Abstract
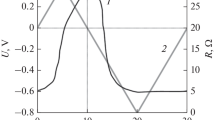
The experimental data on the measurement of resistance and electrical conductivity in a low-resistance mode of operation of a memristor based on germanium selenide with a self-directed conductive channel in the range of switching frequencies and temperatures are presented. In the frequency experiment, the switching frequency effect is conducted at room temperature in the range of 1 to 10 000 Hz. An experiment to study the effect of temperature on resistance and electrical conductivity is carried out in the temperature range –10–65°C at a switching frequency of 10 Hz. The aim of this study is to determine the activation energy of the formation of a conductive channel. It is shown that in the temperature range 22–65°C electrical conductivity obeys the Arrhenius law with an activation energy of 0.19 eV; at temperatures below room temperature, the electrical conductivity is insensitive to temperature changes. The reasons for the low value of the activation energy are discussed.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Chua, L.O., Memristor—missing circuit element, IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory, 1971, vol. 18, pp. 507–519.
Chua, L.O. and Kang, S.M., Memristive devices and systems, Proc. IEEE, 1976, vol. 64, pp. 209–223.
Yang, J.J., Strukov, D.B., and Stewart, D.R., Memristive devices for computing, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2013, vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 13–24.
Bersuker, G., Gilmer, D.C., Veksler, D., Kirsch, P., Vandelli, L., Padovani, A., Larcher, L., McKenna, K., Shluger, A., Iglesias, V., Porti, M., and Nafrıa, M., Metal oxide resistive memory switching mechanism based on conductive filament properties, J. Appl. Phys., 2011, vol. 110, p. 124518.
Kim, K.M., Jeong, D.S., and Hwang, C.S., Nanofilamentary resistive switching in binary oxide system; a review on the present status and outlook, Nanotecnology, 2011, vol. 22, p. 254002.
Waser, R. and Aono, M., Nanoionics-based resistive switching memories, Nat. Mater., 2007, vol. 6, no. 11, pp. 833–840.
Waser, R., Dittmann, R., Staikov, G., and Szot, K., Redox-based resistive switching memories—nanoionic mechanisms, prospects, and challenges, Adv. Mater., 2009, vol. 21, pp. 2632–2663.
Valov, I., Waser, R., Jameson, J.R., and Kozicki, M.N., Electrochemical metallization memories—fundamentals, applications, prospects, Nanotecnology, 2011, vol. 22, p. 254003.
Linn, E., Rosezin, R., Kuegeler, C., and Waser, R., Complementary resistive switches for passive nanocrossbar memories, Nat. Mater., 2010, vol. 9, pp. 403–406.
Campbell, K.A., Self-directed channel memristor for high temperature operation, Microelectron. J., 2017, vol. 59, pp. 10–14.
Campbell, K.A. and Anderson, C.M., Рhase-change memory devices with stacked Ge-chalcogenide/Sn-chalcogenide layers, Microelectron. J., 2007, vol. 38, pp. 52–59.
Edwards, A.H., Campbell, K.A., and Pineda, A.C., Self-trapping of single and paired electrons in Ge2Se3, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 2012, vol. 24, no. 19, p. 195801.
Devasia, A., Kurinec, S., Campbell, K.A., and Raoux, S., Influence of Sn migration on phase transition in GeTe and Ge2Se3 thin films, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2010, vol. 96, p. 141908.
Jarvis, K., Carpenter, R.W., Davis, M., and Campbell, K.A., An investigation of amorphous Ge2Se3 structure for phase change memory devices using fluctuation electron microscopy, J. Appl. Phys., 2009, vol. 106, p. 083507.
Aleshin, A.N. and Enisherlova, K.L., Physicochemical fundamentals of phase formation in silicon layers implanted with oxygen and carbon, Mod. Electron. Mater., 2019, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 77–85.
Abe, H., Yamamoto, S., Miyashita, A., and Siskafus, K.E., Formation mechanism for carbon onions and nanocapsules in C+ ions implanted copper, J. Appl. Phys., 2001, vol. 90, no. 7, pp. 3353–3358.
Esin, V.Ya., Influence of associates within grain boundaries on the parameters of grain boundary diffusion, Extended Abstract of Cand. Sci. Dissertation, Moscow: NITU MISiS, 2011.
Campbell, K.A. and Moore, J.T., Silver-selenide/chalcogenide glass stack for resistance variable memory, US Patent no. 7 151 273, 2006.
Bokshtein, B.S. and Mendelev, M.I., Kratkii kurs fizicheskoi khimii (Short Course of Physical Chemistry), Moscow: CheRo, 1999.
Strukov, D.B. and Williams, R.S., Exponential ionic drift: fast switching and low volatility of thin-film memristors, Appl. Phys. A, 2009, vol. 94, pp. 515–519.
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, grant no. 19-29-03003 MK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aleshin, A.N., Ruban, O.A. Temperature-Frequency Study of Germanium Selenide Memristors with a Self-Directed Current-Conducting Channel. Russ Microelectron 51, 59–67 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063739722020020
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063739722020020