Abstract
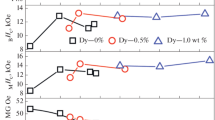
Magnetic properties and microstructure of (Nd,Dy)–Fe–B magnets with Dy in the range from 0 to 10.3 wt % and oxygen less than 0.26 wt % are studied. High-coercivity magnets with Dy 8 wt % have maximum energy density product (BH)max ≥ 35 MG Oe and coercivity МНс ≥ 30 kOe; their operating temperature can be as high as 180°С. Phase composition and structure of (Nd,Dy)–Fe–B magnets were studied by X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy. In addition to the main (Nd,Dy)2Fe14B phase and (Nd,Dy)2O3 oxide, in triple junctions, there are two (Nd, Dy, Fe, М)Ox phases with fcc structure (symmetry group 225, Fm\(\bar {3}\)m) but with different content of O, Fe, and additional elements M (M = Co, Cu, Ga). It was shown that the total content of (Nd,Dy,Fe,М)Ox oxides grew with the total concentrations of oxygen and dysprosium in magnets.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
S. Sugimoto, “Current status and recent topics of rare-earth permanent magnets,” J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 44, No. 6 (2011).
K. Hono and H. Sepehri-Amin, “Strategy for high-coercivity Nd–Fe–B magnets,” Scr. Mater. 67, No. 6, 530–535 (2012).
H. Nakamura, “The current and future status of rare earth permanent magnets,” Scr. Mater. 154, 273–276 (2018).
B. P. Hu, E. Niu, Y. G. Zhao, G. A. Chen, Z. A. Chen, G. S. Jin, J. Zhang, X. L. Rao, and Z. X. Wang, “Study of sintered Nd–Fe–B magnet with high performance of Hcj (kOe) (BH)max (MG Oe) > 75,” AIP Adv. 3, No. 4, 1–17 (2013).
M. Sagawa, S. Hirosawa, K. Tokuhara, H. Yamamoto, S. Fujimura, Y. Tsubokawa, and R. Shimizu, “Dependence of coercivity on the anisotropy field in the Nd2Fe14B-type sintered magnets,” J. Appl. Phys. 61, No. 8, 3559–3561 (1987).
M. Sagawa, S. Fujimura, H. Yamamoto, Y. Matsuura, and K. Hiraga, “Permanent magnet materials based on the rare earth-iron-boron tetragonal compounds,” IEEE Trans. Magn. 20, No. 5, 1584–1589 (1986).
M. Tokunaga, M. Tobise, N. Meguro, and H. Harada, “Microstructure of R–Fe–B sintered magnet,” IEEE Trans. Magn. 22, No. 5, 904–909 (1986).
A. S. Kim and F. E. Camp, “High performance NdFeB magnets (invited),” J. Appl. Phys. 79, No. 8, Part 2A, 5035–5039 (1996).
G. H. Yan, R. J. Chen, Y. Ding, S. Guo, D. Lee, and A. R. Yan, “The preparation of sintered NdFeB magnet with high-coercivity and high temperature-stability,” J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 266, No. 1 (2011).
J. Wang, H. Feng, A. Li, Y. Li, M. Zhu, and W. Li, “Oxide evolution in NdDy–Fe–B magnet during aging process,” J. Rare Earths 30, No. 10, 1020–1023 (2012).
D. Yu. Vasilenko, A. V. Shitov, A. V. Vlasyuga, A. G. Popov, N. V. Kudrevatykh, and N. V. Pechishcheva, “Microstructure and properties of Nd–Fe–B alloys produced by strip casting and of permanent magnets fabricated from them,” Met. Sci. Heat Treat. 56, No. 11, 585–590 (2014).
Q. Zhou, W. Li, Y. Hong, L. Zhao, X. Zhong, H. Yu, L. Huang, and Z. Liu, “Microstructure improvement related coercivity enhancement for sintered NdFeB magnets after optimized additional heat treatment,” J. Rare Earths 36, No. 4, 379–384 (2018).
W. F. Li, H. Sepehri-Amin, T. Ohkubo, N. Hase, and K. Hono, “Distribution of Dy in high-coercivity (Nd,Dy)–Fe–B sintered magnet,” Acta Mater. 59, No. 8, 3061–3069 (2011).
Z. Hu, H. Qu, D. Ma, C. Luo, and H. Wang, “Influence of dysprosium substitution on magnetic and mechanical properties of high intrinsic coercivity Nd–Fe–B magnets prepared by double-alloy powder mixed method,” J. Rare Earths 34, No. 7, 689–694 (2016).
A. A. Lukin, N. B. Kol’chugina, G. S. Burkhanov, N. E. Klyueva, and K. Skotnitseva, “Significance of terbium hydride additions in the microstructure formation and magnetic properties of sintered Nd–Pr–Dy–Fe–B magnets,” Fiz. Khim. Obr. Mater., No. 1, 70–73 (2012).
F. Yang, L. Guo, P. Li, X. Zhao, Y. Sui, Z. Guo, and X. Gao, “Boundary structure modification and magnetic properties of Nd–Fe–B sintered magnets by co-doping with Dy2O3/S powders,” J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 429, 117–123 (2017).
G. S. Burkhanov, N. B. Kolchugina, A. A. Lukin, Y. S. Koshkidko, J. Cwik, K. Skotnicova, and V. Sitnov, “Structure and magnetic properties of Nd–Fe–B magnets prepared from DyH2-containing powder mixtures,” Inorg. Mater.: Appl. Res. 9, No. 3, 509–516 (2018).
L. Liang, T. Ma, P. Zhang, J. Jin, and M. Yan, “Coercivity enhancement of NdFeB sintered magnets by low melting point Dy32.5Fe62Cu5.5 alloy modification,” J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 355, 131–135 (2014).
X. Zhang, S. Guo, C. Yan, L. Cai, R. Chen, D. Lee, and A. Yan, “Improvement of the thermal stability of sintered Nd–Fe–B magnets by intergranular addition of Dy82.3Co17.7,” J. Appl. Phys. 115, No. 17, 3–6 (2014).
X. Li, S. Liu, X. Cao, B. Zhou, L. Chen, A. Yan, and G. Yan, “Coercivity and thermal stability improvement in sintered Nd–Fe–B permanent magnets by intergranular addition of Dy–Mn alloy,” J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 407, 247–251 (2016).
B. Zhou, X. Li, X. Liang, G. Yan, K. Chen, and A. Yan, “Improvement of the magnetic property, thermal stability and corrosion resistance of the sintered Nd–Fe–B magnets with Dy80Al20 addition,” J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 429, 257–262 (2017).
K. Hirota, H. Nakamura, T. Minowa, and M. Honshima, “Coercivity enhancement by the grain boundary diffusion process to Nd–Fe–B sintered magnets,” IEEE Trans Magn. 42, No. 10, 2909–2911 (2006).
N. Oono, M. Sagawa, R. Kasada, H. Matsui, and A. Kimura, “Production of thick high-performance sintered neodymium magnets by grain boundary diffusion treatment with dysprosium-nickel-aluminum alloy,” J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, No. 3–4, 297–300 (2011).
A. G. Popov, D. Yu. Vasilenko, T. Z. Puzanova, A. V. Shitov, and A. V. Vlasyuga, “Effect of diffusion annealing on the hysteretic properties of sintered Nd‒Fe–B magnets,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 111, No. 5, 471–478 (2011).
X. J. Cao, L. Chen, S. Guo, X. B. Li, P. P. Yi, A. R. Yan, and G. L. Yan, “Coercivity enhancement of sintered Nd-Fe-B magnets by efficiently diffusing DyF3 based on electrophoretic deposition,” J. Alloys Compd. 631, 315–320 (2015).
K. Löewe, C. Brombacher, M. Katter, and O. Gutfleisch, “Temperature-dependent Dy diffusion processes in Nd–Fe–B permanent magnets,” Acta Mater. 83, 248–255 (2015).
X. Cao, L. Chen, S. Guo, F. Fan, R. Chen, and A. Yan, “Effect of rare earth content on TbF3 diffusion in sintered Nd–Fe–B magnets by electrophoretic deposition,” Scr. Mater. 131, 24–28 (2017).
S. Hu, K. Peng, and H. Chen, “Influence of annealing temperature on the Dy diffusion process in NdFeB magnets,” J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 426, 340–346 (2017).
J. Di, G. Ding, X. Tang, X. Yang, S. Guo, R. Chen, and A. Yan, “Highly efficient Tb-utilization in sintered Nd–Fe–B magnets by Al added TbH2 grain boundary diffusion,” Scr. Mater. 155, 50–53 (2018).
T. H. Kim, T. T. Sasaki, T. Ohkubo, Y. Takada, A. Kato, Y. Kaneko, and K. Hono, “Microstructure and coercivity of grain boundary diffusion processed Dy-free and Dy-containing Nd–Fe–B sintered magnets,” Acta Mater. 172, 139–149 (2019).
S. Kim, D. S. Ko, H. S. Lee, D. Kim, J. W. Roh, and W. Lee, “Enhancing the coercivity of Nd–Fe–B sintered magnets by consecutive heat treatment–induced formation of Tb-diffused microstructures,” J. Alloys Compd. 780, 574–580 (2019).
W. Zhu, Y. Luo, Z. Wang, X. Bai, H. Peng, and D. Yu, “Magnetic properties and microstructures of terbium coated and grain boundary diffusion treated sintered Nd–Fe–B magnets by magnetron sputtering,” J. Rare Earths 39, No. 2, 167–173 (2021).
D. Yu. Vasilenko, A. V. Shitov, D. Yu. Bratushev, K. I. Podkorytov, V. S. Gaviko, O. A. Golovnya, and A. G. Popov, “Magnetic hysteresis properties and microstructure of high-energy (Nd,Dy)–Fe–B magnets with a low oxygen content,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 122, No. 12, 1261–1270 (2021).
H. Sepehri-Amin, T. Ohkubo, T. Shima, and K. Hono, “Grain boundary and interface chemistry of an Nd–Fe–B-based sintered magnet,” Acta Mater. 60, No. 3, 819–830 (2012).
T. T. Sasaki, T. Ohkubo, and K. Hono, “Structure and chemical compositions of the grain boundary phase in Nd–Fe–B sintered magnets,” Acta Mater. 115, 269–277 (2016).
W. Mo, L. Zhang, Q. Liu, A. Shan, J. Wu, and M. Komuro, “Dependence of the crystal structure of the Nd-rich phase on oxygen content in an Nd–Fe–B sintered magnet,” Scr. Mater. 59, No. 2, 179–182 (2008).
T. T. Sasaki, T. Ohkubo, and K. Hono, “Microstructure of Nd–Fe–B sintered magnets-structure of grain boundaries and interface,” Nippon Kinzoku Gakkaishi 81, No. 1, 2–10 (2017).
O. M. Ragg and I. R. Harris, “A study of the effects of heat treatment on the microstructures and magnetic properties of Cu-added NdFeB type sintered magnets,” J. Alloys Compd. 209, Nos. 1–2, 125–133 (1994).
B. E. Davies, R. S. Mottram, and I. R. Harris, “Recent developments in the sintering of NdFeB,” Mater. Chem. Phys. 67, No. 1–3, 272–281 (2001).
B. E. Davies, A. J. Williams, and I. R. Harris, “The use of contact dilatometry to assess the effect to rare-earth content on the sintering characteristics of NdFeB magnets,” Proc. 18th Int. Workshop on High Performance Magnets and their Applications (2004), pp. 103–105.
A. Jayaraman, “Solid-liquid and solid-solid transformations in rare-earth metals at high pressures,” Phys. Rev. A 139, No. 3, A690–A696 (1965).
A. Nakaue, “Studies of the pressure-temperature phase diagram of Nd, Sm, Gd and Dy,” J. Less-Common Met. 60, 47–58 (1978).
Y. Murakami, T. T. Sasaki, T. Ohkubo, and K. Hono, “Strain measurements from Nd2Fe14B grains in sintered magnets using artificial moiré fringes,” Acta Mater. 101, 101–106 (2015).
N. Tsuji, H. Okazaki, W. Ueno, Y. Kotani, D. Billington, A. Yasui, S. Kawaguchi, K. Sugimoto, K. Toyoki, T. Fukagawa, T. Nishiuchi, Y. Gohda, S. Hirosawa, K. Hono, and T. Nakamura, “Temperature dependence of the crystal structures and phase fractions of secondary phases in a Nd–Fe–B sintered magnet,” Acta Mater. 154, 25–32 (2018).
GOST R 52956-2008 Sintered Hard Magnetic Materials Based on Neodymium–Iron–Boron Alloy. Classification. Main Parameters (2009), pp. 1–8.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Magnetic and structural properties were measured using equipment of Collaborative Access Center “Testing Center of Nanotechnology and Advanced Materials” IMP UB RAS.
Funding
Study of magnetic properties was performed in the framework of state assignment of the Ministry of Education and Science of Russia (theme “Magnet,” no. АААА-А18-118020290129-5). O.A. Golovnia is grateful to RSF project no. 21-72-10104 for support of study of microstructure and phase composition of samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Translated by O. Golovnya
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vasilenko, D.Y., Shitov, A.V., Popov, A.G. et al. Magnetic Hysteresis Properties and Microstructure of High-Coercivity (Nd,Dy)–Fe–B Magnets with Dy less than 10 wt % and Low Oxygen. Phys. Metals Metallogr. 123, 145–154 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X22020107
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X22020107