Exploring autophagy-related prognostic genes of Alzheimer's disease based on pathway crosstalk analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2021.7019Keywords:
Alzheimer's disease (AD), Autophagy, Prognostic signature, Pathway crosstalk, Weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA), Pathway analysis method based on global influence (PAGI)Abstract
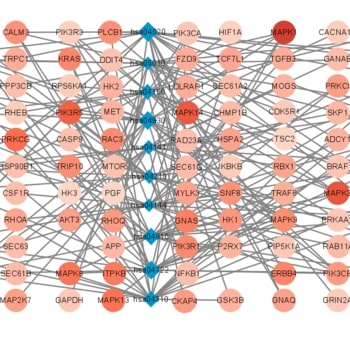
Recent studies have shown that different signaling pathways are involved in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD), with complex molecular connections existing between these pathways. Autophagy is crucial for the degradation and production of pathogenic proteins in AD, and it shows link with other AD-related pathways. However, current methods for identifying potential therapeutic targets for AD are primarily based on single-gene analysis or a single signal pathway, both of which are somewhat limited. Finding other methods is necessary for providing novel underlying AD therapeutic targets. Therefore, given the central role of autophagy in AD and its interplay with its pathways, we aimed to identify prognostic genes related to autophagy within and between these pathways based on pathway crosstalk analysis. The method of pathway analysis based on global influence (PAGI) was applied to find the feature mRNAs involved in the crosstalk between autophagy and other AD-related pathways. Subsequently, the weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) was used to construct a co-expression module of feature mRNAs and differential lncRNAs. Finally, based on 2 autophagy-related crosstalk genes (CD40 and SMAD7), we constructed a prognosis model by multivariate Cox regression, which could predict the overall survival of AD patients with medium-to-high accuracy. In conclusion, we provided an effective method for extracting autophagy-related significant genes based on pathway crosstalk in AD. We found the biomarkers valuable to the AD prognosis, which may also play an essential role in the development and treatment of AD.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Fang Qian, Wei Kong, Shuaiqun Wang

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Funding data
-
Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai
Grant numbers No.18ZR1417200 -
National Natural Science Foundation of China
Grant numbers No.61803257













