Abstract
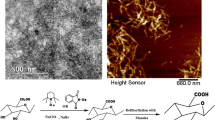
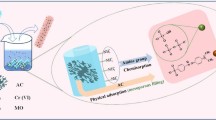
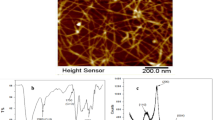
UiO-66-NH2 is an efficient material for removing pollutants from wastewater due to its high specific surface area, high porosity and water stability. However, recycling them from wastewater is difficult. In this study, the cellulose nanofibers mat deacetylated from cellulose acetate nanofibers were used to combine with UiO-66-NH2 by the method of in-situ growth to remove the toxic dye, rose bengal. Compared to previous work, the prepared composite could not only provide ease of separation of UiO-66-NH2 from the water after adsorption but also demonstrate better adsorption capacity (683 mg·g−1 (T = 25 °C, pH = 3)) than that of the simple UiO-66-NH2 (309.6 mg·g−1 (T = 25 °C, pH = 3)). Through the analysis of adsorption kinetics and isotherms, the adsorption for rose bengal is mainly suitable for the pseudo-second-order kinetic model and Freundlich model. Furthermore, the relevant research revealed that the main adsorption mechanism of the composite was electrostatic interaction, hydrogen bonding and π—π interaction. Overall, the approach depicts an efficient model for integrating metal-organic frameworks on cellulose nanofibers to improve metal-organic framework recovery performance with potentially broad applications.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee L W, Pao S Y, Pathak A, Kang D Y, Lu K L. Membrane adsorber containing a new Sm(III)-organic framework for dye removal. Environmental Science: Nano, 2019, 6(4): 1067–1076
Gupta V K, Mittal A, Jhare D, Mittal J. Batch and bulk removal of hazardous colouring agent rose bengal by adsorption techniques using bottom ash as adsorbent. RSC Advances, 2012, 2(22): 8381–8389
Crini G. Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: a review. Bioresource Technology, 2006, 97(9): 1061–1085
McMullan G, Meehan C, Conneely A, Kirby N, Robinson T, Nigam P, Banat I M, Marchant R, Smyth W E. Microbial decolourisation and degradation of textile dyes. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2001, 56(1–2): 81–87
Fu F L, Wang Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: a review. Journal of Environmental Management, 2011, 92(3): 407–418
Dabrowski A. Adsorption—from theory to practice. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2001, 93(1–3): 135–224
Rafatullah M, Sulaiman O, Hashim R, Ahmad A. Adsorption of methylene blue on low-cost adsorbents: a review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 177(1–3): 70–80
Kumar P, Pournara A, Kim K H, Bansal V, Rapti S, Manos M J. Metal-organic frameworks: challenges and opportunities for ionexchange/sorption applications. Progress in Materials Science, 2017, 86: 25–74
Schoenecker P M, Carson C G, Jasuja H, Flemming C J J, Walton K S. Effect of water adsorption on retention of structure and surface area of metal-organic frameworks. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2012, 51(18): 6513–6519
Yazaydin A O, Benin A I, Faheem S A, Jakubczak P, Low J J, Willis R R, Snurr R Q. Enhanced CO2 adsorption in metal-organic frameworks via occupation of open-metal sites by coordinated water molecules. Chemistry of Materials, 2009, 21(8): 1425–1430
Kumar P, Deep A, Kim K H. Metal organic frameworks for sensing applications. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 73: 39–53
Haque E, Lo V, Minett A I, Harris A T, Church T L. Dichotomous adsorption behaviour of dyes on an amino-functionalised metal-organic framework, amino-MIL-101(Al). Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(1): 193–203
Wang H, Yuan X Z, Wu Y, Zeng G M, Chen X H, Leng L J, Li H. Synthesis and applications of novel graphitic carbon nitride/metal-organic frameworks mesoporous photocatalyst for dyes removal. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2015, 174: 445–454
Abdi J, Vossoughi M, Mahmoodi N M, Alemzadeh I. Synthesis of metal-organic framework hybrid nanocomposites based on GO and CNT with high adsorption capacity for dye removal. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 326: 1145–1158
Peterson G W, Lee D T, Barton H F, Epps T H III, Parsons G N. Fibre-based composites from the integration of metal-organic frameworks and polymers. Nature Reviews Materials, 2021, 6(7): 605–621
Wang C H, Cheng P, Yao Y Y, Yamauchi Y, Yan X, Li J S, Na J. In-situ fabrication of nanoarchitectured MOF filter for water purification. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 392: 122164
Yang Y Y, Huang W, Guo Z P, Zhang S Y, Wu F, Huang J J, Yang H J, Zhou Y S, Xu W L, Gu S J. Robust fluorine-free colorful superhydrophobic PDMS/NH2-MIL-125(Ti)@cotton fabrics for improved ultraviolet resistance and efficient oil-water separation. Cellulose, 2019, 26(17): 9335–9348
Lis M J, Caruzi B B, Gil G A, Samulewski R B, Bail A, Scacchetti F A P, Moises M P, Bezerra F M. In-situ direct synthesis of HKUST-1 in wool fabric for the improvement of antibacterial properties. Polymers, 2019, 11(4): 713
Xia L, Ju J G, Xu W, Ding C K, Cheng B W. Preparation and characterization of hollow Fe2O3 ultra-fine fibers by centrifugal spinning. Materials & Design, 2016, 96: 439–445
Ren L Y, Ozisik R, Kotha S P, Underhill P T. Highly efficient fabrication of polymer nanofiber assembly by centrifugal jet spinning: process and characterization. Macromolecules, 2015, 48(8): 2593–2602
Hu M R, Wang Y F, Yan Z F, Zhao G D, Zhao Y X, Xia L, Cheng B W, Di Y B, Zhuang X P. Hierarchical dual-nanonet of polymer nanofibers and supramolecular nanofibrils for air filtration with a high filtration efficiency, low air resistance and high moisture permeation. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2021, 9(24): 14093–14100
Ru J, Wang X M, Wang F B, Cui X L, Du X Z, Lu X Q. UiO series of metal-organic frameworks composites as advanced sorbents for the removal of heavy metal ions: synthesis, applications and adsorption mechanism. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 208: 111577
Butova V V, Soldatov M A, Guda A A, Lomachenko K A, Lamberti C. Metal-organic frameworks: structure, properties, methods of synthesis and characterization. Russian Chemical Reviews, 2016, 85(3): 280–307
Kalwar K, Hu L, Li D L, Shan D. AgNPs incorporated on deacetylated electrospun cellulose nanofibers and their effect on the antimicrobial activity. Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 2018, 29(1): 394–400
Vahidi M, Tavasoli A, Rashidi A M. Preparation of amine functionalized UiO-66, mixing with aqueous N-methyldiethanolamine and application on CO2 solubility. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2016, 28: 651–659
Hasan Z, Khan N A, Jhung S H. Adsorptive removal of diclofenac sodium from water with Zr-based metal-organic frameworks. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 284: 1406–1413
Hashem T, Ibrahim A H, Woll C, Alkordi M H. Grafting zirconium-based metal-organic framework UiO-66-NH2 nanoparticles on cellulose fibers for the removal of Cr(VI) ions and methyl orange from water. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2019, 2(9): 5804–5808
Peterson G W, Lu A X, Epps T H III. Tuning the morphology and activity of electrospun polystyrene/UiO-66-NH2 metal-orgnnic framework composites to enhance chemical warfare agent removal. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(37): 32248–32254
Wang J L, Guo X. Adsorption kinetic models: physical meanings, applications, and solving methods. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 390: 122156
Zaboon S, Abid H R, Yao Z X, Gubner R, Wang S B, Barifcani A. Removal of monoethylene glycol from wastewater by using Zr-metal organic frameworks. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2018, 523: 75–85
Guo X, Wang J L. A general kinetic model for adsorption: theoretical analysis and modeling. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2019, 288: 111100
Wang J L, Guo X. Adsorption isotherm models: classification, physical meaning, application and solving method. Chemosphere, 2020, 258: 127279
Mohammadi N, Khani H, Gupta V K, Amereh E, Agarwal S. Adsorption process of methyl orange dye onto mesoporous carbon material-kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2011, 362(2): 457–462
Lin S, Zhao Y F, Yun Y S. Highly effective removal of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory pharmaceuticals from water by Zr(IV)-based metal- organic framework: adsorption performance and mechanisms. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(33): 28076–28085
Peng Y G, Huang H L, Zhang Y X, Kang C F, Chen S M, Song L, Liu D H, Zhong C L. A versatile MOF-based trap for heavy metal ion capture and dispersion. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 187
Chen Q, He Q Q, Lv M M, Xu Y L, Yang H B, Liu X T, Wei F Y. Selective adsorption of cationic dyes by UiO-66-NH2. Applied Surface Science, 2015, 327: 77–85
Yang D Q, Hennequin B, Sacher E. XPS demonstration of π-π interaction between benzyl mercaptan and multiwalled carbon nanotubes and their use in the adhesion of Pt nanoparticles. Chemistry of Materials, 2006, 18(21): 5033–5038
Ting H, Chi H Y, Lam C H, Chan K Y, Kang D Y. High-permeance metal-organic framework-based membrane adsorber for the removal of dye molecules in aqueous phase. Environmental Science Nano, 2017, 4(11): 2205–2214
Ahmed M A, Abdelbar N M, Mohamed A A. Molecular imprinted chitosan-TiO2 nanocomposite for the selective removal of rose bengal from wastewater. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2018, 107: 1046–1053
Naushad M, Alothman Z A, Awual M R, Alfadul S M, Ahamad T. Adsorption of rose bengal dye from aqueous solution by amberlite Ira-938 resin: kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamic studies. Desalination and Water Treatment, 2016, 57(29): 13527–13533
Cai R, Du Y P, Peng S J, Bi H C, Zhang W Y, Yang D, Chen J, Lim T M, Zhang H, Cao Y C, Yan Q. Synthesis of porous, hollow metal MCO3 (M = Mn, Co, Ca) microstructures and adsorption properties thereof. Chemistry, 2014, 20(2): 421–425
Wang M, Ma Y F, Sun Y, Hong S Y, Lee S K, Yoon B, Chen L, Ci L J, Nam J D, Chen X Y, Suhr J. Hierarchical porous chitosan sponges as robust and recyclable adsorbents for anionic dye adsorption. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 18054
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the Tianjin Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 18JCQNJC71900).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, Y., Xia, L., Zhuang, X. et al. Integrating of metal-organic framework UiO-66-NH2 and cellulose nanofibers mat for high-performance adsorption of dye rose bengal. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 16, 1387–1398 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-022-2154-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-022-2154-2