Abstract
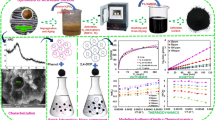
A novel cation–anion adsorbent based on dialdehyde carboxymethyl cellulose (DCMC) and tannin (TA) was produced. The obtained absorbents were characterized by the scanning electron microscopy, energy dispersive spectrometer, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The influences of absorbent dosage, pH values, initial concentration and temperature on Cr(VI) adsorption and Ni(II) adsorption were discussed. Adsorption results were evaluated by four kinetic models and four adsorption isotherms fitting. The adsorption capacities of Cr(VI) and Ni(II) on TA/DCMC were 281.94 mg/g and 43.68 mg/g, respectively. The adsorption kinetics of Cr(VI) and Ni(II) on TA/DCMC were both consistent with the pseudo-second-order kinetics model. Besides, the adsorption data of Cr(VI) fitted into the Langmuir model and the adsorption results of Ni(II) fitted into the Freundlich model. Thermodynamic analysis demonstrated the adsorption was endothermic, spontaneous, and entropy increased process. The restrained adsorption followed the order Cl− > NO− 3 > H2PO− 4 > HCO− 3 for Cr(VI) adsorption and Pb(II) > Ca(II) > Cu(II) > Zn(II) for Ni(II). After 4 recycles, the Cr(VI) and Ni(II) adsorption capacities were 52.89% and 68.95% of the absorbent in first use, respectively. The absorbent shows great potential in water treatment field.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chai WS, Cheun JY, Kumar PS et al (2021) A review on conventional and novel materials towards heavy metal adsorption in wastewater treatment application. J Clean Prod 296:126589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126589
Chen B, Chen YC, Xu LF et al (2020) Research and development on industrial heavy metal wastewater treatment technology. Earth Environ Sci 585:012051. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/585/1/012051
Okoli BJ, Modise JS (2019) Sequestration of Pb(II) and Cr(VI) from aqueous environment using low-cost immobilized tannin resin. SN Appl Sci 1:194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-0199-8
Guarin-Romero JR, Rodruguez-Estupinan P, Giraldo L et al (2019) Simple and competitive adsorption study of nickel(II) and chromium(III) on the surface of the brown algae Durvillaea antarctica. ACS Omega 4:18147–18158. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b02061
Hyder AHMG, Begum SA, Egiebor NO (2015) Adsorption isotherm and kinetic studies of hexavalent chromium removal from aqueous solution onto bone char. J Environ Chem Eng 3:1329–1336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2014.12.005
Magdy YH, Altaher H, Yaqout A (2021) Sustainable adsorption removal of nickel and chromium on eco-friendly industrial waste: equilibrium study. Chem Chem Technol 15:161–169. https://doi.org/10.23939/chcht15.02.161
Gan M, Huang DL, Chen F et al (2021) Enhanced Cr(VI) reduction and Cr(III) coprecipitation through the synergistic effect between sulfide minerals and chemoautotrophic decomposer. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105942
Ao M, Chen XT, Deng THB et al (2022) Chromium biogeochemical behaviour in soil–plant systems and remediation strategies: a critical review. J Hazard Mater 424:127233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127233
Hajizadeh Z, Valadi K, Taheri-Ledari R et al (2020) Convenient Cr(VI) removal from aqueous samples: executed by a promising clay-based catalytic system, magnetized by Fe3O4 nanoparticles and functionalized with humic acid. ChemistrySelect 5:2441. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201904672
Abdulaziz MA, Bakri AA, Al-Zaharini SA et al (2019) Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution by the pod of acacia gerrardii. Pol J Chem Technol 21:14–19. https://doi.org/10.2478/pjct-2019-0014
Qu YP, Li XJ, Lin L et al (2021) Study on the adsorption of nickel (II) in water by modified dried duckweed. E 3S Web Conf 245:03083. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202124503083
Djaenudin W, Hariyadi HR et al (2017) Removal of nickel ion from electroplating wastewater using double chamber electrodeposition cell (DCEC) reactor partitioned with water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) leaves. IOP Conf Ser 60:012020. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/60/1/012020
He ZJ, Song H, Cui YN et al (2014) Porous spherical cellulose carrier modified with polyethyleneimine and its adsorption for Cr(III) and Fe(III) from aqueous solutions. Chin J Chem Eng 22:984–990. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2014.07.001
Zhao CL, Zheng HL, Sun YJ et al (2016) Fabrication of tannin-based dithiocarbamate biosorbent and its application for Ni(II) ion removal. Water Air Soil Poll 228:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3593-0
Eivazzadeh-Keihan R, Radinekiyan F, Asgharnasl S et al (2020) A natural and eco-friendly magnetic nanobiocomposite based on activated chitosan for heavy metals adsorption and the in-vitro hyperthermia of cancer therapy. J Mater Res Technol 9(6):12244–12259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.08.096
Baghani AN, Mahvi AH, Gholami M et al (2016) One-pot synthesis, characterization and adsorption studies of amine-functionalized magnetite nanoparticles for removal of Cr (VI) and Ni (II) ions from aqueous solution: kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. J Environ Health Sci 14:11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40201-016-0252-0
Awual MR, Yaita T, Taguchi T et al (2014) Selective cesium removal from radioactive liquid waste by crown ether immobilized new class conjugate adsorbent. J Hazard Mater 278:227–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.06.011
Maleki A, Hajizadeh Z, Sharifi V et al (2019) A green, porous and eco-friendly magnetic geopolymer adsorbent for heavy metals removal from aqueous solutions. J Clean Prod 215:1233–1245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.01.084
Li ZM, Zou P, Yang JZ et al (2020) A functionalized tannin-chitosan bentonite composite with superior adsorption capacity for Cr(VI). J Polym Eng 41:34–43. https://doi.org/10.1515/polyeng-2020-0133
Lugo L, Martin A, Diaz J et al (2020) Implementation of modified acacia tannin by Mannich reaction for removal of heavy metals (Cu, Cr and Hg). Water-Sui 12:352. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020352
Pei Y, Chu S, Chen Y et al (2017) Tannin-immobilized cellulose hydrogel fabricated by a homogeneous reaction as a potential adsorbent for removing cationic organic dye from aqueous solution. Int J Bio Macromol 103:254–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.05.072
Issaoui H, Sallem F, Lafaille J et al (2021) Biosorption of heavy metals from water onto phenolic foams based on tannins and lignin alkaline liquor. Int J Environ Res 15:369–381. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-021-00313-5
Chen L, Zhou HJ, Hao L et al (2020) Dialdehyde carboxymethyl cellulose-zein conjugate as water-based nanocarrier for improving the efficacy of pesticides. Ind Crop Prod 150:112358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.112358
Dacrory S, Haggag EA, Masoud AM et al (2020) Innovative synthesis of modified cellulose derivative as a uranium adsorbent from carbonate solutions of radioactive deposits. Cellulose 27:7093–7108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03272-w
Asere TG, Mincke S, Folens K et al (2019) Dialdehyde carboxymethyl cellulose cross-linked chitosan for the recovery of palladium and platinum from aqueous solution. React Funct Polym 141:145–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2019.05.008
Tan H, Wu B, Li C et al (2015) Collagen cryogel cross-linked by naturally derived dialdehyde carboxymethyl cellulose. Carbohyd Polym 129:17–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.04.029
Li HL, Wu B, Mu CD et al (2011) Concomitant degradation in periodate oxidation of carboxymethyl cellulose. Carbohyd Polym 84:881–886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.12.026
Li ZM, Wu WW, Jiang WY et al (2020) Preparation and regeneration of a thermo-sensitive adsorbent material: methyl cellulose/calcium alginate beads (MC/CABs). Polym Bull 77:1707–1728. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-02808-w
Jiang XL, Yang Z, Peng YF et al (2016) Preparation, characterization and feasibility study of dialdehyde carboxymethyl cellulose as a novel crosslinking reagent. Carbohyd Polym 137:631–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.10.078
Wan CC, Li J (2016) Graphene oxide/cellulose aerogels nanocomposite: preparation, pyrolysis, and application for electromagnetic interference shielding. Carbohyd Polym 150:172–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.05.051
Lee J, Park S, Roh H et al (2018) Preparation and characterization of superabsorbent polymers based on starch aldehydes and carboxymethyl cellulose. Polymers 10:605. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10060605
Yu JG, Chang PR, Ma XF (2010) The preparation and properties of dialdehyde starch and thermoplastic dialdehyde starch. Carbohyd Polym 79:296–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2009.08.005
Zhang LM, Liu P, Wang YG et al (2011) Study on physico–chemical properties of dialdehyde yam starch with different aldehyde group contents. Thermochim Acta 512:196–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2010.10.006
Eivazzadeh-Keihan R, Khalili F, Aliabadi HAM et al (2020) Alginate hydrogel-polyvinyl alcohol/silk fibroin/magnesium hydroxide nanorods: a novel scaffold with biological and antibacterial activity and improved mechanical properties. Int J Biol Macromol 162:1959–1971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.08.090
Maleki A, Firouzi-Haji R, Hajizadeh Z (2018) Magnetic guanidinylated chitosan nanobiocomposite: a green catalyst for the synthesis of 1,4-dihydropyridines. Int J Biol Macromol 116:320–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.05.035
Hu T, Liu Q, Liu QZ et al (2019) Toxic Cr removal from aqueous media using catechol-amine copolymer coating onto as-prepared cellulose. Carbohyd Polym 209:291–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.01.046
Nakajima A, Baba Y (2004) Mechanism of hexavalent chromium adsorption by persimmon tannin gel. Water Res 38:2859–2864. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2004.04.005
Zheng HJ, Zhang ST, Yang CY et al (2021) Simultaneous removal of Ni(II) and Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by froth flotation using PNIPAM-CS intelligent nano-hydrogels as collector. J Mol Liq 342:117551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117551
Monser L, Adhoum N (2009) Tartrazine modified activated carbon for the removal of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Cr(III). J Hazard Mater 161:263–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.03.120
Maleki A, Mohammad M, Emdadi Z et al (2020) Adsorbent materials based on a geopolymer paste for dye removal from aqueous solutions. Arab J Chem 13:3017–3025. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2018.08.011
Yao QX, Xie JJ, Liu JX et al (2014) Adsorption of lead ions using a modified lignin hydrogel. J Polym Res 21:465. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-014-0465-9
D’Arcy M, Weiss D, Bluck M et al (2011) Adsorption kinetics, capacity and mechanism of arsenate and phosphate on a bifunctional TiO2–Fe2O3 bi-composite. J Colloid Interf Sci 364:205–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2011.08.023
Cantuaria ML, Neto AFD, Nascimento ES et al (2016) Adsorption of silver from aqueous solution onto pre-treated bentonite clay: complete batch system evaluation. J Clean Prod 112:1112–1121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.07.021
Cheng C, Jia MY, Cui LL et al (2020) Adsorption of Cr(VI) ion on tannic acid/graphene oxide composite aerogel: kinetics, equilibrium, and thermodynamics studies. Biomass Convers Bior. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-020-00899-4
Sun XB, Zhang JY, Ding GW et al (2020) Tannin-based biosorbent encapsulated into calcium alginate beads for Cr(VI) removal. Water Sci Technol 81:936–948. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2020.178
Kummer G, Schonhart M, Fernandes MG et al (2018) Development of nanofibers composed of chitosan/Nylon 6 and tannin/nylon 6 for effective adsorption of Cr(VI). J Polym Environ 26:4073–4084. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-018-1281-9
Xu QH, Wang YL, Jin LQ et al (2017) Adsorption of Cu (II), Pb (II) and Cr (VI) from aqueous solutions using black wattle tannin-immobilized nanocellulose. J Hazard Mater 339:91–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.06.005
Aloma I, Martin-Lara MA, Rodriguez IL et al (2012) Removal of nickel (II) ions from aqueous solutions by biosorption on sugarcane bagasse. J Taiwan Inst Chem E 43:275–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2011.10.011
Thevannan A, Mungroo R, Niu CH (2010) Biosorption of nickel with barley straw. Bioresour Technol 101:1776–1780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.10.035
Amin M, Chetpattananondh P (2019) Biochar from extracted marine Chlorella sp. residue for high efficiency adsorption with ultrasonication to remove Cr(VI), Zn(II) and Ni(II). Bioresour Technol 289:121578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121578
Bao SY, Yang WW, Wang YJ (2020) Highly efficient and ultrafast removal of Cr(VI) in aqueous solution to ppb level by poly(allylamine hydrochloride) covalently cross-linked amino-modified graphene oxide. J Hazard Mater 409:124470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124470
Yuan CB, Zhang Y, Yao JS et al (2021) Facile synthesis of polyethylene glycol@tannin-amine microsphere towards Cr(VI) removal. Polymers 13:1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071035
Kong QP, Wei JY, Hu Y et al (2019) Fabrication of terminal amino hyperbranched polymer modified graphene oxide and its prominent adsorption performance towards Cr(VI). J Hazard Mater 363:161–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.09.084
Peng GL, Deng SB, Liu FL et al (2019) Superhigh adsorption of nickel from electroplating wastewater by raw and calcined electroplating sludge waste. J Clean Prod 246:118948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118948
Lu SQ, Li HM, Sun JY et al (2018) Promoting the methanol oxidation catalytic activity by introducing surface nickel on platinum nanoparticles. Nano Res 11:2058–2068. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1822-x
Wang YY, Ren FQ, Lou ZN et al (2021) Hydroxyl-assisted nitrogen-containing group modified persimmon tannin with enhanced recovery capacity for Mo(VI) in aqueous solution. J Chem Technol Biot 96:188–198. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.6527
Jiang WY, Xing YH, Wang TS et al (2020) Green synthesis of tannin-polyethylenimine adsorbent for removal of Cu(II) from aqueous solution. J Chem Eng Data 65:5593–5605. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.0c00720
Funding
Financial support from Guangxi Science Foundation Funded Project (Grant No. 2021GXNSFAA075006). Open Project of Guangxi Key Laboratory of Bio-refinery (Grant No. GXKLB20-01). The Undergraduates Innovation and Entrepreneurship Program in Guangxi (Grant No. 202110593198).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, M., Yan, W., Zhang, L. et al. A Noval Cation–Anion Absorbent of Tannin-Dialdehyde Carboxymethyl Cellulose for Removal of Cr(VI) and Ni(II) from Aqueous Solutions with High Adsorption Capacity. J Polym Environ 30, 3495–3514 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-022-02451-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-022-02451-z