Abstract
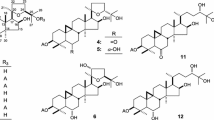
The methanol extract from the leaves of Ilex paraguariensis A. St.-Hil. (Aquifoliaceae), popularly known as mate, maté, or yerba maté, inhibits the intracellular triglyceride accumulation in HepG2 cells and suppresses the plasma triglyceride elevation in olive oil-treated mice. Three new triterpene saponins, termed mateosides I (1), II (2), and III (3), were isolated from the extract along with 29 known compounds. The structures of 1–3 were elucidated based on chemical and spectroscopic evidence. Among the isolates, principal saponin constituents, 2 and matesaponins 1 (7) and 2 (9), potently inhibited the triglyceride accumulation in HepG2 cells simultaneously treated with oleic acid and high glucose. In vivo assay of the methanol extract of I. paraguariensis revealed that 7 and 9 showed anti-hyperlipidemic activities in olive oil-treated mice. These results suggested that the saponin constituents of I. paraguariensis could be valuable bioactive marker for the anti-obesogenic activity.
Graphical abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
References
The Plant List. http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-2861242. Accessed 18 Dec 2021.
Gruenwald J, Brendler T, Jaenicke C (2007) PDR for herbal medicines, 4th edn. Thomson Healthcare Inc., Montvale, pp 572–573
Heck CI, de Mejia EG (2007) Yerba mate tea (Ilex paraguariensis): a comprehensive review on chemistry, health implications, and technological considerations. J Food Sci 72:R138–R151
Bracesco N, Sanchez AG, Contreras V, Menini T, Gugliucci A (2011) Recent advances on Ilex paraguariensis research: minireview. J Ethnopharmacol 136:378–384
Gambero A, Ribeiro ML (2015) The positive effects of yerba maté (Ilex paraguariensis) in obesity. Nutrients 7:730–750
Cardozo Junior EL, Morand C (2016) Interest of mate (Ilex paraguariensis A. St.-Hil.) as a new natural functional food to preserve human cardiovascular health—a review. J Funct Foods 21:440–454
Gan R-Y, Zhang D, Wang M, Corke H (2018) Health benefits of bioactive compounds from the genus Ilex, a source of traditional caffeinated beverages. Nutrients 10:1682
Sugimoto S, Nakamura S, Yamamoto S, Yamashita C, Oda Y, Matsuda H, Yoshikawa M (2009) Brazilian natural medicines. III. Structures of triterpene oligoglycosides and lipase inhibitors from mate, leaves of Ilex paraguariensis. Chem Pharm Bull 57:257–261
Hussein GME, Matsuda H, Nakamura S, Hamao M, Akiyama T, Tamura K, Yoshikawa M (2011) Mate tea (Ilex paraguariensis) promotes satiety and body weight lowering in mice: involvement of glucagon-like peptide-1. Biol Pharm Bull 34:1849–1855
Hussein GME, Matsuda H, Nakamura S, Akiyama T, Tamura K, Yoshikawa M (2011) Protective and ameliorative effects of maté (Ilex paraguariensis) on metabolic syndrome in TSOD mice. Phytomedicine 19:88–97
Zapata FJ, Rebollo-Hernanz M, Novakofski JE, Nakamura MT, de Mejia EG (2020) Caffeine, but not other phytochemicals, in mate tea (Ilex paraguariensis St. Hilaire) attenuates high-fat-high-sucrose-diet-driven lipogenesis and body fat accumulation. J Funct Foods 64:103646
Rocha DS, Model JFA, Von Dentz M, Maschio J, Ohlweiler R, Lima MV, de Souza SK, Sarapio E, Vogt ÉL, Waszczuk M, Martiny S, Bassani VL, Kucharski LC (2021) Adipose tissue of female Wistar rats respond to Ilex paraguariensis treatment after ovariectomy surgery. J Tradit Complement Med 11:238–248
Gebara KS, Gasparotto Junior A, Palozi RAC, Morand C, Bonetti CI, Gozzi PT, de Mello MRF, Costa TA, Cardozo Junior EL (2021) A randomized crossover intervention study on the effect a standardized maté extract (Ilex paraguariensis A. St.-Hil.) in men predisposed to cardiovascular risk. Nutrients 13:14
Medeiros MS, Schumacher-Schuh AF, Altmann V, de Mello Rieder CR (2021) A case-control study of the effects of Chimarrão (Ilex paraguariensis) and coffee on Parkinson’s disease. Front Neurol 12:619535
Lorini A, Damin FM, de Oliveira DN, Crizel RL, Godoy HT, Galli V, Meinhart AD (2021) Characterization and quantification of bioactive compounds from Ilex peraguariensis residue by HPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS from plants cultivated under different cultivation systems. J Food Sci 86:1599–1619
Muraoka O, Morikawa T, Zhang Y, Ninomiya K, Nakamura S, Matsuda H, Yoshikawa M (2009) Novel megastigmanes with lipid accumulation inhibitory and lipid metabolism-promoting activities in HepG2 cells from Sedum sarmentosum. Tetrahedron 65:4142–4148
Morikawa T, Ninomiya K, Zhang Y, Yamada T, Nakamura S, Matsuda H, Muraoka O, Hayakawa T, Yoshikawa M (2012) Flavonol glycosides with lipid accumulation inhibitory activity from Sedum sarmentosum. Phytochem Lett 5:53–58
Morikawa T, Ninomiya K, Miyake S, Miki Y, Okamoto M, Yoshikawa M, Muraoka O (2013) Flavonol glycosides with lipid accumulation inhibitory activity and simultaneous quantitative analysis of 15 polyphenols and caffeine in the flower buds of Camellia sinensis from different regions by LCMS. Food Chem 140:353–360
Morikawa T, Nagatomo A, Oka T, Miki Y, Taira N, Shibano-Kitahara M, Hori Y, Muraoka O, Ninomiya K (2019) Glucose tolerance-improving activity of helichrysoside in mice and its structural requirements for promoting glucose and lipid metabolism. Int J Mol Sci 20:6322
Shimoda H, Ninomiya K, Nishida N, Yoshino T, Morikawa T, Matsuda H, Yoshikawa M (2003) Anti-hyperlipidemic sesquiterpenes and new sesquiterpene glycosides from the leaves of artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.): structure requirement and mode of action. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13:223–228
Yoshikawa M, Morikawa T, Yamamoto K, Kato Y, Nagatomo A, Matsuda H (2005) Floratheasaponins A-C, acylated oleanane-type triterpene oligoglycosides with anti-hyperlipidemic activities from flowers of the tea plant (Camellia sinensis). J Nat Prod 68:1360–1365
Matsuda H, Nakamura S, Morikawa T, Muraoka O, Yoshikawa M (2016) New biofunctional effects of the flower buds of Camellia sinensis and its bioactive acylated oleanane-type triterpene oligoglycosides. J Nat Med 70:689–701
Morikawa T, Li X, Nishida E, Ito Y, Matsuda H, Nakamura S, Muraoka O, Yoshikawa M (2008) Perennisosides I-VII, acylated triterpene saponins with antihyperlipidemic activities from the flowers of Bellis perennis. J Nat Prod 71:828–835
Morikawa T, Muraoka O, Yoshikawa M (2010) Pharmaceutical food science: search for anti-obese constituents from medicinal foods—anti-hyperlipidemic saponin constituents from the flowers of Bellis perennis. Yakugaku Zasshi 130:673–678
Asao Y, Morikawa T, Xie Y, Okamoto M, Hamao M, Matsuda H, Muraoka O, Yuan D, Yoshikawa M (2009) Structures of acetylated oleanane-type triterpene saponins, rarasaponins IV, V, and VI, and anti-hyperlipidemic constituents from the pericarps of Sapindus rarak. Chem Pharm Bull 57:198–203
Morikawa T, Chaipech S, Matsuda H, Hamao M, Umeda Y, Sato H, Tamura H, Ninomiya K, Yoshikawa M, Pongpiriyadacha Y, Hayakawa T, Muraoka O (2012) Anti-hyperlipidemic constituents from the bark of Shorea roxburghii. J Nat Med 66:516–524
Melek FR, Miyase T, El-Gindy MR, Abdel-Khalik SM, Ghaly NS, El-Kady M (2000) Saponins from Fagonia glutinosa. Pharmazie 55:772–776
Taketa ATC, Breitmaier E, Schenkel EP (2004) Triterpenes and triterpenoidal glycosides from the fruits of Ilex paraguariensis (Maté). J Braz Chem Soc 15:205–211
Nakanishi T, Tanaka K, Murata H, Somekawa M, Inada A (1993) Phytochemical studies of seeds of medicinal plants. III. Ursolic acid and oleanolic acid glycosides from seeds of Patrinia scabiosaefolia Fischer. Chem Pharm Bull 41:183–186
Gosmann G, Schenkel EP (1989) A new saponin from mate, Ilex paraguariensis. J Nat Prod 52:1367–1370
De Andrade FDP, Piacente S, Pizza C, Vilegas W (2002) Studies on the constituents of a Brazilian folk infusion. Isolation and structure elucidation of new triterpene saponins from Ilex amara leaves. J Agric Food Chem 50:255–261
Gosmann G, Guillaume D (1995) Triterpenoid saponins from Ilex paraguariensis. J Nat Prod 58:438–441
Kraemer KH, Taketa ATC, Schenkel EP, Gosmann G, Guillaume D (1996) Matesaponin 5, a highly polar saponin from Ilex paraguariensis. Phytochemistry 42:1119–1122
Nishimura K, Miyase T, Noguchi H (1999) Triterpenoid saponins from Ilex kudincha. J Nat Prod 62:1128–1133
Ouyang M-A, Yang C-R, Chen Z-L, Wang H-Q (1996) Tritepenes and triterpenoid glycosides from the leaves of Ilex kudincha. Phytochemistry 41:871–877
Ouyang M-A, Yang C-R, Wu Z-J (2001) Triterpenoid saponins from the leaves of Ilex kudincha. JANPR 3:31–42
Shimizu S, Ishihara N, Umehara K, Miyase T, Ueno A (1988) Sesquiterpene glycosides and saponins from Cynara cardunculus L. Chem Pharm Bull 36:2466–2474
Kinjo J, Uemura H, Nakamura M, Nohara T (1994) Two new triterpenoidal glycosides from Medicago polymorpha L. Chem Pharm Bull 42:1339–1341
Hata C, Kakuno M, Yoshikawa K, Arihara S (1992) Triterpenoid saponins of Aquifoliaceous plants. V. Ilexosides XV–XIX from the barks of Ilex crenata Thunb. Chem Pharm Bull 40:1990–1992
Ouyang M-A, Wang H-Q, Liu Y-Q, Yang C-R (1997) Triterpenoid saponins from the leaves of Ilex latifolia. Phytochemistry 45:1501–1505
Song N, Xu W, Guan H, Liu X, Wang Y, Nie X (2007) Several flavonoids from Capsella bursa-pastoris (L.) Medic. Asian J Tradit Med 2:218–222
These isolates were identified by comparison of their physical and spectral data with those of commercially available samples
Zhang Y, Nakamura S, Pongpiriyadacha Y, Matsuda H, Yoshikawa M (2008) Absolute structures of new megastigmane glycosides, foliasalaciosides E1, E2, E3, F, G, H, and I from the leaves of Salacia chinensis. Chem Pharm Bull 56:547–553
Nakatani N, Kayano S, Kikuzaki H, Sumino K, Katagiri K, Mitani T (2000) Identification, quantitative determination, and antioxidative activities of chlorogenic acid isomers in Prune (Prunus domestica L.). J Agric Food Chem 48:5512–5516
Grassi-Zampieron R, França LV, Carollo CA, do Carmo Vieira M, Oliveros-Bastidas A, de Siqueira JM (2010) Comparative profiles of Achyrocline alata (Kunth) DC. and A. satureioides (Lam.) DC., Asteraceae, applying HPLC-DAD-MS. Braz J Pharmacogn 20:575–579
Lee EJ, Kim JS, Kim HP, Lee J-H, Kang SS (2010) Phenolic constituents from the flower buds of Lonicera japonica and their 5-lipoxygenase inhibitory activities. Food Chem 120:134–139
Gao H, Huang Y-N, Gao B, Xu P-Y, Inagaki C, Kawabata J (2008) α-Glucosidase inhibitory effect by the flower buds of Tussilago farfara L. Food Chem 106:1195–1201
Kim JY, Cho J-Y, Ma Y-K, Park KY, Lee S-H, Ham K-S, Lee HJ, Park K-H, Moon J-H (2011) Dicaffeoylquinic acid derivatives and flavonoid glucosides from glasswort (Salicornia herbacea L.) and their antioxidative activity. Food Chem 125:55–62
Morikawa T, Imura K, Akagi Y, Muraoka O, Ninomiya K (2018) Ellagic acid glycosides with hepatoprotective activity from traditional Tibetan medicine Potentilla anserina. J Nat Med 72:317–325
Morikawa T, Nakanishi Y, Inoue N, Manse Y, Matsuura H, Hamasaki S, Yoshikawa M, Muraoka O, Ninomiya K (2020) Acylated iridoid glycosides with hyaluronidase inhibitory activity from the rhizomes of Picrorhiza kurroa Royle ex Benth. Phytochemistry 169:112185
Morikawa T, Inoue N, Nakanishi Y, Manse Y, Matsuura H, Okino K, Hamasaki S, Yoshikawa M, Muraoka O, Ninomiya K (2020) Collagen synthesis-promoting and collagenase inhibitory activities of constituents isolated from the rhizomes of Picrorhiza kurroa Royle ex Benth. Fitoterapia 143:104584
Hidaka K, Ito M, Matsuda Y, Kohda H, Yamasaki K, Yamahara J, Chisaka T, Kawakami Y, Sato T, Kagei K (1987) New triterpene saponins from Ilex pubescens. Chem Pharm Bull 35:524–529
Kakuno T, Yoshikawa K, Arihara S (1992) Triterpenoid saponins from Ilex crenata fruit. Phytochemistry 31:3553–3557
Cheng J-J, Zhang L-J, Cheng H-L, Chiou C-T, Lee I-J, Kuo Y-H (2010) Cytotoxic hexacyclic triterpene acids from Euscaphis japonica. J Nat Prod 73:1655–1658
Morikawa T, Ninomiya K, Imura K, Yamaguchi T, Akagi Y, Yoshikawa M, Hayakawa T, Muraoka O (2014) Hepetoprotective triterpenes from traditional Tibetan medicine Potentilla anserina. Phytochemistry 102:169–181
El-Hassan AY, Ibrahim EM, Al-Mulhim FA, Nabhan AA, Chammas MY (1992) Fatty infiltration of the liver: analysis of prevalence, radiological and clinical features and influence on patient management. Br J Radiol 65:774–778
Bellentani S, Tiribelli C, Saccoccio G, Sodde M, Fratti N, de Martin C, Cristianini G (1994) Prevalence of chronic liver disease in the general population of northern Italy: the dionysos study. Hepatology 20:1442–1449
Marchesini G, Brizi M, Morselli-Labate AM, Bianchi G, Bugianesi E, McCullough AJ, Forlani G, Melchionda N (1999) Association of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with insulin resistance. Am J Med 107:450–455
Marceau P, Biron S, Hould F-S, Marceau S, Simard S, Thung SN, Kral JG (1999) Liver pathology and the metabolic syndrome X in severe obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84:1513–1517
Auwerx J, Schoonjans K, Fruchart J-C, Staels B (1996) Regulation of triglyceride metabolism by PPARs: fibrates and thiazolidinediones have distinct effects. J Atheroscler Thromb 3:81–89
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully thank the Division of Joint Research Center, Kindai University, for the NMR and MS measurements. We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.com) for English language editing.
Funding
This work was supported by the JSPS KAKENHI, Japan [Grant Numbers 18K06726 (T.M.) and 18K06739 (K.N.)].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagatomo, A., Inoue, N., Konno, T. et al. Ursane-type triterpene oligoglycosides with anti-hepatosteatosis and anti-hyperlipidemic activity from the leaves of Ilex paraguariensis A. St.-Hil.. J Nat Med 76, 654–669 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-022-01614-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-022-01614-5