Abstract
Purpose
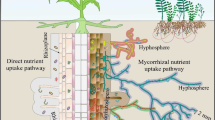
Roots bridge aboveground and belowground systems, and play a pivotal role in structuring root-associated organisms via influencing food resources and habitat conditions. Most studies focused on the relationships between plant identity and root-associated organisms, however, little is known about how root traits affect nematode communities within the rhizosphere.
Methods
We investigated the relationships between root traits of four plant species and nematode abundance, community structure and trophic complexity in an ex-arable field.
Results
While the relative abundance of herbivores was negatively associated with specific root length (SRL), specific root area (SRA), root length density (RLD) and root C: N ratio, free-living nematodes were positively affected by these traits, implying a multifaceted effect of root traits on root-associated organisms. Importantly, we found that finer root systems promoted the complexity of rhizosphere nematode community, by increasing the relative abundance of high trophic-level nematodes (i.e., omnivores and predators) and enhancing nematode diversity.
Conclusions
Our findings suggest that root traits could comprehensively shape soil community structure and interactions, and provide new insights into soil biodiversity conservation and functional maintenance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barberan A, Bates ST, Casamayor EO, Fierer N (2012) Using network analysis to explore co-occurrence patterns in soil microbial communities. ISME J 6:343–351
Bardgett RD (2017) Plant trait-based approaches for interrogating belowground function. Biol Environ 117:1–13
Bardgett RD, van der Putten WH (2014) Belowground biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Nature 515:505–511
Bardgett RD, Wardle DA (2010) Aboveground-belowground linkages: biotic interactions, ecosystem processes, and global change. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Bardgett RD, Mommer L, De Vries FT (2014) Going underground: root traits as drivers of ecosystem processes. Trends Ecol Evol 29:692–699
Bastian M, Heymann S, Jacomy M (2009) Gephi: an open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. Third international AAAI conference on weblogs and social media. ICWSM, California, USA
Bergmann J, Weigelt A, Van der Plas F, Laughlin D, Kuyper T, Guerrero-Ramírez N, Valverde-Barrantes O, Bruelheide H, Freschet G, Iversen C, Kattge J, McCormack M, Meier I, Rillig M, Roumet C, Semchenko M, Sweeney C, Ruijven J, York L, Mommer L (2020) The fungal collaboration gradient dominates the root economics space in plants. Sci Adv 6:eaba3756
Bongers T (1990) The maturity index: an ecological measure of environmental disturbance based on nematode species composition. Oecologia 83:14–19
Bongers T, Bongers M (1998) Functional diversity of nematodes. Appl Soil Ecol 10:239–251
Briar SS, Fonte SJ, Park I, Six J, Scow K, Ferris H (2011) The distribution of nematodes and soil microbial communities across soil aggregate fractions and farm management systems. Soil Biol Biochem 43:905–914
Bukovinszky T, van Frank FJ, Jongema Y, Dickel M (2008) Direct and indirect effects of resource quality on food web structure. Science 319:804–807
Chase JM, Abrams PA, Grover JP, Diehl S, Chesson P, Holt RD, Richards SA, Nisbet RM, Case TJ (2002) The interaction between predation and competition: a review and synthesis. Ecol Lett 5:302–315
Cornelissen JHC, Lavorel S, Garnier E, Díaz S, Buchmann N, Gurvich DE, Reich PB, ter Steege H, Morgan HD, van der Heijden MGA, Pausas JG, Poorter H (2003) A handbook of protocols for standardised and easy measurement of plant functional traits worldwide. Aust J Bot 51:335–380
Cortois R, Veen GF, Duyts H, Abbas M, Strecker T, Kostenko O, Eisenhauer N, Scheu S, Gleixner G, De Deyn GB, van der Putten WH (2017) Possible mechanisms underlying abundance and diversity responses of nematode communities to plant diversity. Ecosphere 8:e01719
Csardi G, Nepusz T (2006) The igraph software package for complex network research. Int J Complex Syst 1695:1–9
De Deyn GB, Raaijmakers CE, van Ruijven J, Berendse F, van der Putten WH (2004) Plant species identity and diversity effects on different trophic levels of nematodes in the soil food web. Oikos 106:576–586
De Deyn GB, Cornelissen JHC, Bardgett RD (2008) Plant functional traits and soil carbon sequestration in contrasting biomes. Ecol Lett 11:516–531
Eisenhauer N, Migunova VD, Ackermann M, Ruess L, Scheu S (2011) Changes in plant species richness induce functional shifts in soil nematode communities in experimental grassland. PLoS ONE 6:e24087
Erktan A, Or D, Scheu S (2020) The physical structure of soil: determinant and consequence of trophic interactions. Soil Biol Biochem 148:107876
Fort F, Volaire F, Guilioni L, Barkaoui K, Navas ML, Roumet C (2017) Root traits are related to plant water-use among rangeland Mediterranean species. Funct Ecol 31:1700–1709
Franco ALC, Gherardi LA, de Tomasel CM, Andriuzzi WS, Ankrom KE, Shaw EA, Bach EM, Sala OE, Wall DH (2019) Drought suppresses soil predators and promotes root herbivores in mesic, but not in xeric grasslands. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116:12883–12888
Freschet GT, Roumet C, Comas LH, Weemstra M, Bengough AG, Rewald B, Bardgett RD, De Deyn GB, Johnson D, Klimešová J, Lukac M, McCormack ML, Meier IC, Pagès L, Poorter H, Prieto I, Wurzburger N, Zadworny M, Bagniewska-Zadworna A, Blancaflor EB, Brunner I, Gessler A, Hobbie SE, Iversen CM, Mommer L, Picon-Cochard C, Postma JA, Rose L, Ryser P, Scherer-Lorenzen M, Soudzilovskaia NA, Sun T, Valverde-Barrantes OJ, Weigelt A, York LM, Stokes A (2020) Root traits as drivers of plant and ecosystem functioning: current understanding, pitfalls and future research needs. New Phytol 232:1123–1158
Fry EL, De Long JR, Álvarez Garrido L, Alvarez N, Carrillo Y, Castañeda-Gómez L, Chomel M, Dondini M, Drake JE, Hasegawa S, Hortal S, Jackson BG, Jiang M, Lavallee JM, Medlyn BE, Rhymes J, Singh BK, Smith P, Anderson IC, Bardgett RD, Baggs EM, Johnson D (2018) Using plant, microbe, and soil fauna traits to improve the predictive power of biogeochemical models. Methods Ecol Evol 10:146–157
Fujii S, Berg MP, Cornelissen JHC (2020) Living litter: dynamic trait spectra predict fauna composition. Trends Ecol Evol 35:886–896
Gough EC, Owen KJ, Zwart RS, Thompson JP (2021) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi acted synergistically with Bradyrhizobium sp. to improve nodulation, nitrogen fixation, plant growth and seed yield of mung bean (Vigna radiata) but increased the population density of the root-lesion nematode Pratylenchus thornei. Plant Soil 465:431–452
Greinwald K, Gebauer T, Treuter L, Kolodziej V, Musso A, Maier F, Lustenberger F, Scherer-Lorenzen M (2021) Root density drives aggregate stability of soils of different moraine ages in the Swiss Alps. Plant Soil 468:439–457
Han M, Zhu B (2021) Linking root respiration to chemistry and morphology across species. Glob Chang Biol 27:190–201
Hayes DC, Seastedt TR (1987) Root dynamics of tallgrass prairie in wet and dry years. Can J Bot 65:787–791
Heinen R, Hannula SE, De Long JR, Huberty M, Jongen R, Kielak A, Steinauer K, Zhu F, Bezemer TM (2020) Plant community composition steers grassland vegetation via soil legacy effects. Ecol Lett 23:973–982
Herve MR, Erb M (2019) Distinct defense strategies allow different grassland species to cope with root herbivore attack. Oecologia 191:127–139
Hobbie SE (1992) Effects of plant-species on nutrient cycling. Trends Ecol Evol 7:336–339
Hobbie SE (2015) Plant species effects on nutrient cycling: revisiting litter feedbacks. Trends Ecol Evol 30:357–363
Huang J, Liu W, Yang S, Yang L, Peng Z, Deng M, Xu S, Zhang B, Ahirwal J, Liu L (2021) Plant carbon inputs through shoot, root, and mycorrhizal pathways affect soil organic carbon turnover differently. Soil Biol Biochem 160:108322
Jin K, White PJ, Whalley WR, Shen J, Shi L (2017) Shaping an optimal soil by root-soil interaction. Trends Plant Sci 22:823–829
Legay N, Clément JC, Grassein F, Lavorel S, Lemauviel-Lavenant S, Personeni E, Poly F, Pommier T, Robson TM, Mouhamadou B, Binet MN (2020) Plant growth drives soil nitrogen cycling and N-related microbial activity through changing root traits. Fungal Ecol 44:100910
Li Z, Wang F, Su F, Wang P, Li S, Bai T, Wei Y, Liu M, Chen D, Zhu W, Eviner V, Wang Y, Hu S (2021) Climate change drivers alter root controls over litter decomposition in a semi-arid grassland. Soil Biol Biochem 158:108278
Liu M, Chen X, Qin J, Wang D, Griffiths B, Hu F (2008) A sequential extraction procedure reveals that water management affects soil nematode communities in paddy fields. Appl Soil Ecol 40:250–259
Ma Z, Guo D, Xu X, Lu M, Bardgett RD, Eissenstat DM, McCormack ML, Hedin LO (2018) Evolutionary history resolves global organization of root functional traits. Nature 555:94–97
Neher DA (2001) Role of nematodes in soil health and their use as indicators. J Nematol 33:161–168
Neher DA (2010) Ecology of plant and free-living nematodes in natural and agricultural soil. Annu Rev Phytopathol 48:371–394
Neutel AM, Heesterbeek JAP, van de Koppel J, Hoenderboom G, Vos A, Kaldeway C, Berendse F, de Ruiter PC (2007) Reconciling complexity with stability in naturally assembling food webs. Nature 449:599–602
Newman MEJ (2003) The structure and function of complex networks. SIAM Rev 45:167–256
Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Friendly M, Kindt R, Legendre P, McGlinn D, Minchin PR, O’Hara RB, Simpson GL, Solymos P, Stevens MHH, Szöcs E, Wagner H (2020) Vegan: community ecology package. version 2.5-7. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan
Otfinowski R, Coffey V (2020) Can root traits predict communities of soil nematodes in restored northern prairies? Plant Soil 453:459–471
Paine RT (1966) Food web complexity and species diversity. Am Nat 100:65–75
Pérez-Harguindeguy N, Díaz S, Garnier E, Lavorel S, Poorter H, Jaureguiberry P, Bret-Harte MS, Cornwell WK, Craine JM, Gurvich DE, Urcelay C, Veneklaas EJ, Reich PB, Poorter L, Wright IJ, Ray P, Enrico L, Pausas JG, de Vos AC, Buchmann N, Funes G, Quétier F, Hodgson JG, Thompson K, Morgan HD, Steege H, Sack L, Blonder B, Poschlod P, Vaieretti MV, Conti G, Staver AC, Aquino S, Cornelissen JHC (2013) New handbook for standardised measurement of plant functional traits worldwide. Aust J Bot 61:167–234
Picot A, Monnin T, Loeuille N, Leroux S (2019) From apparent competition to facilitation: impacts of consumer niche construction on the coexistence and stability of consumer-resource communities. Funct Ecol 33:1746–1757
Poorter H, Niklas KJ, Reich PB, Oleksyn J, Poot P, Mommer L (2012) Biomass allocation to leaves, stems and roots: meta-analyses of interspecific variation and environmental control. New Phytol 193:30–50
Qiu Y, Guo L, Xu X, Zhang L, Zhang K, Chen M, Zhao Y, Burkey KO, Shew HD, Zobel RW, Zhang Y, Hu S (2021) Warming and elevated ozone induce tradeoffs between fine roots and mycorrhizal fungi and stimulate organic carbon decomposition. Sci Adv 7:eabe9256
R Core Team (2021) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R foundation for statistical computing, Vienna. http://www.R-project.org/
Ramachandran S, Renault S, Markham J, Verdugo J, Albornoz M, Avila-Sakar G (2020) Lower nitrogen availability enhances resistance to whiteflies in tomato. Plants (Basel) 9:1096
Ritz K, Trudgill DL (1999) Utility of nematode community analysis as an integrated measure of the functional state of soils: perspectives and challenges. Plant Soil 212:1–11
Roumet C, Urcelay C, Díaz S (2006) Suites of root traits differ between annual and perennial species growing in the field. New Phytol 170:357–368
Shao Y, Wang X, Zhao J, Wu J, Zhang W, Neher DA, Li Y, Lou Y, Fu S, Kardol P (2016) Subordinate plants sustain the complexity and stability of soil micro-food webs in natural bamboo forest ecosystems. J Appl Ecol 53:130–139
Siebert J, Ciobanu M, Schadler M, Eisenhauer N (2020) Climate change and land use induce functional shifts in soil nematode communities. Oecologia 192:281–294
Sikder MM, Vestergård M (2020) Impacts of root metabolites on soil nematodes. Front Plant Sci 10:1792
Soil Survey Staff (1999) Soil taxonomy: a basic system of soil classification for making and interpreting soil surveys. Natural Resources Conservation Service, Department of Agriculture, Washington
Sparks DL, Page AL, Helmke PA, Loeppert RH, Soltanpour PN, Tabatabai MA, Johnston CT, Sumner ME (1996) Methods of soil analysis: chemical methods. Soil Science Society of America, Madison
Spitzer CM, Lindahl B, Wardle DA, Sundqvist MK, Gundale MJ, Fanin N, Kardol P (2021) Root trait-microbial relationships across tundra plant species. New Phytol 229:1508–1520
Sweeney CJ, de Vries FT, van Dongen BE, Bardgett RD (2021) Root traits explain rhizosphere fungal community composition among temperate grassland plant species. New Phytol 229:1492–1507
Thakur MP, Geisen S (2019) Trophic regulations of the soil microbiome. Trends Microbiol 27:771–780
Thakur MP, Reich PB, Fisichelli NA, Stefanski A, Cesarz S, Dobies T, Rich RL, Hobbie SE, Eisenhauer N (2014) Nematode community shifts in response to experimental warming and canopy conditions are associated with plant community changes in the temperate-boreal forest ecotone. Oecologia 175:713–723
Thakur MP, van der Putten WH, Wilschut RA, Veen GFC, Kardol P, van Ruijven J, Allan E, Roscher C, van Kleunen M, Bezemer TM (2021) Plant-Soil Feedbacks and Temporal Dynamics of Plant Diversity-Productivity Relationships. Trends Ecol Evol 36:651–661
van den Hoogen J, Geisen S, Routh D et al (2019) Soil nematode abundance and functional group composition at a global scale. Nature 572:194–191
Viketoft M (2008) Effects of six grassland plant species on soil nematodes: a glasshouse experiment. Soil Biol Biochem 40:906–915
Violle C, Navas M-L, Vile D, Kazakou E, Fortunel C, Hummel I, Garnier E (2007) Let the concept of trait be functional! Oikos 116:882–892
Wallace HR (1968) The dynamics of nematode movement. Annu Rev Phytopathol 6:91–114
Wang X, Zabowski D (1998) Nutrient composition of Douglas-fir rhizosphere and bulk soil solutions. Plant Soil 200:13–20
Wang B, Wu Y, Chen D, Hu S, Bai Y, Zhou G (2021) Legacy effect of grazing intensity mediates the bottom-up controls of resource addition on soil food webs. J Appl Ecol 58:976–987
Wardle DA, Yeates GW, Williamson W, Bonner KI (2003) The response of a three trophic level soil food web to the identity and diversity of plant species and functional groups. Oikos 102:45–56
Wardle DA, Bardgett RD, Klironomos JN, Setala H, van der Putten WH, Wall DH (2004) Ecological linkages between aboveground and belowground biota. Science 304:1629–1633
Wasilewska L (1997) Soil invertebrates as bioindicators, with special reference to soil-inhabiting nematodes. Russ J Nematol 5:113–126
Xiong D, Wei C, Wubs ERJ, Veen GF, Liang W, Wang X, Li Q, Putten WH, Han X, Ordonez A (2019) Nonlinear responses of soil nematode community composition to increasing aridity. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 29:117–126
Xiong D, Wei C, Wang X, Lu X, Fang S, Li Y, Wang X, Liang W, Han X, Bezemer TM, Li Q (2021) Spatial patterns and ecological drivers of soil nematode beta-diversity in natural grasslands vary among vegetation types and trophic position. J Anim Ecol 90:1367–1378
Yan X, Diez J, Huang K, Li S, Luo X, Xu X, Su F, Jiang L, Guo H, Hu S (2020) Beyond resource limitation: an expanded test of the niche dimension hypothesis for multiple types of niche axes. Oecologia 193:689–699
Yeates GW (1999) Effects of plants on nematode community structure. Annu Rev Phytopathol 37:127–149
Yeates GW, Bongers T, De Goede RGM, Freckman DW, Georgieva SS (1993) Feeding habits in soil nematode families and genera-an outline for soil ecologists. J Nematol 25:315–331
Zhang P, Li B, Wu J, Hu S (2019) Invasive plants differentially affect soil biota through litter and rhizosphere pathways: a meta-analysis. Ecol Lett 22:200–210
Zhang C, Wang J, Ren Z, Hu Z, Tian S, Fan W, Chen X, Griffiths BS, Hu F, Liu M (2020) Root traits mediate functional guilds of soil nematodes in an ex-arable field. Soil Biol Biochem 151:108038
Zhou G, Zhou X, Liu R, Du Z, Zhou L, Li S, Liu H, Shao J, Wang J, Nie Y, Gao J, Wang M, Zhang M, Wang X, Bai SH, Wang F (2020) Soil fungi and fine root biomass mediate drought-induced reductions in soil respiration. Funct Ecol 34:2634–2643
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Foundation of Sciences in China (42077047), National Key R&D program (2021YFD1700202), and China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA (Green manure, CARS-22). We thank Wenqing Fan, Shanyi Tian, Yanhong Cheng and Qianru Huang for providing support in field and sampling.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Research design was performed by Xiaoyun Chen and Manqiang Liu. Experiment and data collection were performed by Jingru Zhang and Chongzhe Zhang. Data analysis was performed by Jingru Zhang and Yiheng Tao. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Jingru Zhang, Zhengkun Hu, Chongzhe Zhang, Xiaoyun Chen and Manqiang Liu, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Feike A. Dijkstra.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 43.8 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Hu, Z., Zhang, C. et al. Roots with larger specific root length and C: N ratio sustain more complex rhizosphere nematode community. Plant Soil 477, 693–706 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-022-05465-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-022-05465-7