabkhas of Abu Dhabi, U.A.E.: a stable isotope study. J Geol 89:185–198
Micallef A, Paull C, Saadatkhah N, Bialik O (2021) The role of fluid seepage in the erosion of Mesozoic carbonate escarpments. J Geophys Res 126:e2021JF006387
Miller KG, Browning JV, Schmelz WJ, Kopp RE, Mountain GS, Wright JD (2020) Cenozoic sea-level and cryospheric evolution from deep-sea geochemical and continental margin records. Sci Adv Rev. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aaz1346
Murray J (1890) The Maltese Islands with special reference to their geological structure. Geogr Mag 6:449–488
Mutti M, Droxler A, Cunnignham A (2005) Evolution of the Northern Nicaragua Rise during the Oligocene-Miocene: drowning by environmental factors. Sed Geol 175:237–258
Nebelsick J, Kroh A (2002) The stormy path from life to death assemblages: the formation and preservation of mass accumulations of fossil sand dollars. Palaios 17:378–393
Pedley H (1978) A new lithostratigraphical and palaeoenvironmental interpretation for the coralline limestone Formation of the Maltese Islands. Overseas Geol Miner Resources 54:1–17
Pedley M, Debono G, Yeaman M (1993) Mesozoic structuring and volcanics along the Pelagian-Ionian boundary. In: Max MD, Colantoni P (eds) Geological Development of the Sicilian-Tunisian Platform, vol 58. UNESCO reports in Marine Science, pp 81–86
Pomar L (2001) Types of Carbonate platforms: a genetic approach. Basin Res 13:313–334
Pomar L, Hallock P (2007) Changes in coral-reef structure through the Miocene in the Mediterranean province: adaptive versus environmental influence. Geology 35(10):899–902
Pomar L, Baceta J, Hallock P, Mateu-Vicens G, Basso D (2017) Reef building and carbonate production modes in the west-central Tethys during the Cenozoic. Mar Pet Geol 83:261–304
Racey A (2001) A review of Eocene Nummulite accumulations: structure, fomration and reservoir potential. J Pet Geol 24:79–100
Read J (1985) Carbonate platform facies models. AAPG Bull 69:1–21
Read J (1995) Overview of carbonate platform sequences, cycle stratigraphy and reservoirs in greenhouse and ice-house worlds. In: Read J, Kerans C, Weber L (eds) Milankovitch sea level changes, cycles and reservoirs on carbonate paltforms in greenhouse and ice-house worlds, SEPM Short Course notes, vol 35, pp. 1–102
Read JF (1998) Phanerozoic carbonate ramps from greenhouse, transitional and ice-house worlds: clues from field and modelling studies. In: Wright PV, Burchette TP (eds) Carbonate ramps, vol 149. Geological Society. London, Special Publications, pp 107–135
Reeh G, Aifa T (2008) Age of the source of the Jarrafa gravity and magnetic anomalies offshore Libya and its geodynamic implications. J Geodyn 45:217–233
Reich S, DiMartino E, Todd J, Wesselingh F, Renema W (2015) Indirect palaeo-seagrass indicators (IPSIs): a review. Earth Sci Rev 143:161–186
Reuter M, Werner P, Harzhauser M, Kroh A, Bassi D (2008) Termination of the Arabian shelf sea: Stacked cyclic sedimentary patterns and timing (Oligocene/Miocene, Oman). Sed Geol 212:12–24
Riusciadelli G, Shiner P (2018) Isolated carbonate platforms of the Mediterranean and their seismic expression—searching for a paradigm. Leading Edge 37:492–501
Saint-Martin J, Chaix C, Cahuzac B, Moisette P, Andre J-P (2021) Les faunes coralliennes de l’Oligocène de Malte: biodiversité et paléoenvironnement. Annales De Paléontologie 107:1–25
Schattner U, Ben-Avraham Z (2017) Transform margin of the northern Levant, eastern Mediterranean: from formation to reactivation. Tectonics 26:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007TC002112,2007
Schlager W (1981) The paradox of drowned reefs and carbonate platforms. Geol Soc Am Bull 92:197–211
Schramm MW, Livraga G (1986) Vega field and the potential of Ragusa Basin, offshore Sicily. In: Halbouty M (ed) Future petroleum provinces of the World. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Memoir, vol 40, pp 559–566
Scoffin T (1970) The trapping and binding of subtidal carbonate sediments by marine vegetation in Bimini Lagoon, Bahamas. Sediment Petrology 40:249–273
Serra-Kiel J, Hottinger L, Caus E, Drobne K, Ferrandez C, Jauhri A et al (1998) Larger foraminifieral biostratigraphy of the Tethyan Paleocene and Eocene. Bull De La Societé Géologique De France 169:281–299
Shahzad K, Betzler C, Ahmed N, Qayyum F, Spezzaferri S, Qadir A (2018) Growth and demise of a Paleogene isolated carbonate platform of the offshore Indus basin, Pakistan: effects of regional and local controlling factors. Mar Micropaleontol 140:33–45
Sultana D, Burgess P, Bosence D (2022) How do carbonate factories influence carbonate platform morphology? Exploring production-transport interactions with numerical modelling. Sedimentology 69:372–393
Swei G, Tucker M (2012) Impact of diagenesis on reservoir quality in carbonate ramps: Gialo Formation (middle Eocene), Sirt Basin, Libya. J Pet Geol 35:25–48
Swift D, Thorne J (1991) Sedimentation on continental margins: a general model for shelf sedimentation. In: Swift D, Oertel G, Tillman R, Thorne J (eds) Shelf Sand and Sandstone Bodies, vol. Spec. Publ. 14, pp 3–31. Int. Assoc. Sedimentol
Torelli L, Grasso M, Mazzoldi G, Peis D, Gori D (1995) Cretaceous to Neogene structural evolution of the Lampedusa Shelf (Pelagian Sea, Central Mediterranean). Terra Nova 7:200–212
Tucker ME, Wright VP (1990) Carbonate sedimentology. Blackwell Scinetific Publications, Oxford
Venin E, van Buchem F, Joseph P, Gaumet F, Sonnenfeld M, Rebelle M, Jemia HF, Zijlstra H (2003) A 3D outcrop analogue model for Ypresian nummulitic carbonate reservoirs: Jebel Ousselat, northern Tunisia. Pet Geosci 9:145–161
Walther J (1894) Einleitung in die geologie als historische wissenschaft: Beobachtungen über die bildung der gesteine und ihrer organischen einschlüsse, vol 3. G. Fischer, Jena
Wanless H (1981) Fining upwards sedimentary sequences generated in sea grass beds. J Sediment Petrol 51:445–454
Whitaker F, Smart P, Jones G (2004) Dolomitization: from conceptual to numerical models. Geol Soc Spec Publ 235:99–139
Wieland-Schuster U, Schuster F, Harzhauser M, Mandic O, Kroh A, Rogl F et al (2004) Stratigraphy and palaeoecology of Oligocene and Early Miocene sedimentary sequences of the Mesohellenic Basin (NW Greece). Cour. Forsch.-Inst Senckenberg 248:1–55
Wilson S, Blake C, Berges J, Maggs C (2004) Environmental tolerances of free-living coralline algae (maerl): implications for European marine conservation. Biol Cons 120:283–293
Wray J (1977) Calcareous algae. Elsevier
Zachos J, Pagani M, Sloan L, Thomas E, Billups K (2001) Trends, rythms and aberrations in global Climate 65 Ma to Present. Science 292:686–693
Zarcone G, DiStefano P (2008) Mesozoic discontinuities in the Panormide Carbonate Platform: constraints on the palaeogeography of the central Mediterranean. Rend. online SGI, vol 2. Note Brevi, pp 191–194. www.socgeol.it
Acknowledgements
BP and Total are thanked for providing well data. Thin sections were made at Durham University and analysed at Geoscience Malta Consulting. This study is partly based on the author’s PhD thesis. The Editor, Prof Maurice Tucker (Bristol) and reviewers are thanked for their support and suggestions.
Funding
The author did not receive support from any organization for submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gatt, P. Facies, depositional environments and drowning of Tethyan isolated carbonate platforms: the Paleogene carbonates of Malta. Facies 68, 9 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10347-022-00648-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10347-022-00648-1