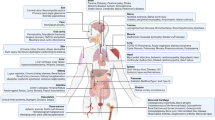
Abstract
As a key signaling molecule, cationic antimicrobial peptide LL37 helps mediate intracellular and extracellular signal transduction. It interacts with various cells facilitating tissue repair and plays a vital role in the defense against pathogens. LL37 acts as a broad-spectrum antimicrobial, possessing antitumor and antiviral properties. It promotes angiogenesis, co-operates with growth factors, antagonizes inflammatory media, participates in immune regulation, and helps tissue repair and growth. These biological effects are closely related to the information exchange between LL37 and various cells, in particular mesenchymal stem cells. Gaining a thorough understanding of the molecular mechanism of communication between LL37 and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells is crucial. However, work on tissue repair remains at an early stage. This paper reviews the main signal transduction mechanisms operating between LL37 and mesenchymal stem cells in bone and subsequent effects on cell proliferation, migration, and osteogenic differentiation.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Abdel-Magid AF (2013) FPRL-1 receptor modulators may provide treatment for inflammation. ACS Med Chem Lett 4:574–575. https://doi.org/10.1021/ml400179m
Bernardo ME, Fibbe WE (2013) Mesenchymal stromal cells: sensors and switchers of inflammation. Cell Stem Cell 13:392–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2013.09.006
Bo Z, Lijuan Y, Zongyue Z, Yixiao F, Xi W, Xiaoxing W, Huaxiu L, Jing Z, Meng Z, Mikhail P, William W, Fang H, Yukun M, Kevin Q, Huimin D (2020) Leptin potentiates BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells through the activation of JAK/STAT signaling. Stem Cells Dev 29:498–510. https://doi.org/10.1089/scd.2019.0292
Brown MD, Sacks DB (2008) Compartmentalised MAPK pathways. Handb Exp Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-72843-6_9
Bruno S, Deregibus MC, Camussi G (2015) The secretome of mesenchymal stromal cells: role of extracellular vesicles in immunomodulation. Immunol Lett 168:154–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imlet.2015.06.007
Cao W, Cao K, Cao J, Wang Y, Shi Y (2015) Mesenchymal stem cells and adaptive immune responses. Immunol Lett 168:147–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imlet.2015.06.003
Caplan AI, Correa D (2011) The MSC: an injury drugstore. Cell Stem Cell 9:11–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2011.06.008
Caplan AI, Sorrell JM (2015) The MSC curtain that stops the immune system. Immunol Lett 168:136–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imlet.2015.06.005
Coffelt SB, Marini FC, Watson K, Zwezdaryk KJ, Dembinski JL, LaMarca HL, Tomchuck SL, zu Bentrup KH, Danka ES, Henkle SL, Scandurro AB (2009) The pro-inflammatory peptide LL-37 promotes ovarian tumor progression through recruitment of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:3806–3811. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0900244106
De Y, Chen Q, Schmidt AP, Anderson GM, Wang JM, Wooters J, Oppenheim JJ, Chertov O (2000) LL-37, the neutrophil granule- and epithelial cell-derived cathelicidin, utilizes formyl peptide receptor-like 1 (FPRL1) as a receptor to chemoattract human peripheral blood neutrophils, monocytes, and T cells. J Exp Med 192:1069–1074. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.192.7.1069
Durr UH, Sudheendra US, Ramamoorthy A (2006) LL-37, the only human member of the cathelicidin family of antimicrobial peptides. Biochim Biophys Acta 1758:1408–1425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2006.03.030
Esfandiyari R, Halabian R, Behzadi E, Sedighian H, Jafari R, Imani Fooladi AA (2019) Performance evaluation of antimicrobial peptide ll-37 and hepcidin and β-defensin-2 secreted by mesenchymal stem cells. Heliyon. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02652
Frasca L, Lande R (2012) Role of defensins and cathelicidin LL37 in auto-immune and auto-inflammatory diseases. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 13:1882–1897. https://doi.org/10.2174/138920112802273155
Furuta T, Miyaki S, Ishitobi H, Ogura T, Kato Y, Kamei N, Miyado K, Higashi Y, Ochi M (2016) Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote fracture healing in a mouse model. Stem Cells Transl Med 5:1620–1630. https://doi.org/10.5966/sctm.2015-0285
Gaestel M (2015) MAPK-activated protein kinases (MKs): novel insights and challenges. Front Cell Dev Biol 3:88. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2015.00088
Guerra AD, Rose WE, Hematti P, Kao WJ (2017) Minocycline modulates NFkappaB phosphorylation and enhances antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus aureus in mesenchymal stromal/stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther 8:171. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-017-0623-1
He Y, Mu C, Shen X, Yuan Z, Liu J, Chen W, Lin C, Tao B, Liu B, Cai K (2018) Peptide LL-37 coating on micro-structured titanium implants to facilitate bone formation in vivo via mesenchymal stem cell recruitment. Acta Biomater 80:412–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2018.09.036
Honczarenko M, Le Y, Swierkowski M, Ghiran I, Glodek AM, Silberstein LE (2006) Human bone marrow stromal cells express a distinct set of biologically functional chemokine receptors. Stem Cells 24:1030–1041. https://doi.org/10.1634/stemcells.2005-0319
Horibe K, Nakamichi Y, Uehara S, Nakamura M, Koide M, Kobayashi Y, Takahashi N, Udagawa N (2013) Roles of cathelicidin-related antimicrobial peptide in murine osteoclastogenesis. Immunology. https://doi.org/10.1111/imm.12146
Huang CC, Narayanan R, Alapati S, Ravindran S (2016) Exosomes as biomimetic tools for stem cell differentiation: applications in dental pulp tissue regeneration. Biomaterials 111:103–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.09.029
Kittaka M, Shiba H, Kajiya M, Fujita T, Iwata T, Rathvisal K, Ouhara K, Takeda K, Fujita T, Komatsuzawa H, Kurihara H (2013) The antimicrobial peptide LL37 promotes bone regeneration in a rat calvarial bone defect. Peptides 46:136–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2013.06.001
Koczulla R, von Degenfeld G, Kupatt C, Krötz F, Zahler S, Gloe T, Issbrücker K, Unterberger P, Zaiou M, Lebherz C, Karl A, Raake P, Pfosser A, Boekstegers P, Welsch U, Hiemstra PS, Vogelmeier C, Gallo RL, Clauss M, Bals R (2003) An angiogenic role for the human peptide antibiotic LL-37/hCAP-18. J Clin Invest 111:1665–1672. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci17545
Koon HW, Shih DQ, Chen J, Bakirtzi K, Hing TC, Law I, Ho S, Ichikawa R, Zhao D, Xu H, Gallo R, Dempsey P, Cheng G, Targan SR, Pothoulakis C (2011) Cathelicidin signaling via the toll-like receptor protects against colitis in mice. Gastroenterology 141:1852–63.e3. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2011.06.079
Kortesidis A, Zannettino A, Isenmann S, Shi S, Lapidot T, Gronthos S (2005) Stromal-derived factor-1 promotes the growth, survival, and development of human bone marrow stromal stem cells. Blood 105:3793–3801. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2004-11-4349
Krasnodembskaya A, Song Y, Fang X, Gupta N, Serikov V, Lee JW, Matthay MA (2010) Antibacterial effect of human mesenchymal stem cells is mediated in part from secretion of the antimicrobial peptide LL-37. Stem Cells 28:2229–2238. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.544
Lai Y, Gallo RL (2009) AMPed up immunity: how antimicrobial peptides have multiple roles in immune defense. Trends Immunol 30:131–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2008.12.003
Li Z, Song Y, Yuan P, Guo W, Hu X, Xing W, Ao L, Tan Y, Wu X, Ao X, He X, Jiang D, Liang H, Xu X (2020) Antibacterial fusion protein BPI21/LL-37 modification enhances the therapeutic efficacy of hUC-MSCs in sepsis. Mol Ther 28:1806–1817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.05.014
Liu W, Dong SL, Xu F, Wang XQ, Withers TR, Yu HD, Wang X (2013) Effect of intracellular expression of antimicrobial peptide LL-37 on growth of escherichia coli strain TOP10 under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57:4707–4716. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00825-13
Liu Z, Yuan X, Liu M, Fernandes G, Zhang Y, Yang S, Ionita CN, Yang S (2018) Antimicrobial peptide combined with BMP2-modified mesenchymal stem cells promotes calvarial Repair in an osteolytic model. Mol Ther 26:199–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.09.011
Lu Z, Chen Y, Dunstan C, Roohani-Esfahani S, Zreiqat H (2017) Priming adipose stem cells with tumor necrosis factor-alpha preconditioning potentiates their exosome efficacy for bone regeneration. Tissue Eng A 23:1212–1220. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.tea.2016.0548
Mookherjee N, Brown KL, Bowdish DM, Doria S, Falsafi R, Hokamp K, Roche FM, Mu R, Doho GH, Pistolic J, Powers JP, Bryan J, Brinkman FS, Hancock RE (2006) Modulation of the TLR-mediated inflammatory response by the endogenous human host defense peptide LL-37. J Immunol 176:2455–2464. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.176.4.2455
Murakami M, Lopez-Garcia B, Braff M, Dorschner RA, Gallo RL (2004) Postsecretory processing generates multiple cathelicidins for enhanced_topical antimicrobial defense. J Immunol 172:3070–3077. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.172.5.3070
Murphy MB, Moncivais K, Caplan AI (2013) Mesenchymal stem cells: environmentally responsive therapeutics for regenerative medicine. Exp Mol Med 45:e54. https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2013.94
Nakamichi Y, Horibe K, Takahashi N, Udagawa N (2014) Roles of cathelicidins in inflammation and bone loss. Odontology 102:137–146. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10266-014-0167-0
Noore J, Noore A, Li B (2013) Cationic antimicrobial peptide LL-37 is effective against both extra- and Intracellular Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57:1283–1290. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.01650-12
Pearson G, Robinson F, Gibson TB, Bing-E Xu, Karandikar M, Berman K, Cobb MH (2001) Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: regulation and physiological functions. Endocr Rev 22:153–183. https://doi.org/10.1210/edrv.22.2.0428
Pittenger MF (1999) Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science 284:143–147. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.284.5411.143
Quesenberry PJ, Aliotta J, Deregibus MC, Camussi G (2015) Role of extracellular RNA-carrying vesicles in cell differentiation and reprogramming. Stem Cell Res Ther 6:153. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-015-0150-x
Raik S, Kumar A, Bhattacharyya S (2018) Insights into cell-free therapeutic approach: role of stem cell “soup-ernatant.” Biotechnol Appl Biochem 65:104–118. https://doi.org/10.1002/bab.1561
Ramos R, Silva JP, Rodrigues AC, Costa R, Guardao L, Schmitt F, Soares R, Vilanova M, Domingues L, Gama M (2011) Wound healing activity of the human antimicrobial peptide LL37. Peptides 32:1469–1476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2011.06.005
Sall J, Carlsson M, Gidlof O, Holm A, Humlen J, Ohman J, Svensson D, Nilsson BO, Jonsson D (2013) The antimicrobial peptide LL-37 alters human osteoblast Ca2+ handling and induces Ca2+-independent apoptosis. J Innate Immun 5:290–300. https://doi.org/10.1159/000346587
Sho T, Koji S, Yuji S, Hitoshi K, Kazuhisa O, Yasushi H, Yoko Y, Xiuju D, Mikiko T, Hiroshi N, Lujun Y, Shigeki H, Akihiko Y, Motoyuki S, Koji H (2013) Induction of keratinocyte migration via transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor by the antimicrobial peptide transactivation of the epidermal growth induction of keratinocyte migration via LL-37. J Immunol 175:4662–4668. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.175.7.4662
Sorensen OE, Follin P, Johnsen AH, Calafat J, Tjabringa GS, Hiemstra PS, Borregaard N (2001) Human cathelicidin, hCAP-18, is processed to the antimicrobial peptide LL-37 by extracellular cleavage with proteinase 3. Blood 97:3951–3959. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.v97.12.3951
Stoorvogel W, Kleijmeer MJ, Geuze HJ, Ga R (2002) The biogenesis and functions of exosomes. Traffic 3:321–330. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0854.2002.30502.x
Svensson D, Westman J, Wickstrom C, Jonsson D, Herwald H, Nilsson BO (2015) Human endogenous peptide p33 inhibits detrimental effects of LL-37 on osteoblast viability. J Periodontal Res 50:80–88. https://doi.org/10.1111/jre.12184
Tomasinsig L, Zanetti M (2005) The cathelicidins–structure, function and evolution. Curr Protein Pept Sci 6:23–34. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389203053027520
Tripathi S, Verma A, Kim EJ, White MR, Hartshorn KL (2014) LL-37 modulates human neutrophil responses to influenza A virus. J Leukoc Biol 96:931–938. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.4A1113-604RR
Vandamme D, Landuyt B, Luyten W, Schoofs L (2012) A comprehensive summary of LL-37, the factotum human cathelicidin peptide. Cell Immunol 280:22–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellimm.2012.11.009
Viswanathan A, Painter RG, Lanson NA, Wang G (2007) Functional expression of N-formyl peptide receptors in human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells 25:1263–1269. https://doi.org/10.1634/stemcells.2006-0522
Wang L, Li Y, Chen X, Chen J, Gautam SC, Xu Y, Chopp M (2013) MCP-1, MIP-1, IL-8 and ischemic cerebral tissue enhance human bone marrow stromal cell migration in interface culture. Hematology 7:113–117. https://doi.org/10.1080/10245330290028588
Warren JL, John JOS (1998) Jaks and STATs_ biological implications. Annu Rev Immunol 16:293–322. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.16.1.293
Xiao T, Devaraj B, Hm JZ, Min W (2015) P2X7 receptor regulates internalization of antimicrobial peptide LL-37 by human macrophages that promotes intracellular pathogen clearance. J Immunol 195:1191–1201. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1402845
Xu N, He D, Shao Y, Qu Y, Ye K, Memet O, Zhang L, Shen J (2020) Lung-derived exosomes in phosgene-induced acute lung injury regulate the functions of mesenchymal stem cells partially via miR-28-5p. Biomed Pharmacother 121:109603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109603
Yamasaki K, Schauber J, Coda A, Lin H, Dorschner RA, Schechter NM, Bonnart C, Descargues P, Hovnanian A, Gallo RL (2006) Kallikrein-mediated proteolysis regulates the antimicrobial effects of cathelicidins in skin. FASEB J 20:2068–2080. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.06-6075com
Yang Y, Choi H, Seon M, Cho D, Bang SI (2016) LL-37 stimulates the functions of adipose-derived stromal/stem cells via early growth response 1 and the MAPK pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther 7:58. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-016-0313-4
Yin J, Fu-Shin XY (2010) LL-37 via EGFR transactivation to promote high glucose-attenuated epithelial wound healing in organ-cultured corneas. Investig Opthalmol Vis Sci. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.09-3904
Yu X, Quan J, Long W, Chen H, Wang R, Guo J, Lin X, Mai S (2018) LL-37 inhibits LPS-induced inflammation and stimulates the osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs via P2X7 receptor and MAPK signaling pathway. Exp Cell Res 372:178–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2018.09.024
Zasloff M (2019) Antimicrobial peptides of multicellular organisms: my perspective. Antimicrobial peptides. Advances in experimental medicine and biology 2019. Springer, Singapore, pp 3–6
Zhang Z, Cherryholmes G, Chang F, Rose DM, Schraufstatter I, Shively JE (2009) Evidence that cathelicidin peptide LL-37 may act as a functional ligand for CXCR2 on human neutrophils. Eur J Immunol 39:3181–3194. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.200939496
Zhang J, Liu X, Li H, Chen C, Hu B, Niu X, Li Q, Zhao B, Xie Z, Wang Y (2016) Exosomes/tricalcium phosphate combination scaffolds can enhance bone regeneration by activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther 7:136. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-016-0391-3
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was supported by the General program of Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China (2019M66166) and Liaoning Provincial Doctoral Fund (20180540065) in respect of the writing and publication of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YZ and ZL contributed to the study design, study performance, and preparation of the manuscript. ZL and YZ contributed to literature analysis and interpretation, and preparation and revision of the manuscript. FL and GZ contributed to the study performance. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Y., Lu, F., Zhang, G. et al. Overview of signal transduction between LL37 and bone marrow-derived MSCs. J Mol Histol 53, 149–157 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-021-10048-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-021-10048-4