Abstract
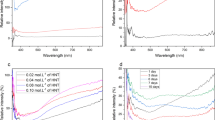
The AlN–Ce:YAG composite ceramic is an effective phosphor for high-power laser illumination. The thermal properties of an AlN–Ce:YAG composite phosphor were studied to suppress thermal quenching. This composite ceramic has a high heat dissipation effect owing to the dispersion of AlN particles, which exhibit high thermal conductivity. Exciting the phosphor with a high-power-density laser beam concentrates heat in a narrow area. The heat is efficiently dissipated by the AlN particles, thereby reducing the phosphor temperature. A new technique was developed to estimate the thermal conductivity from the emission spectrum and the spot center temperature of the composite ceramic. The heat value was calculated by subtracting the power of the emission spectrum from the incident laser power. The spot center temperature was measured using a thermographic camera. The thermal conductivity was simulated by inputting the heat value and spot center temperature into the model of the phosphor sample. It was clarified that the thermal conductivity improved, as the AlN particle content increased. This result is consistent with the measurements obtained using the laser flash method. This technique is useful for designing lighting systems, as it enables the estimation of thermal conductivity when light is emitted from a condensing spot.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pattison, P.M., Hansen, M., Tsao, J.Y.: LED lighting efficacy: status and directions. C. R. Phys. 19, 134–145 (2018)
Kuritzky, L.Y., Speck, J.S.: Lighting for the 21st century with laser diodes based on non-basal plane orientations of GaN. MRS Commun. 5, 463–473 (2015)
Wierer, J.J., Tsao, J.Y., Sizov, D.S.: Comparison between blue lasers and light-emitting diodes for future solid-state lighting. Laser Photon. Rev. 7, 963–993 (2013)
Basu, C., Meinhardt-Wollweber, M., Roth, B.: Light source design for spectral tuning in biomedical imaging. Adv. Opt. Technol. 2, 313–321 (2013)
Wierer, J.J., Tsao, J.Y., Sizov, D.S.: The potential of III-nitride laser diodes for solid-state lighting. Phys. Status Solidi 11, 674–677 (2014)
Kitazono, T., Kita, Y., Hoshino, S., Mori, T., Harata, S., Saito, T., Yatsuda, Y.: Laser scanning headlamp, The 7th Laser Display and Lighting Conference 2018 (LDC'18), Yokohama, Japan, LDC5-2 (2018)
George, N.C., Denault, K.A., Seshadri, R.: Phosphors for solid-state white lighting. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 43, 481–501 (2013)
Robbins, D.J., Cockayne, B., Glasper, J.L., Lent, B.: The temperature dependence of rare-earth activated garnet phosphors: intensity and lifetime measurements on undoped and Ce-Doped. J. Electrochem. Soc. 126, 1213 (1979)
Ma, Y., Lan, W., Xie, B., Hu, R., Luo, X.: An optical-thermal model for laser-excited remote phosphor with thermal quenching. J. Heat Mass Transf. 116, 694–702 (2018)
Bachmann, V., Ronda, C., Meijerink, A.: Temperature quenching of yellow Ce3+ luminescence in YAG: Ce. Chem. Mater. 21, 2077–2084 (2009)
Ueda, J., Dorenbos, P., Bos, A.J.J., Meijerink, A., Tanabe, S.: Insight into the thermal quenching mechanism for Y3Al5O12:Ce3+ through thermoluminescence excitation spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. 119(44), 25003–25008 (2015)
Inoue, T., Ohashi, Y., Ito, T.: Application of laser to headlamps and thermal design, the 7th laser display and lighting conference 2018 (LDC'18), Yokohama, Japan, LDC5-3 (2018)
Song, Y.H., Ji, E.K., Jeong, B.W., Jung, M.K., Kim, E.Y., Yoon, D.H.: High power laser-driven ceramic phosphor plate for outstanding efficient white light conversion in application of automotive lighting. Sci. Rep. 6, 31206 (2016)
Li, S., Zhu, Q., Tang, D., Liu, X., Ouyang, G., Cao, L., Hirosaki, N., Nishimura, T., Huang, Z., Xie, R.J.: Al2O3–YAG: Ce composite phosphor ceramic: a thermally robust and efficient color converter for solid state laser lighting. J. Mater. Chem. 4, 8648–8654 (2016)
Zheng, P., Li, S., Wei, R., Wang, L., Zhou, T.L., Xu, Y.R., Takeda, T., Hirosaki, N., Xie, R.J.: Unique design strategy for laser-driven color converters enabling superhigh-luminance and high-directionality white light. Laser Photon. Rev. 13, 10 (2019)
Song, Y.H., Ji, E.K., Jeong, B.W., Jung, M.K., Kim, E.Y., Lee, C.W., Yoon, D.H.: Design of laser-driven high-efficiency Al2O3/YAG: Ce3+ ceramic converter for automotive lighting: fabrication, luminous emittance, and tunable color space. Dyes Pigm. 139, 688–692 (2017)
Xu, M., Chang, J., Wang, J., Wu, C., Hu, F.: Al2O3-YAG: Ce composite ceramics for high-brightness lighting. Opt. Express 27, 872–885 (2019)
Hu, S., Zhang, Y., Wang, Z., Zhou, G., Xue, Z., Zhang, H., Wang, S.: Phase composition, microstructure and luminescent property evolutions in “light-scattering enhanced” Al2O3-Y3Al5O12: Ce3+ ceramic phosphors. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 38, 3268–3278 (2018)
Sai, Q., Zhao, Z., Xia, C., Xu, X., Wu, F., Di, J., Wang, L.: Ce-doped Al2O3YAG eutectic and its application for white LEDs. Opt. Mater. 35, 2155–2159 (2013)
Liu, Z., Li, S., Huang, Y., Wang, L., Yao, Y., Long, T., Yao, X., Liu, X., Huang, Z.: Composite ceramic with high saturation input powder in solid-state laser lighting: microstructure, properties, and luminous emittances. Ceram. Int. 44, 20232–20238 (2018)
Wang, J., Tang, X., Zheng, P., Li, S., Zhou, T., Xie, R.J.: Thermally self-managing YAG: Ce–Al2O3 color converters enabling high-brightness laser-driven solid state lighting in a transmissive configuration. J. Mater. Chem. 7, 3901–3908 (2019)
Klein, P.H., Croft, W.J.: Thermal conductivity, diffusivity, and expansion of Y2O3, Y3 Al5O12, and LaF3 in the range 77°-300°K. J. Appl. Phys. 38, 1603–1607 (1967)
Fujioka, K., Yagasaki, K., Sawada, T., Minemoto, H., Fuji, H., Yamamoto, K.: AlN–Ce-doped yttrium aluminum garnet composite ceramic phosphor for high-power laser lighting. Opt. Mater. 121, 111507 (2021)
Kurokawa, Y., Utsumi, K., Takamizawa, H.: Development and microstructural characterization of high-thermal-conductivity aluminum nitride ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 71, 588–594 (1998)
Kanechika, Y., Azuma, M., Fukushima, H.: Optimum sintering conditions for optical properties of translucent aluminum nitride ceramics. Chin. Sci. Bull. 54, 842–845 (2009)
Zhang, H., Wang, H., Gu, H., Zong, X., Tu, B., Xu, P., Wang, B., Wang, W., Liu, S., Fu, Z.: Preparation of transparent MgO·1.8Al2O3 spinel ceramics by aqueous gelcasting, presintering and hot isostatic pressing. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 38, 4057–4063 (2018)
Senatsky, Y., Shirakawa, A., Sato, Y., Hagiwara, J., Lu, J., Ueda, K., Yagi, H., Yanagitani, T.: Nonlinear refractive index of ceramic laser media and perspectives of their usage in a high-power laser-driver. Laser Phys. Lett. 1, 500–506 (2004)
Katz, M., Route, R.K., Hum, D.S., Parameswaran, K.R., Miller, G.D., Fejer, M.M.: Vapor-transport equilibrated near-stoichiometric lithium tantalite for frequency-conversion applications. Opt. Lett. 29, 1775–1777 (2004)
Sato, Y., Taira, T.: The studies of thermal conductivity in GdVO4, YVO4, and Y3Al5O12 measured by quasi-one-dimensional flash method. Opt. Express 14, 10528–10536 (2006)
Liu, J.B., Wang, Z.F., Liu, H., Wang, X.T., Ma, Y.: Mechanical and thermal properties of MgAl2O4-Y3Al5O12 ceramic composites. Solid State Phenom. 281, 255–260 (2018)
Boey, Y.C., Song, X.L., Gu, Z.Y., Tok, A.: AlON phase formation in a tape-cast Al2O3/AlN composite. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 89, 478–480 (1999)
McCauley, J.W., Patel, P., Chen, M., Gilde, G., Strassburger, E., Paliwal, B., Ramesh, K.T., Dandekar, D.P.: AlON: A brief history of its emergence and evolution. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 29, 223–236 (2009)
Angle, J.P., Wang, Z., Dames, C., Mecartney, M.L.: Comparison of two-phase thermal conductivity models with experiments on dilute ceramic composites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 96, 2935–2942 (2013)
Agari, Y., Ueda, A., Nagai, S.: Thermal conductivity of a polymer composite. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 49, 1625–1634 (1993)
Monden, K.: High thermal conducting composites using percolation theory. Charact. Miner. Metals Mater. 2017, 385–392 (2017)
Maxwell-Garnett, J.C.: Colours in metal glasses and in metallic films. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 203, 385 (1904)
Bruggeman, D.A.G.: Berechnung verschiedener physikalischer Konstanten von heterogenen Systemen. Ann. Phys. 24, 636 (1935)
Landauer, R.: The electrical resistance of binary metallic mixtures. J. Appl. Phys. 23, 779 (1952)
Eucken, A.: Thermal conductivity of ceramic refractory materials, calculation from thermal conductivity of constituents. Ceram. Abstr. 11, 353–360 (1932)
Brailsford, A.D., Major, K.G.: The thermal conductivity of aggregates of several phases, including porous materials. Br. J. Appl. Phys. 15, 313 (1964)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sawada, T., Fuji, H., Yagasaki, K. et al. Thermal properties of AlN–Ce:YAG composite ceramic phosphor for laser lighting. Opt Rev 29, 276–285 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10043-022-00737-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10043-022-00737-0