Abstract
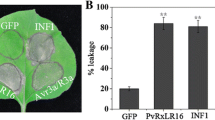
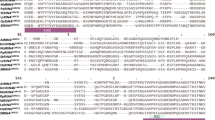
Recognition of avirulence (AVR) proteins by cognate plant resistance proteins leads to effector-triggered immunity. Previous reports have indicated that the Phytophthora infestans avirulence effector 3b (PiAVR3b) can trigger a hypersensitive response when recognized by resistance protein Rpi-R3b. However, the molecular mechanisms by which the PiAVR3b triggers immune responses are largely unknown. Here, we investigated the variation of PiAVR3b in diverse P. infestans isolates and found that they show the presence/absence polymorphisms. The allelic variation of PiAVR3b showed three polymorphic residues at positions 41, 85 and 124. Truncation and expression analysis showed that a 61-amino acid region in the C-terminus half of PiAVR3b was enough to trigger Rpi-R3b-mediated cell death. In addition, we found that a paralogue of PiAVR3b, PITG_18221, escaped recognition by Rpi-R3b. Microscopic imaging revealed that PiAVR3b was located in both the nucleus and cytoplasm. The nuclear localization of PiAVR3b was required for the Rpi-R3b-mediated immunity. Finally, we proved that both SGT1 and HSP90 are essential for PiAVR3b-triggered cell death. Our results provide a basis for further investigation of how PiAVR3b triggers plant immunity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, R. G., Deb, D., Fedkenheuer, K., & McDowell, J. M. (2015). Recent progress in RXLR effector research. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 28(10), 1063–1072. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-01-15-0022-CR
Armstrong, M. R., Whisson, S. C., Pritchard, L., Bos, J. I., Venter, E., Avrova, A. O., Rehmany, A. P., Böhme, U., Brooks, K., Cherevach, I., Hamlin, N., White, B., Fraser, A., Lord, A., Quail, M. A., Churcher, C., Hall, N., Berriman, M., Huang, S., et al. (2005). An ancestral oomycete locus contains late blight avirulence gene Avr3a, encoding a protein that is recognized in the host cytoplasm. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102(21), 7766–7771. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0500113102
Bos, J. I., Kanneganti, T. D., Young, C., Cakir, C., Huitema, E., Win, J., Armstrong, M. R., Birch, P. R., & Kamoun, S. (2006). The C-terminal half of Phytophthora infestans RXLR effector AVR3a is sufficient to trigger R3a-mediated hypersensitivity and suppress INF1-induced cell death in Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant Journal, 48(2), 165–176. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02866.x
Champouret, N., Bouwmeester, K., Rietman, H., van der Lee, T., Maliepaard, C., Heupink, A., van de Vondervoort, P. J., Jacobsen, E., Visser, R. G., van der Vossen, E. A., Govers, F., & Vleeshouwers, V. G. (2009). Phytophthora infestans isolates lacking class I ipiO variants are virulent on Rpi-blb1 potato. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 22(12), 1535–1545. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-22-12-1535
Du, Y., Berg, J., Govers, F., & Bouwmeester, K. (2015). Immune activation mediated by the late blight resistance protein R1 requires nuclear localization of R1 and the effector AVR1. New Phytologist, 207(3), 735–747. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13355
Gao, C., Xu, H., Huang, J., Sun, B., Zhang, F., Savage, Z., Duggan, C., Yan, T., Wu, C. H., Wang, Y., Vleeshouwers, V. G. A. A., Kamoun, S., Bozkurt, T. O., & Dong, S. (2020). Pathogen manipulation of chloroplast function triggers a light-dependent immune recognition. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 117(17), 9613–9620. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2002759117
Gilroy, E. M., Breen, S., Whisson, S. C., Squires, J., Hein, I., Kaczmarek, M., Turnbull, D., Boevink, P. C., Lokossou, A., Cano, L. M., Morales, J., Avrova, A. O., Pritchard, L., Randall, E., Lees, A., Govers, F., van West, P., Kamoun, S., Vleeshouwers, V. G. A. A., et al. (2011). Presence/absence, differential expression and sequence polymorphisms between PiAVR2 and PiAVR2-like in Phytophthora infestans determine virulence on R2 plants. New Phytologist, 191(3), 763–776. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.03736.x
Haverkort, A. J., Boonekamp, P. M., Hutten, R., Jacobsen, E., Lotz, L. A. P., Kessel, G. J. T., Vossen, J. H., & Visser, R. G. F. (2016). Durable late blight resistance in potato through dynamic varieties obtained by cisgenesis: Scientific and societal advances in the DuRPh project. Potato Research, 59(1), 35–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11540-015-9312-6
Hein, I., Gilroy, E. M., Armstrong, M. R., & Birch, P. R. (2009). The zig-zag-zig in oomycete-plant interactions. Molecular Plant Pathology, 10(4), 547–562. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1364-3703.2009.00547.x
Huang, G., Liu, Z., Gu, B., Zhao, H., Jia, J., Fan, G., Meng, Y., Du, Y., & Shan, W. (2019). An RXLR effector secreted by Phytophthora parasitica is a virulence factor and triggers cell death in various plants. Molecular Plant Pathology, 20(3), 356–371. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12760
Jiang, R., Li, J., Tian, Z., Du, J., Armstrong, M., Baker, K., Tze-Yin Lim, J., Vossen, J. H., He, H., Portal, L., Zhou, J., Bonierbale, M., Hein, I., Lindqvist-Kreuze, H., & Xie, C. (2018). Potato late blight field resistance from QTL dPI09c is conferred by the NB-LRR gene R8. Journal of Experimental Botany, 69(7), 1545–1555. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ery021
Jones, J. D., & Dangl, J. L. (2006). The plant immune system. Nature, 444(7117), 323–329. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05286
Kadota, Y., Shirasu, K., & Guerois, R. (2010). NLR sensors meet at the SGT1-HSP90 crossroad. Trends in Biochem Sciences, 35(4), 199–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2009.12.005
Kang, H., Nguyen, Q. M., Iswanto, A. B. B., Hong, J. C., Bhattacharjee, S., Gassmann, W., & Kim, S. H. (2021). Nuclear localization of HopA1Pss61 is required for effector-triggered immunity. Plants (Basel), 10(5), 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10050888
Li, G., Huang, S., Guo, X., Li, Y., Yang, Y., Guo, Z., Kuang, H., Rietman, H., Bergervoet, M., Vleeshouwers, V. G., van der Vossen, E. A., Qu, D., Visser, R. G., Jacobsen, E., & Vossen, J. H. (2011). Cloning and characterization of R3b; members of the R3 superfamily of late blight resistance genes show sequence and functional divergence. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 24(10), 1132–1142. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-11-10-0276
Lin, X., Song, T., Fairhead, S., Witek, K., Jouet, A., Jupe, F., Witek, A. I., Karki, H. S., Vleeshouwers, V. G. A. A., Hein, I., & Jones, J. D. G. (2020). Identification of Avramr1 from Phytophthora infestans using long read and cDNA pathogen-enrichment sequencing (PenSeq). Molecular Plant Pathology, 21(11), 1502–1512. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12987
Liu, Y., Burch-Smith, T., Schiff, M., Feng, S., & Dinesh-Kumar, S. P. (2004). Molecular chaperone Hsp90 associates with resistance protein N and its signaling proteins SGT1 and Rar1 to modulate an innate immune response in plants. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279(3), 2101–2108. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M310029200
Livak, K. J., & Schmittgen, T. D. (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods, 25(4), 402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Monino-Lopez, D., Nijenhuis, M., Kodde, L., Kamoun, S., Salehian, H., Schentsnyi, K., Stam, R., Lokossou, A., Abd-EI-Haliem, A., Visser, R. G. F., & Vossen, J. H. (2021). Allelic variants of the NLR protein Rpi-chc1 differentially recognize members of the Phytophthora infestans PexRD12/31 effector superfamily through the leucine-rich repeat domain. Plant Journal, 107(1), 182–197. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.15284
Morales, J. G., Gaviria, A. E., & Gilchrist, E. (2020). Allelic variation and selection in effector genes of Phytophthora infestans (Mont.) de Bary. Pathogens, 9(7), 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9070551
Oh, S. K., Young, C., Lee, M., Oliva, R., Bozkurt, T. O., Cano, L. M., Win, J., Bos, J. I., Liu, H. Y., van Damme, M., Morgan, W., Choi, D., Van der Vossen, E. A., Vleeshouwers, V. G., & Kamoun, S. (2009). In planta expression screens of Phytophthora infestans RXLR effectors reveal diverse phenotypes, including activation of the Solanum bulbocastanum disease resistance protein Rpi-blb2. Plant Cell, 21(9), 2928–2947. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.109.068247
Peart, J. R., Lu, R., Sadanandom, A., Malcuit, I., Moffett, P., Brice, D. C., Schauser, L., Jaggard, D. A., Xiao, S., Coleman, M. J., Dow, M., Jones, J. D., Shirasu, K., & Baulcombe, D. C. (2002). Ubiquitin ligase-associated protein SGT1 is required for host and nonhost disease resistance. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 99(16), 10865–10869. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.152330599
Rietman, H., Bijsterbosch, G., Cano, L. M., Lee, H. R., Vossen, J. H., Jacobsen, E., Visser, R. G., Kamoun, S., & Vleeshouwers, V. G. (2012). Qualitative and quantitative late blight resistance in the potato cultivar Sarpo Mira is determined by the perception of five distinct RXLR effectors. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 25(7), 910–919. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-01-12-0010-R
Saunders, D. G., Breen, S., Win, J., Schornack, S., Hein, I., Bozkurt, T. O., Champouret, N., Vleeshouwers, V. G., Birch, P. R., Gilroy, E. M., & Kamoun, S. (2012). Host protein BSL1 associates with Phytophthora infestans RXLR effector AVR2 and the Solanum demissum immune receptor R2 to mediate disease resistance. Plant Cell, 24(8), 3420–3434. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.112.099861
Thilliez, G. J. A., Armstrong, M. R., Lim, T. Y., Baker, K., Jouet, A., Ward, B., van Oosterhout, C., Jones, J. D. G., Huitema, E., Birch, P. R. J., & Hein, I. (2019). Pathogen enrichment sequencing (PenSeq) enables population genomic studies in oomycetes. New Phytologist, 221(3), 1634–1648. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.15441
van Poppel, P. M., Guo, J., van de Vondervoort, P. J., Jung, M. W., Birch, P. R., Whisson, S. C., & Govers, F. (2008). The Phytophthora infestans avirulence gene Avr4 encodes an RXLR-dEER effector. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 21(11), 1460–1470. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-21-11-1460
Wang, H., Ren, Y., Zhou, J., Du, J., Hou, J., Jiang, R., Wang, H., Tian, Z., & Xie, C. (2017). The cell death triggered by the nuclear localized RxLR effector PITG_22798 from Phytophthora infestans is suppressed by the effector AVR3b. International Journal of Mollecular Sciences, 18(2), 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020409
Whisson, S. C., Boevink, P. C., Moleleki, L., Avrova, A. O., Morales, J. G., Gilroy, E. M., Armstrong, M. R., Grouffaud, S., van West, P., Chapman, S., Hein, I., Toth, I. K., Pritchard, L., & Birch, P. R. (2007). A translocation signal for delivery of oomycete effector proteins into host plant cells. Nature, 450(7166), 115–118. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06203
Whisson, S. C., Boevink, P. C., Wang, S., & Birch, P. R. (2016). The cell biology of late blight disease. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 34, 127–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2016.09.002
Xiang, J., Li, X., Yin, L., Liu, Y., Zhang, Y., Qu, J., & Lu, J. (2017). A candidate RxLR effector from Plasmopara viticola can elicit immune responses in Nicotiana benthamiana. BMC Plant Biology, 17(1), 75. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-017-1016-4
Yang, B., Wang, Q., Jing, M., Guo, B., Wu, J., Wang, H., Wang, Y., Lin, L., Wang, Y., Ye, W., Dong, S., & Wang, Y. (2017). Distinct regions of the Phytophthora essential effector Avh238 determine its function in cell death activation and plant immunity suppression. New Phytologist, 214(1), 361–375. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14430
Zhang, X., Liu, B., Zou, F., Shen, D., Yin, Z., Wang, R., He, F., Wang, Y., Tyler, B. M., Fan, W., Qian, W., & Dou, D. (2019). Whole genome re-sequencing reveals natural variation and adaptive evolution of Phytophthora sojae. Frontiers in Microbiology, 10, 2792. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02792
Zheng, X., McLellan, H., Fraiture, M., Liu, X., Boevink, P. C., Gilroy, E. M., Chen, Y., Kandel, K., Sessa, G., Birch, P. R., & Brunner, F. (2014). Functionally redundant RXLR effectors from Phytophthora infestans act at different steps to suppress early flg22-triggered immunity. PLoS Pathogens, 10(4), e1004057. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1004057
Acknowledgments
We thank Lina Yang (Fujian Agricultural and Forestry University) for providing P. infestans isolates AH9-7, AS-15, AH8-7, Pd21203.
Funding
This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number 31800134, 32060499) and the Yunnan Fundamental Research Projects (Grant number 2019FB023, 202101AT070110).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hongyang Wang and Yindi Zhang performed most experiments and prepared the manuscript; Hongying Luan, Aie Chen, Jing Liu, and Jie Lu performed data analysis, microscopy study and repeated cell death statistics; Wei Tang and Canhui Li designed experiments and improved the manuscript quality. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 126 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Zhang, Y., Luan, H. et al. Nuclear localization and the C-terminus region of PiAVR3b from Phytophthora infestans are required for recognition by the resistance protein Rpi-R3b. Eur J Plant Pathol 163, 483–493 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-022-02491-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-022-02491-0