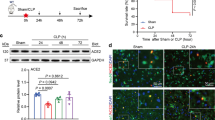
Abstract
Cognitive dysfunction caused by sepsis-associated encephalopathy (SAE) is still poorly understood. It is reported that vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) exerts its anti-inflammatory effects in multiple diseases, while its biological function in SAE remains unclear. We aimed to figure out whether VIP has influence on sepsis-induced neuroinflammation and cognitive dysfunction. To induce sepsis, rats were subjected to cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) operation. Morris water maze test and fear conditioning test were conducted to reveal cognitive dysfunctions. TUNEL assay was performed to evaluate apoptosis. We found out that the expression of VIP was downregulated in the hippocampus of septic rats. VIP was verified to attenuate sepsis-induced memory impairment following CLP. Additionally, we examined apoptosis and inflammation in rats’ hippocampus. It is worth noting that VIP inhibited the apoptosis in the hippocampus and reduced the productions of proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β. Furthermore, our data confirmed that VIP was involved in regulating the TLR-4/NF-κB signaling. In conclusion, VIP inhibited neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment in hippocampus of septic rats through the TLR-4/NF-κB signaling pathway.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Andonegui G et al (2018) Targeting inflammatory monocytes in sepsis-associated encephalopathy and long-term cognitive impairment JCI. Insight 3:e99364. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.99364
Barichello T et al (2019) Long-term cognitive outcomes after sepsis: a translational systematic review. Mol Neurobiol 56:186–251. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1048-2
Barrientos RM, Kitt MM, Watkins LR, Maier SF (2015) Neuroinflammation in the normal aging hippocampus. Neuroscience 309:84–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.03.007
Becker K, Jährling N, Saghafi S, Dodt H-U (2013) Dehydration and clearing of whole mouse brains and dissected hippocampi for ultramicroscopy. Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2013:683–684. https://doi.org/10.1101/pdb.prot075820
Belcheva I, Ivanova M, Tashev R, Belcheva S (2009) Differential involvement of hippocampal vasoactive intestinal peptide in nociception of rats with a model of depression. Peptides 30:1497–1501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2009.05.015
Cecconi M, Evans L, Levy M, Rhodes A (2018) Sepsis and septic shock. Lancet (london, England) 392:75–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(18)30696-2
Chaudhury D, Loh DH, Dragich JM, Hagopian A, Colwell CS (2008) Select cognitive deficits in vasoactive intestinal peptide deficient mice. BMC Neurosci 9:63. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2202-9-63
Chen Y et al (2017) 2-Cl-MGV-1 ameliorates apoptosis in the thalamus and hippocampus and cognitive deficits after cortical infarct in rats. Stroke 48:3366–3374. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.117.019439
Chen S et al (2020) Maf1 ameliorates sepsis-associated encephalopathy by suppressing the NF-kB/NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway. Front Immunol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.594071
Cunha-Reis D, Caulino-Rocha A, Correia-de-Sá P (2021) Vipergic Neuroprotection in Epileptogenesis: Challenges and Opportunities Pharmacological Research 164:105356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105356
Danielski LG et al (2020) NLRP3 activation contributes to acute brain damage leading to memory impairment in sepsis-surviving rats. Mol Neurobiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-020-02089-9
de Souza FRO, Ribeiro FM, Lima PMD (2021) Implications of VIP and PACAP in Parkinson’s disease: what do we know so far? Curr Med Chem 28:1703–1715. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867327666200320162436
Delgado M, Ganea D (2003) Vasoactive intestinal peptide prevents activated microglia-induced neurodegeneration under inflammatory conditions: potential therapeutic role in brain trauma FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for. Exp Biol 17:1922–1924. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.02-1029fje
Gilbert JA (2018) Sepsis care bundles: a work in progress The Lancet. Respir Med 6:821–823. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2213-2600(18)30362-x
Gonzalez-Rey E, Anderson P, Delgado M (2007) Emerging roles of vasoactive intestinal peptide: a new approach for autoimmune therapy. Annals Rheumatic Dis. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2007.078519
Gotts JE, Matthay MA (2016) Sepsis: pathophysiology and clinical management. BMJ (clinical Research Ed). https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.i1585
Goursaud S et al (2015) The anti-inflammatory peptide stearyl-norleucine-VIP delays disease onset and extends survival in a rat model of inherited amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Exp Neurol 263:91–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2014.09.022
Haberham ZL, van den Brom WE, Venker-van Haagen AJ, Baumans V, de Groot HN, Hellebrekers LJ (1999) EEG evaluation of reflex testing as assessment of depth of pentobarbital anaesthesia in the rat. Lab Anim 33:47–57. https://doi.org/10.1258/002367799780578570
Helbing D-L, Böhm L, Witte OW (2018) Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy CMAJ 190:E1083–E1083. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.180454
Hosokawa K, Gaspard N, Su F, Oddo M, Vincent JL, Taccone FS (2014) Clinical neurophysiological assessment of sepsis-associated brain dysfunction: a systematic review. Critical Care (london, England) 18:674. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-014-0674-y
Huang CT, Lue JH, Cheng TH, Tsai YJ (2020) Glycemic control with insulin attenuates sepsis-associated encephalopathy by inhibiting glial activation via the suppression of the nuclear factor kappa B and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways in septic rats. Brain Res 1738:146822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2020.146822
Ivanova M, Belcheva S, Belcheva I, Stoyanov Z, Tashev R (2014) Modulatory effect of VIP injected into hippocampal CA1 area on anxiety in olfactory bulbectomized rats. Acta Neurobiol Exp 74:317–327
Jönsson M, Norrgård O, Hansson M, Forsgren S (2007) Decrease in binding for the neuropeptide VIP in response to marked inflammation of the mucosa in ulcerative colitis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1107:280–289. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1381.030
Kim E et al (2017) Dexmedetomidine confers neuroprotection against transient global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats by inhibiting inflammation through inactivation of the TLR-4/NF-κB pathway. Neurosci Lett 649:20–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2017.04.011
Knierim JJ (2015) The Hippocampus Curr Biol 25:R1116–R1121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2015.10.049
Korkmaz OT, Ay H, Aytan N, Carreras I, Kowall NW, Dedeoglu A, Tuncel N (2019) Vasoactive intestinal peptide decreases β-amyloid accumulation and prevents brain atrophy in the 5xFAD mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Mol Neurosci 68:389–396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-018-1226-8
Kuncová J et al (2011) Tissue concentrations of vasoactive intestinal peptide are affected by peritonitis-induced sepsis and hemofiltration in pigs. Physiolog Res 60:531–540. https://doi.org/10.33549/physiolres.932051
Li Z, Trakooljul N, Hadlich F, Ponsuksili S, Wimmers K, Murani E (2021) Transcriptome analysis of porcine PBMCs reveals lipopolysaccharide-induced immunomodulatory responses and crosstalk of immune and glucocorticoid receptor signaling. Virulence 12:1808–1824
Liang Y, Chen S, Yang Y, Lan C, Zhang G, Ji Z, Lin H (2018) Vasoactive intestinal peptide alleviates osteoarthritis effectively via inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway. J Biomed Sci 25:25. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-018-0410-z
Liu T et al (2019) Astragalus polysaccharide from Astragalus Melittin ameliorates inflammation via suppressing the activation of TLR-4/NF-κB p65 signal pathway and protects mice from CVB3-induced virus myocarditis International. J Biol Macromol 126:179–186
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)). Method (san Diego, Calif) 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Luo L, Wu J, Qiao L, Lu G, Li J, Li D (2020) Sestrin 2 attenuates sepsis-associated encephalopathy through the promotion of autophagy in hippocampal neurons. J Cell Mol Med 24:6634–6643. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.15313
Martinez C et al (2002) Anti-inflammatory role in septic shock of pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:1053–1058. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.012367999
Mazeraud A, Bozza FA, Sharshar T (2018) Sepsis-associated Encephalopathy Is Septic. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 197:698–699. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201712-2593ED
Molnár L, Fülesdi B, Németh N, Molnár C (2018) Sepsis-associated encephalopathy: A review of literature. Neurol India 66:352–361. https://doi.org/10.4103/0028-3886.227299
Nayak R (2020) Bright Hippocampi: Diffusion MR imaging of hypoglycemic encephalopathy. J Assoc Physicians India 68:76–76
Piva S, McCreadie VA, Latronico N (2015) Neuroinflammation in sepsis: sepsis associated delirium. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets 15:10–18. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871529x15666150108112452
Prescott HC, Angus DC (2018) Enhancing Recovery from Sepsis: A Review Jama 319:62–75. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2017.17687
Qiu JF, Zhang ZQ, Chen W, Wu ZY (2007) [Protective effects of vasoactive intestinal peptide on septic shock rats] Zhonghua wai ke za zhi [Chinese journal of surgery] 45:196–199
Robba C, Crippa IA, Taccone FS (2018) Septic Encephalopathy. Curr Neurol Neurosci Reports 18:82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-018-0895-6
Rostène WH (1984) Neurobiological and neuroendocrine functions of the vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP). Progress Neurobiol 22:103–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/0301-0082(84)90022-4
Samuvel DJ, Shunmugavel A, Singh AK, Singh I, Khan M (2016) S-Nitrosoglutathione ameliorates acute renal dysfunction in a rat model of lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis. J Pharm Pharmacol 68:1310–1319. https://doi.org/10.1111/jphp.12608
Schaeffler A et al (2009) Fatty acid-induced induction of Toll-like receptor-4/nuclear factor-kappaB pathway in adipocytes links nutritional signalling with innate immunity. Immunology 126:233–245. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.02892.x
Shen J, Xu L, Qu C, Sun H, Zhang J (2018) Resveratrol prevents cognitive deficits induced by chronic unpredictable mild stress: Sirt1/miR-134 signalling pathway regulates CREB/BDNF expression in hippocampus in vivo and in vitro. Behav Brain Res 349:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2018.04.050
Song Q, Fan C, Wang P, Li Y, Yang M, Yu SY (2018) Hippocampal CA1 βCaMKII mediates neuroinflammatory responses via COX-2/PGE2 signaling pathways in depression. J Neuroinflammation 15:338. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-018-1377-0
Sun GY et al (2018) Vasoactive intestinal peptide overexpression mediated by lentivirus attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice by inhibiting inflammation. Mol Immunol 97:8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2018.03.002
Takashima A, Maeda Y, Itoh S (1993) Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) causes memory impairment in passive avoidance responding of the rat. Peptides 14:1067–1071. https://doi.org/10.1016/0196-9781(93)90088-x
Tunçel N, Töre F, Sahintürk V, Ak D, Tunçel M (2000) Vasoactive intestinal peptide inhibits degranulation and changes granular content of mast cells: a potential therapeutic strategy in controlling septic shock. Peptides 21:81–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0196-9781(99)00177-1
Tunçel N, Korkmaz OT, Tekin N, Şener E, Akyüz F, Inal M (2012) Antioxidant and anti-apoptotic activity of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) against 6-hydroxy dopamine toxicity in the rat corpus striatum. J Mol Neurosci 46:51–57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-011-9618-z
Tyrtyshnaia AA, Lysenko LV, Madamba F, Manzhulo IV, Khotimchenko MY, Kleschevnikov AM (2016) Acute neuroinflammation provokes intracellular acidification in mouse hippocampus. J Neuroinflammation 13:283. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-016-0747-8
Wang YM et al (2019) Paclitaxel alleviated sepsis-induced acute lung injury by activating MUC1 and suppressing TLR-4/NF-κB pathway. DDDT 13:3391–3404. https://doi.org/10.2147/dddt.S222296
Xia DY, Zhang HS, Wu LY, Zhang XS, Zhou ML, Hang CH (2017) Pentoxifylline Alleviates Early Brain Injury After Experimental Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Rats: Possibly via Inhibiting TLR 4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Neurochem Res 42:963–974. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-2129-0
Xu CL, Guo Y, Qiao L, Ma L, Cheng YY (2018) Recombinant expressed vasoactive intestinal peptide analogue ameliorates TNBS-induced colitis in rats. World J Gastroenterol 24:706–715. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i6.706
Yamaga S, Shime N, Sonneville R, de Montmollin E, Timsit JF (2017) Risk factors for sepsis-associated encephalopathy. Intensive Care Med 43:1548–1549. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-017-4875-0
Yelkenli İH, Ulupinar E, Korkmaz OT, Şener E, Kuş G, Filiz Z, Tunçel N (2016) Modulation of corpus striatal neurochemistry by astrocytes and Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide (VIP) in Parkinsonian rats. J Mol Neurosci 59:280–289. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-016-0757-0
Yu Y et al (2020) Hydrogen gas alleviates blood-brain barrier impairment and cognitive dysfunction of septic mice in an Nrf2-dependent pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106585
Zhang Y et al (2018) Shikonin inhibits myeloid differentiation protein 2 to prevent LPS-induced acute lung injury. British J Pharmacol 175:840–854. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.14129
Zhang J, Kong X, Shi Q, Zhao B (2019) MicroRNA-383–5p acts as a potential prognostic biomarker and an inhibitor of tumor cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in breast cancer. Cancer Biomark. https://doi.org/10.3233/CBM-190704
Zhao CC et al (2019) Lnc SMAD5-AS1 as ceRNA inhibit proliferation of diffuse large B cell lymphoma via Wnt/β-catenin pathway by sponging miR-135b-5p to elevate expression of APC. Cell Death Dis 10:252. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1479-3
Zhou Y et al (2020) Vasoactive intestinal peptide suppresses the NLRP3 inflammasome activation in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury mice and macrophages. Biomed Pharmacotherapy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109596
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The study was supported by the Bureau of Science & Technology and Intellectual Property Nanchong City (No. 19SXHZ0091), and the Scientific research project of Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College (No. ZX-2021–056).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that there are no conflicts of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Yun, D., Dong, B. et al. VIP alleviates sepsis-induced cognitive dysfunction as the TLR-4/NF-κB signaling pathway is inhibited in the hippocampus of rats. J Mol Histol 53, 369–377 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-022-10068-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-022-10068-8