Abstract
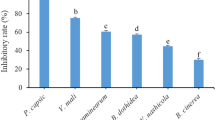
Leaf mold, which is cause by Cladosporium paeoniae, is one of the most serious diseases on peony, causing reduced growth, flower discolouration and peony seed oil reduction. In order to screen fungicides for the control of peony leaf mold, this paper investigated the inhibitory activity of four fungicides, pyraclostrobin, phenamacril, flutolanil and boscalid, on the growth and development of Cladosporium paeoniae using the coating plate method, and further determined the field control efficacy of the fungicides against leaf mold using fungicide sprays. The results showed that pyraclostrobin had strong inhibitory activity against all developmental stages of the fungus, with EC50 of 0.0045, 0.0013, 0.0184 and 0.0072 μg/mL for conidial germination, germ tube elongation, mycelial growth and conidial production, respectively. Phenamacril strongly inhibited germ tube elongation and conidial production, with EC50 of 0.3358 and 0.1368 μg/mL respectively, and also inhibited conidial germination, but had little effect on mycelial growth. Both flutolanil and boscalid showed weak inhibition of conidial germination and germ tube growth with EC50 above 25 μg/mL. Boscalid had strong inhibitory effects on mycelial growth and conidia production, with EC50 less than 2.2 μg/mL, but flutolanil had almost no inhibitory effects on mycelial growth and could even promote sporulation of the pathogen. Although all four fungicides inhibited elongation of germ tubes, none of them had significant teratogenic effects on germ tubes and conidia production. Compared with the control group without any spraying, all four fungicides significantly decreased the disease index in the field after application, and all achieved more than 60% control efficacy on the disease; with the increase of the dilution of the fungicide, the control efficacy was reduced. Pyraclostrobin and phenamacril are recommended for use as protective fungicides before the appearance of leaf mold, while after disease occurrence, pyraclostrobin and boscalid are recommended.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adki, K. M., & Kulkarni, Y. A. (2021). Neuroprotective effect of paeonol in streptozotocin- induced diabetes in rats. Life Sciences, 271, 119202. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9452(98)00161-7
Ali, M. E., Gunn, M., Stackhouse, T., Waliullah, S., Guo, B. Z., Culbreath, A., & Renneman, T. (2021). Sensitivity of Aspergillus flavus isolates from peanut seeds in Georgia to Azoxystrobin, a Quinone outside inhibitor (QoI) fungicide. Journal of Fungi, 7, 284–284. https://doi.org/10.3390/JOF7040284
Amaro, A. C. E., Ramos, R. P. R., Macedo, A. C., Ono, E. O., & Rodrigues, J. D. (2018). Effects of the fungicides azoxystrobin, pyraclostrobin and boscalid on the physiology of Japanese cucumber. Scientia Horticulturae, 228, 66–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2017.10.016
Avenot, H. F., & Michailides, T. J. (2020). Occurrence and extent of Boscalid resistance in populations of Alternaria alternata from California pistachio orchards. Plant Disease, 104, 306–314. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-04-19-0699-SR
Chen, Y., Wang, W. X., Zhang, A. F., Gu, C. Y., Zhou, M. G., & Gao, T. C. (2011). Activity of the fungicide JS399-19 against fusarium head blight of wheat and the risk of resistance. Agricultural Sciences in China, 10, 1906–1913. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1671-2927(11)60191-0
Chen, Y., Huang, T. T., Chen, C. J., Hou, Y. P., Zhang, A. F., Wang, W. X., Gao, T. C., & Zhou, M. G. (2012). Sensitivity of fusarium verticillioides isolates from rice to a novel cyanoacrylate fungicide. Crop Protection, 39, 106–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2012.03.016
Cui, K. D., He, L. M., Li, T. T., Mu, W., & Liu, F. (2020). Development of boscalid resistance in Botrytis cinerea and an efficient strategy for resistance management. Plant Disease. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-05-20-1009-RE
Dominguez, A. N., Emmert, G. E., Gil, D. M., & Álvarez, R. M. S. (2021). Experimental and theoretical vibrational study of the fungicide pyraclostrobin. Spectrochimica Acta - Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 259. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SAA.2021.119888
Du, J. k., Song, D. B., Li, J. W., Li, Y. H., Li, B. H., & Li, L. (2021). Paeonol triggers apoptosis in HeLa cervical cancer cells: The role of mitochondria-related caspase pathway. Psychopharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00213-021-05811-0
Fang, Z. D. (1998). Plant disease research methods (third edition) (pp. 359–397). China Agriculture Press.
FRAC Code List ©*2020: Fungal control agents sorted by cross resistance pattern and mode of action (including FRAC Code numbering).
Opinions of the General Office of the State Council on accelerating the development of woody oilseed industry. (2015). General Office of the State Council of the People's Republic of China.
Hnátová, M., Gbelská, Y., Obernauerová, M., Šubíková, V., & Šubík, J. (2003). Cross-resistance to strobilurin fungicides in mitochondrial and nuclear mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Folia Microbiologica, 48, 496–500. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931331
Hou, Y. P., Zheng, Z. T., Xu, S., Chen, C. J., & Zhou, M. G. (2013). Proteomic analysis of fusarium graminearum treated by the fungicide JS399-19. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 107, 86–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2013.05.009
Hou, Y., Xu, J. Q., Song, Y. Z., Hu, G. J., Du, S. F., & Kang, Y. B. (2014). Effects of carbendazim, difenoconazole and azoxystrobin on mycelial growth and conidial germination of Alternaria suffruticosae. Journal of Plant Protection, 41, 367–372. https://doi.org/10.13802/j.cnki.zwbhxb.2014.03.017
Kang, Y. B., Shang, H. S., & Cheng, Y. M. (2007). Inhibition activities of paeonol to plant pathogenic fungi in vitro. Journal of Plant Protection, 6, 580–584. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:0577-7518.2007.06.004
Lan, B. Q., Li, J. Y., & Duan, X. Q. (2002). Encyclopedia of Chinese tree Peony (volume one) (pp. 269–277). Science and technology of China press.
Liu, S. M., Hai, F., Tian, Y. E., & Liu, X. (2017). Toxicity of four fungicides cinerea and their mixtures to Botrytis from tomato. Plant Protection, 43, 230–234. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0529-1542.2017.02.042
Liu, S. M., Fu, L. Y., Tan, H. H., Jiang, J., Che, Z. P., Tian, Y. E., & Chen, G. Q. (2020). Resistance to boscalid in Botrytis cinerea from greenhouse grown tomato. Plant Disease. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-05-20-1009-RE
Metz, N., Adolf, B., Chaluppa, N., Hückelhoven, R., & Hausladen, H. (2019). Occurrence of sdh mutations in German Alternaria solani isolates and potential impact on Boscalid sensitivity in vitro, in the greenhouse, and in the field. Plant Disease, 103, 3065–3071. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-03-19-0617-RE
Qiu, Z. K., Liu, X., Tang, D., Zhang, Z., Fan, Q. H., Pan, Y. Y., Chen, Y. Y., Huang, M. Y., Zhu, T., Wang, Y. L., Cheng, X. F., & Chen, J. S. (2018). Cytoprotective effects of paeoniflorin are associated with translocator protein 18 kDa. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 107, 19–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00213-021-05811-0
Schubert, K., Braun, U., Groenewald, J. Z., & Crous, P. W. (2007). Cladosporium leaf-blotch and stem rot of Paeonia spp. caused by Dichocladosporium chlorocephalum gen. Nov. Studies in Mycology, 58, 95–104. https://doi.org/10.3114/sim.2007.58.04
Shi, G. A., Jiao, D. X., Jiao, Y. P., Yang, H. A., Han, M. W., Wu, Y. Q., & Shi, B. R. (2014). Development prospects and strategies of oil tree Peony industry in China. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association, 29, 124–128. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1006-4958.2016.12.010
Tian, Y. E., Che, Z. P., Sun, D., He, J. X., Liu, S. M., & Lin, X. M. (2019a). In vitro effects of five different classes of fungicides on growth and development of Botrytis cinerea isolated from tree Peony in China. HortScience, 54, 1984–1988. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI14431-19
Tian, Y. E., Che, Z. P., Sun, D., Yang, Y. Y., Lin, X. M., Liu, S. M., Liu, X. Y., & Gao, J. (2019b). Resistance identification of tree Peony cultivars of different flowering time to gray mold pathogen Botrytis cinerea. HortScience, 54, 328–330. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI13626-18
Wang, X. J., Liang, H. Y., Guo, D. L., Guo, L. L., Duan, X. J., Jia, Q. S., & Hou, X. G. (2019). Integrated analysis of transcriptomic and proteomic data from tree peony (P. ostii) seeds reveals key developmental stages and candidate genes related to oil biosynthesis and fatty acid metabolism. Horticulture Research, 6, 599–611. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41438-019-0194-7
Xu, J. Q., Yang, G. F., Tian, J., & Kang, Y. B. (2015). Effect of eight fungicides on mycelial of Cylindrocladium canadense causing Peony leaf spot. Northern Horticulture, 14, 114–117. https://doi.org/10.11937/bfyy.201515030
Xu, J. Q., Yang, G. F., Tian, J., & Diao, X. W. (2016a). Effects of fungicides on growth and development of Hainesia Iythri cacsing coelomycete leaf spot of Paeonia suffruticosa. Plant Protection, 42, 86–91. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0529-1542.2016.05.014
Xu, J. Q., Yang, G. F., Tian, J., Hu, J. G., Li, H. K., & Lin, X. M. (2016b). Effects of seven fungicides on growth and development of Phyllosticta commonsii causing yellow leaf spot of Paeonia suffruticosa. Journal of Henan Agricultural University, 50, 229–234. https://doi.org/10.16445/j.cnki.1000-2340.2016.02.015
Xu, J. Q., Yang, G. F., Tian, J., Che, Z. P., & Kang, Y. B. (2016c). Effects of carbendazim, tebuconazole and azoxystrobin on sporulation and conidial germination of Cladosporium paeoniae causing tree peony red spot. Journal of Plant Protection, 43, 850–857. https://doi.org/10.13802/j.cnki.zwbhxb.2016.05.020
Xu, J. Q., Ping, Z. L., Liu, Y., Ma, S. C., Xu, D. C., Yang, L., Zheng, W., Liu, S. M., Xia, Y. F., & Lin, X. M. (2017). Inhibitory activity of fludioxonil to four pathogenic fungi of peony leaves. Scientia Agricultural Sinica, 50, 4036–4045. https://doi.org/10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2017.20.018
Xu, J. Q., Zhang, L. Z., Tang, H. J., Xu, D. C., Fan, Y. L., & Li, W. L. (2018). Peony diseases and their symptom identification in Luoyang. Forest Pest and Disease., 37, 35–38. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1671-0886.2018.01.009
Xu, C., Li, M. X., Zhou, Z. H., Li, J. S., Chen, D. M., Duan, Y. B., & Zhou, M. G. (2019). Impact of five succinate dehydrogenase inhibitors on DON biosynthesis of Fusarium asiaticum, causing fusarium head blight in wheat. Toxins, 11, 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11050272
Yan, Z. G., Xie, L. H., Li, M. C., Yuan, M., Tian, Y., Sun, D. Y., Zhang, Y. L., & Niu, L. X. (2021). Phytochemical components and bioactivities of novel medicinal food-Peony roots. Food Research International, 140, 109902. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODRES.2020.109902
Zhao, C., Zhang, X. F., Hua, H. H., Han, C. G., & Wu, X. H. (2019). Sensitivity of Rhizoctonia spp. to flutolanil and characterization of the point mutation in succinate dehydrogenase conferring fungicide resistance. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 155, 13–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-019-01739-6
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Central Plains Scholars Fund of Henan Province (202101510003), the Key Research Project of Higher Education Institutions of Henan Provincial Education Department (Grant No. 19A210010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that the research complies with ethical standards.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chai, Q., Xu, J., Guo, Y. et al. Inhibitory activity of three types of fungicides on Cladosporium paeoniae and their control efficacy against paeony leaf mold. Eur J Plant Pathol 163, 707–717 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-022-02509-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-022-02509-7