Abstract
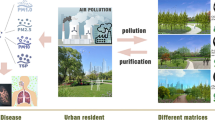
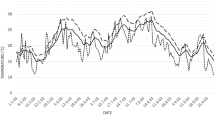
At present, the focus on greenway construction in China is shifting from production protection and environment beautification to ecological protection and leisure and recreation. The ways in which to explore a comprehensive and efficient ecological health functional greenway plant landscape model are of particular importance for greenway construction and community belt park management. In the present study, nine landscape configuration patterns of three green space structure types (trees-shrubs-grass, trees-grass, and shrubs-grass) in typical community demonstrative belt park greenways in Changchun Fitness Park in Beijing were selected as the study objects on which to perform quantitative study and evaluation of the single and comprehensive effects of six core ecological health factors, namely green space landscape beauty degree, negative air ions, human comfort, PM2.5, and bacteria and noise reduction. The results show that the ecological health care effects of the greenways differ due to various community structures. The score range of the plant landscape beauty of spatial composition groups is − 1.333 to 0.932, the highest value of air negative ions released in summer reaches 1176 cm−3, and the reduction rate of PM2.5 concentration is 1.94–12.21%. The greenways have a strong effect on improving human comfort in spring, summer and autumn. The temperature difference inside and outside the green spaces is as high as 3 ℃, the humidification is about 20%, the net noise attenuation rate is 0.10–11.36%, and the bacteria reduction rate reaches up to 50–60%. The comprehensive index method was used to evaluate the six-core health factor system, the range of the comprehensive index of ecological health function of the three types of green space structures was 2.3187–10.3334, and the overall order was trees-shrubs-grass > trees-grass > shrubs-grass. The three landscape configuration patterns that were screened with better ecological health care effects can be used for the construction of the urban community belt park greenways.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao F (2015) Preliminary study on ecological health function of the typical urban green spaces and of the green ways in Beijing. Beijing Forestry University, Beijing
Begum BA, Biswas SK, Hopke PK (2006) Temporal variations and spatial distribution of ambient PM2.2 and PM10 concentrations in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Sci Total Environ 358(3):36–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.05.031
Chen L, Sun B, Tan G, Li Z (2015) The air anion characteristics of city greenbelt plant community in Guangzhou. J Northwest for Univ 30(1):227–232. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2015.01.39
Duan M, Wang Y, Liu J (2017) Comprehensive evaluation of ecological health functions of green space in Beijing Purple Bamboo Park. Chin J Ecol 36(7):1973–1983. https://doi.org/10.13292/j.1000-4890.201707.031
Fadhil A, Waheeb R (2021) A greenway for sustainable transportation of the university campus: Diyala University as a case study. Earth Environ Sci 75(1):120–128. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/754/1/012013
Haesung A, Jeongwoo L, Andy H (2021) Does urban greenway design affect air pollution exposure? A case study of Seoul, South Korea. Sustain Cities Soc 72:103018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2021.103038
Kurazumi Y, Kondo E, Fukagawa K, Hashimoto R, Nyilas A, Sakoi T, Tsuchikawa T (2017) The influence of foliage plants on psychological and physiological responses. Health 9(4):601–621. https://doi.org/10.4236/health.2017.94043
Li Q, Cheng W, Zheng J, Xie T, Lu T (2019) Influence of greenspace landscape pattern on PM2.5 in the center urban area of Nanchang, China. Chin J Appl Ecol 30(11):3855–3862. https://doi.org/10.13287/j.1001-9332.201911.018
Luo Y, Li X, H X et al (2009) Effects of different plant deployment models on bacteria control in urban green areas. Chin Urban Forest 3(6):23–25. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1672-4925.2005.06.006
Maleki K, Hosseini SM (2011) Investigation of the effect of leaves, branches and canopies of trees on noise pollution reduction. Ann Environ Sci 5(1):2–7
McKinney ML (2016) Urbanization as a major cause of biotic homogenization. Biol Conserv 127(3):247–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2005.09.005
Ottoni Callista A, Joanie SG, Meghan W et al (2021) Safety perceptions of older adults on an urban greenway: interplay of the social and built environment. Health Place 70:102605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healthplace.2021.102605
Pan G, Wang X (2016) Planning and design of Beijing three hills and five gardens greenway system. J Beijing Univ Agric 31(02):102–106. https://doi.org/10.13473/j.cnki.issn.1002-3186.2016.0221
Rao H (2016) Research on current situation and countermeasure of Jiaxing ecological greenway network planning and construction. Zhejiang A&F University, Hangzhou
Ren B, Li W, Liu X, Cong R (2015a) Research on plant diversity in urban greenways of Beijing. Chin Landsc Archit 31(8):10–14. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-6664.2015.08.003
Ren Q, Xu Z, Dang L (2015b) Effects of urban road protection green-belt on reducing airborne microbes concentration. Ecol Environ Sci 24(5):825–830. https://doi.org/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2015.05.016
Stanhope J, Breed MF, Weinstein P (2020) Exposure to greenspaces could reduce the high global burden of pain. Environ Res 2020:109641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109641
Twohig-Bennett C, Jones A (2018) The health benefits of the great outdoors: a systematic review and meta-analysis of greenspace exposure and health outcomes. Environ Res 166:628–637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2018.06.030
Wang L, Zheng G (2016) Effecton and factors affecting noise reduction by plant communitiesat parks in Fuzhou Fujian. J Agric Sci 31(1):63–69. https://doi.org/10.19303/j.issn.1008-0384.2016.01.013
Wang Y, Duan M, Liu J (2017) The ecological health function effects of green spaces of Beixiaohe Park in Beijing. Sci Tech Eng 17(18):31–40. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2017.18.005
Wang H, Wang B, Niu X (2020) Study on the change of negative air ion concentration and its influencing factors at different spatio temporal scales. Glob Ecol Conserv 23(8):e01008–e01008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gecco.2020.e01008
Wei J, Li H, Wang Y, Xu X (2021) The cooling and humidifying effects and the thresholds of plant community structure parameters in urban aggregated green infrastructure. Forests 12(2):111–123. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12020111
Yang C, Wang R, Wang Y-R (2021) Research progress in ecological healthcare function of urban green spaces. World for Res 34(5):32–36. https://doi.org/10.13348/j.cnki.sjlyyj.2021.0058.y
Yu H, Guo J, Li E-J, Pei S-X (2021) Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of negative air ionin Platycladus orientalis forest of Jiulong mountain, Beijing. For Res 34(3):174–179. https://doi.org/10.13275/j.cnki.lykxyj.2021.03.020
Zhou B, Lu J, Hua Z (2020) Study on ecological service benefits of urban greenway based on i-tree model. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis 32(12):2201–2210. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2020.12.11
Acknowledgements
We thank Lianghua Qi and Xuan Hu for all of their help and suggestions on our project. We are also grateful to the editors and anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments on the original manuscript.
Funding
The work was supported by Beijing Natural Science Foundation Municipality (8192018); National Natural Science Foundation of China (31770751); Beijing Science and Technology Planning Project (Z161100001116065).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Duan, M., Wang, Q. et al. Ecological health care effect of healthy greenways in urban community belt parks. Landscape Ecol Eng 18, 247–262 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11355-022-00495-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11355-022-00495-w