Abstract
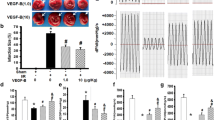
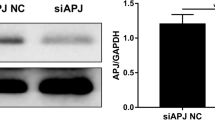
In this work, we investigated the in vitro and in vivo functions of bisphosphonate of zoledronate (Zd) in hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R) injured human embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (hES-CMs). In the in vitro setting, the effects of Zd on hES-CM survival and differentiation were examined. We found that low and medium concentrations (<2 µm) of Zd did not induce cell death of hES-CMs. 0.5 µm Zd protected H/R-induced hES-CM apoptosis but did not affect key differentiation proteins, including hcTnl, PECM-1 Cnx43 and Pan-Cadherin. In addition, Zd-induced TrkA/B phosphorylation and promoted VEGF to counter the apoptotic effect of H/R injury. In the in vivo animal model of myocardial infarction, Zd treatment promoted the survival of hES-CMs by inducing PECAM1 and hcTnl. Thus, we concluded that Zd protected H/R-induced hES-CM apoptosis in vitro and promoted hES-CM survival in vivo. These data may facilitate the development of human embryonic stem cells into clinical applications for patients with ischemic heart disease.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Original data were available upon request.
References
Heusch, G., Libby, P., Gersh, B., Yellon, D., Bohm, M., Lopaschuk, G., & Opie, L. (2014). Cardiovascular remodelling in coronary artery disease and heart failure. Lancet, 383(9932), 1933–1943.
Lippi, G., Franchini, M. & & Cervellin, G. (2013). Diagnosis and management of ischemic heart disease. Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis, 39(2), 202–213.
Boateng, S., & Sanborn, T. (2013). Acute myocardial infarction. Disease-A-Month, 59(3), 83–96.
Welch, T. D., Yang, E. H., Reeder, G. S. & & Gersh, B. J. (2012). Modern management of acute myocardial infarction. Current Problems in Cardiology, 37(7), 237–310.
Minicucci, M. F., Azevedo, P. S., Polegato, B. F., Paiva, S. A., & Zornoff, L. A. (2011). Heart failure after myocardial infarction: clinical implications and treatment. Clinical Cardiology, 34(7), 410–414.
Widgerow, A. D. (2014). Ischemia-reperfusion injury: influencing the microcirculatory and cellular environment. Annals of Plastic Surgery, 72(2), 253–260.
Hausenloy, D. J., & Yellon, D. M. (2013). Myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: a neglected therapeutic target. Journal of Clin Investigation, 123(1), 92–100.
Kennedy-Lydon, T., & Rosenthal, N. (2015). Cardiac regeneration: epicardial mediated repair. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 282(1821), 20152147.
Mehta, A., & Shim, W. (2013). Cardiac stem cell therapy: stemness or commitment? Cell Transplantation, 22(1), 1–14.
Young, P. P., & Schafer, R. (2015). Cell-based therapies for cardiac disease: a cellular therapist’s perspective. Transfusion, 55(2), 441–451. quiz 440.
Beqqali, A., van Eldik, W., Mummery, C. & & Passier, R. (2009). Human stem cells as a model for cardiac differentiation and disease. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 66(5), 800–813.
Nir, S. G., David, R., Zaruba, M., Franz, W. M., & Itskovitz-Eldor, J. (2003). Human embryonic stem cells for cardiovascular repair. Cardiovascular Research, 58(2), 313–323.
Acimovic, I., Vilotic, A., Pesl, M., Lacampagne, A., Dvorak, P., Rotrekl, V., & Meli, A. C. (2014). Human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes as research and therapeutic tools. Biomedical Research International, 2014, 512831.
Laflamme, M. A., Chen, K. Y., Naumova, A. V., Muskheli, V., Fugate, J. A., Dupras, S. K., Reinecke, H., Xu, C., Hassanipour, M., & Police, S., et al. (2007). Cardiomyocytes derived from human embryonic stem cells in pro-survival factors enhance function of infarcted rat hearts. Nature Biotechnology, 25(9), 1015–1024.
Terrovitis, J. V., Smith, R. R., & Marban, E. (2010). Assessment and optimization of cell engraftment after transplantation into the heart. Circulation Research, 106(3), 479–494.
Caspi, O., Huber, I., Kehat, I., Habib, M., Arbel, G., Gepstein, A., Yankelson, L., Aronson, D., Beyar, R., & Gepstein, L. (2007). Transplantation of human embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes improves myocardial performance in infarcted rat hearts. Journal of American College of Cardiology, 50(19), 1884–1893.
Henning, R. J. (2011). Stem cells in cardiac repair. Future Cardiology, 7(1), 99–117.
Bock, O., & Felsenberg, D. (2008). Bisphosphonates in the management of postmenopausal osteoporosis–optimizing efficacy in clinical practice. Clinical Interventions in Aging, 3(2), 279–297.
Coleman, R. E. (2004). Bisphosphonates: clinical experience. Oncologist, 9(Suppl 4), 14–27.
Hughes, D. E., Wright, K. R., Uy, H. L., Sasaki, A., Yoneda, T., Roodman, G. D., Mundy, G. R., & Boyce, B. F. (1995). Bisphosphonates promote apoptosis in murine osteoclasts in vitro and in vivo. Journal of Bone Mineral Research, 10(10), 1478–1487.
Fleisch, H. (1989). Bisphosphonates: a new class of drugs in diseases of bone and calcium metabolism. Recent Results in Cancer Research, 116, 1–28.
Watts, N. B. & & Diab, D. L. (2010). Long-term use of bisphosphonates in osteoporosis. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 95(4), 1555–1565.
Tsai, S. H., Huang, P. H., Chang, W. C., Tsai, H. Y., Lin, C. P., Leu, H. B., Wu, T. C., Chen, J. W., & Lin, S. J. (2012). Zoledronate inhibits ischemia-induced neovascularization by impairing the mobilization and function of endothelial progenitor cells. PLoS One, 7(7), e41065.
Seist, R., Tong, M., Landegger, L. D., Vasilijic, S., Hyakusoku, H., Katsumi, S., McKenna, C. E., Edge, A. S. B., & Stankovic, K. M. (2020). Regeneration of cochlear synapses by systemic administration of a bisphosphonate. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience, 13, 87.
Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. edn. Washington (DC); 1996.
Zhu, W. Z., Van Biber, B., & Laflamme, M. A. (2011). Methods for the derivation and use of cardiomyocytes from human pluripotent stem cells. Methods in Molecular Biology, 767, 419–431.
Hsieh, A., Feric, N. T., & Radisic, M. (2015). Combined hypoxia and sodium nitrite pretreatment for cardiomyocyte protection in vitro. Biotechnology Progess, 31(2), 482–492.
Luo, J., Weaver, M. S., Cao, B., Dennis, J. E., Van Biber, B., Laflamme, M. A., & Allen, M. D. (2014). Cobalt protoporphyrin pretreatment protects human embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes from hypoxia/reoxygenation injury in vitro and increases graft size and vascularization in vivo. Stem Cells Translational Medicine, 3(6), 734–744.
Wang, H. C., Zhang, H. F., Guo, W. Y., Su, H., Zhang, K. R., Li, Q. X., Yan, W., Ma, X. L., Lopez, B. L., & Christopher, T. A., et al. (2006). Hypoxic postconditioning enhances the survival and inhibits apoptosis of cardiomyocytes following reoxygenation: role of peroxynitrite formation. Apoptosis, 11(8), 1453–1460.
Cai, J., Yi, F. F., Yang, X. C., Lin, G. S., Jiang, H., Wang, T., & Xia, Z. (2007). Transplantation of embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes improves cardiac function in infarcted rat hearts. Cytotherapy, 9(3), 283–291.
Huwer, H., Winning, J., Vollmar, B., Welter, C., Lohbach, C., Menger, M. D., & Schafers, H. J. (2003). Long-term cell survival and hemodynamic improvements after neonatal cardiomyocyte and satellite cell transplantation into healed myocardial cryoinfarcted lesions in rats. Cell Transplantation, 12(7), 757–767.
Fazmin, IT, Huang, CL, Jeevaratnam, K. Bisphosphonates and atrial fibrillation: revisiting the controversy. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 2020.
Loke, Y. K., Jeevanantham, V., & Singh, S. (2009). Bisphosphonates and atrial fibrillation: systematic review and meta-analysis. Drug Safety, 32(3), 219–228.
Arslan, C., Aksoy, S., Dizdar, O., Dede, D. S., Harputluoglu, H., & Altundag, K. (2011). Zoledronic acid and atrial fibrillation in cancer patients. Support Care Cancer, 19(3), 425–430.
Ilgezdi, Z. D., Aktas, I., Dogan Metin, F., Kepez, A., Unlu Ozkan, F., Silte, A. D., Yilmaz Kaysin, M., Kivrak, T., Cincin, A., & Erdogan, O. (2015). Acute effect of zoledronic acid infusion on atrial fibrillation development in patients with osteoporosis. The Anatolian Journal of Cardiology, 15(4), 320–324.
Wang, Z., Wang, S. P., Shao, Q., Li, P. F., Sun, Y., Luo, L. Z., Yan, X. Q., Fan, Z. Y., Hu, J. & & Zhao, J. et al. (2019). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor mimetic, 7,8-dihydroxyflavone, protects against myocardial ischemia by rebalancing optic atrophy 1 processing. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 145, 187–197.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: LX; Methodology: LX Validation: LX; Formal analysis and investigation: HW, WZ; Writing—original draft preparation: HW; Writing—review and editing: LX; Resources: LX, Supervision: LX.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Zhao, WS. & Xu, L. Bisphosphonate of Zoledronate Has Antiapoptotic Effect on Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Injury in Human Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes Through Trk Signaling Pathway. Cell Biochem Biophys 80, 435–442 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-021-01031-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-021-01031-7