Abstract
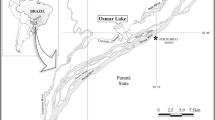
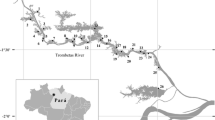
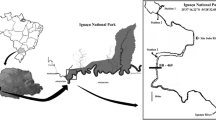
The Amazon floodplains are complex systems influenced by the annual hydrological regime with an effect on the structuring of physical, chemical and biological processes. Thus, we evaluated the relationship of environmental factors with the composition and variation of functional groups based on morphology (MBFG) during the hydrological year in an Amazonian floodplain lake, with monthly sampling (2013 to 2014). We used analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Kruskal–Wallis to show differences in physicochemical variables between hydroperiods. We performed permutation analysis of variance (PERMANOVA) to assess the dissimilarity of morphofunctional groups between hydroperiods and also of environmental data between the months of the study and RDA redundancy analysis to assess the relationship between MBFGs and environmental data. It was registered 101 taxa distributed in eight taxonomic categories and was grouped into 5 MBFGs (III, IV, V, VI and VII), with Chlorophyceae (31 taxa) and Cyanobacteria (27 taxas) with the higher number of taxa. Furthermore, there was a dominance of Cyanobacteria in the total biovolume, which form blooms (MBFGs III and VII) during the periods of falling and low water in lake, influenced mainly by the reduction in the availability of light and an increase in temperature. In another scenario, the dominance of MBFGs V and VI occurred during periods of rising and high water with association with carbon compounds, rainfall, SRP and NO2. Thus, our results demonstrate that the availability of light, the concentration of nutrients and temperature were the most important variables for the morphofunctional structuring of phytoplankton in aquatic system.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson MJ (2001) A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecol. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-9993.2001.01070.pp.x
Barbosa HTB, Soares MGM (2017) Hydrological seasons fast identification applied to Jaitêua and São Lourenço lakes, Manacapuru, Amazonas State. Acta Fish 3:73–81. https://doi.org/10.2312/Actafish.2017.5.3.73-81
Barbosa CCF, Novo EMLM, Melack JM, Gastil-Buhl M, Pereira Filho W (2010) Geospatial analysis of spatiotemporal patterns of pH, total suspended sediment and chlorophyll-a on the Amazon floodplain. Limnology 11:155–166. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10201-009-0305-5
Becker V, Caputo L, Ordóñez J, Marcé R, Armengol J, Crossetti LO, Huszar VL (2010) Driving factors of the phytoplankton functional groups in a deep Mediterranean reservoir. Water Resour 44(11):3345–3354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.03.018
Bittencourt MM, Amadio SA (2007) Proposal for rapid identification of hydrological periods in lowland areas of the Solimões-Amazonas river near Manaus. Acta Amazon (português) 37:303–308. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0044-59672007000200019
Bonnet MP, Barroux G, Seyler P, Pecly G, Moreira-Turcq P, Lagane C, Cochonneau G, Viers J, Seyler F, Guyot JL (2005) Seazonal links between the Amazon corridor and its flood plain: the case of the várzea of Curuai. IAHS Publ. 294:69–77. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/271852898. Accessed 28 Jun 2019
Bonnet MP, Barroux G, Martinez JM, Seyler F, Moreira-Turcq P, Cochonneau G, Melack JM, Boaventura G, Maurice-Bourgoin L, Leon JG, Roux E, Calmant S, Kosuth P, Guyot JL, Seyler P (2008) Floodplain hydrology in an Amazon floodplain lake (Lago Grande de Curuaı´). J Hydrol 349:18–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2007.10.055
Bonnet MP, Pinel S, Garnier J, Bois J, Boaventura G, Seyler P (2017) Amazonian floodplain water balance based on modelling and analyses of hydrologic and electrical conductivity data. Hydrol Process 31:1702–1718. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.11138
Bozelli RL, Thomaz SM, Padial AA, Lopes PM, Bini LM (2015) Floods decrease zooplankton beta diversity and environmental heterogeneity in an Amazonian floodplain system. Hydrobiologia 753:233–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-015-2209-1
Brasil J, Huszar VLM (2011) The role of functional traits in continental phytoplankton ecology (in Portuguese). Oecol Aust 15:799–834. https://doi.org/10.4257/oeco.2011.1504.04
Brasil J, Attayde JL, Vasconcelos FR, Dantas DDF, Huszar VLM (2016) Drought-induced water-level reduction favors cyanobacteria blooms in tropical shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 770:145–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-015-2578-5
Cao J, Hou Z, Li Z, Chu Z, Yang P, Zheng B (2018) Succession of phytoplankton functional groups and their driving factors in a subtropical plateau lake. Sci Total Environ 631–632:1127–1137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.026
Cardoso SJ, Nabout JC, Farjalla VF, Lopes PM, Bozelli LR, Huszar VLM (2017) Environmental factors driving phytoplankton taxonomic and functional diversity in Amazonian floodplain lakes. Hydrobiologia 802:115–130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-017-3244-x
Carmichael W (1994) The toxins of cyanobacteria. Sci Am 270:78–86. https://doi.org/10.1038/scientificamerican19:4-78
Casali S, Calijuri MC, Barbarisi B, Renó VF, Affonso AG, Barbosa C, Silva TSF, Novo EMLM (2011) Impact of the 2009 extreme water level variation on phytoplankton community structure in lower Amazon floodplain lakes. Acta Limnol Bras 23:260–270. https://doi.org/10.1590/S2179-975X2012005000001
Cole GA (1994) Textbook of limnology, 4th edn. Waveland Press, Illinois, p 412p
Crossetti LO, Becker V, Cardoso LS, Rodrigues LR, Costa LS, Motta-Marques D (2013) Is phytoplankton functional classification a suitable tool to investigate spatial heterogeneity in a subtropical shallow lake? Limnologica 43:157–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.limno.2012.08.010
Forsberg BR, Melack JM, Richey JE, Pimentel T (2017) Regional and seasonal variability in planktonic photosynthesis and planktonic community respiration in Amazon floodplain lakes. Hydrobiologia 800:187–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-017-3222-3
Gianuca AT, Declerck SA, Lemmens P, De Meester L (2017) Effects of dispersal and environmental heterogeneity on the replacement and nestedness components of β-diversity. Ecology 98:525–553. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecy.1666 (PMID: 27870011)
Guiry MD, Guiry GM (2018). Algae base. World-wide electronic publication. http://www.algaebase.org. Accessed 28 Jun 2019
Hillebrand H, Dürselen C, Kirschtel D, Pollingher U, Zohary T (1999) Biovolume calculation for pelagic and benthic microalgae. J Phycol 35:403–424. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1529-8817.1999.3520403.x
Huszar VLM, Reynolds CS (1997) Phytoplankton periodicity and sequences of dominance in on Amazonian flood-plain lake (Lago Batata, Pará, Brazil): responses to gradual environmental change. Hydrobiologia 346:169–181. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1002926318409
Huszar VLM, Nabout JC, Appel MO, Santos JBO, Abe SD, Silva LHS (2015) Environmental and not spatial processes (directional and non-directional) shape the phytoplankton composition and functional groups in a large subtropical river basin. J Plankton Res 37:1190–1200. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fbv084
Junk WJ (2001) The flood pulse concept of large rivers: learning from the tropics. SIL Proc 27:3950–3953. https://doi.org/10.1080/03680770.1998.11901733
Junk WJ, Wantzen KM (2003) The flood pulse concept: new aspects, approaches and applications—an update. In: Abell R, Thieme M, Brenner BL (eds) Proceeding soft the second international symposium on the management to flare rivers for fisheries. Thailand DC, Bangkok, pp 117–140
Junk WJ, Bayley PB, Sparks RE (1989) The flood pulse concept in river-floodplain systems. Can J Fishers Aquatic 106:110–127
Junk WJ, Piedade MTF, Schöngart J, Wittmann F (2012) A classification of major natural habitats of Amazonian white-water river floodplains (várzeas). Wetlands Ecol Manage 20:461–475. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11273-012-9268-0
Junk WJ, Piedade MT, Lourival R, Wittmann F, Kandus P, Bozelli R, Esteves FA, Cunha C, Maltchik L, Schöngart J, Schaeffer-Novelli Y, Agostinho A, Nobrega R, Camargo E (2015) Definition and classification of Brazilian wetlands (UAs): scientific basis for a new policy on protection and sustainable management. In: Nunes da Cunha C, Piedade MT F, Junk WJ, (eds) Classification and design of Brazilian wetlands and their Macro habitats (in Portuguese), Cuiabá Mato Grosso, Brazil. DC, pp. 13–82.
Köppen W, Geiger R (1928) Klimate der Erde. Gotha: Verlag Justus Perthes. Wall-map 150cmx200cm.
Kraus CN, Bonnet MP, Nogueira IS, Lobo MMPS, Motta Marques D, Garnier J (2019a) Unraveling flooding dynamics and nutrients’ controls upon phytoplankton functional dynamics in Amazonian floodplain lakes. Water 11:154
Kraus CN, Bonnet MP, de Souza Nogueira I, Souza Lobo MTMP, da Motta Marques D, Garnier J, Cardoso Galli Vieira L (2019b) Unraveling flooding dynamics and nutrients’ controls upon phytoplankton functional dynamics in Amazonian floodplain lakes. Water 11(1):154. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11010154
Kruk C, Segura AM (2012) The habitat template of phytoplankton morphology-based functional groups. Hydrobiologia 698:191–202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-012-1072-6
Kruk C, Mazzeo N, Lacerot G, Reynolds CS (2002) Classification schemes for phytoplankton: a local validation of a functional approach to the analysis of species temporal replacement. J Plank Res 24:901–912. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/24.9.901
Kruk C, Huszar VLM, Peeters EHM, Bonilla S, Costa LS, Lurling M, Reynolds CS, Scheffer M (2010) A morphological classification capturing functional variation in phytoplankton. Fresh Water Biol 55:614–627. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2009.02298.x
Kruk C, Peeters ETHM, Van Nes EH, Huszar VLM, Costa LS, Scheffer M (2011) Phytoplankton community composition can be predicted best in terms of morphological groups. Limnol Oceanogr 56:110–118
Kruk C, Segura AM, Costa LS, Lacerot G, Kosten S, Peeters ETHM, Huszar VLM, Mazzeo N, Scheffer M (2017) Functional redundancy increases towards the tropics in lake phytoplankton. J Plank Res 39:518–530. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fbw083
Legendre P, Borcard D (2018) Box-Cox-chord transformations for community composition data prior to beta diversity analysis. Ecography 41(11):1820–1824. https://doi.org/10.1111/ecog.03498
Lobo MTMPS, Nogueira IS, Sgarbi LF, Kraus CN, Bomfim EO, Garnier J, Marques DM, Bonnet MP (2018) Morphology-based functional groups as the best tool to characterize shallow lake-dwelling phytoplankton on an Amazonian floodplain. Ecol Indic 95:579–588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.07.03
Lund JWG, Kipling C, Cren L (1958) The inverted microscope method of estimating algal number and the statistical basis of estimation by counting. Hydrobiologia 11:143–170
Mackereth FJH, Heron J, Talling JF (1978) Water analysis: some revised methods for Limnologists. (Freshwater biological association scientific publication, 36). K Titus Wilson & Sons Ltda, Kendal, p 117
Margalef R (1978) Phytoplankton communities in up welling areas. Oecol Aquat 3:97–132
Maurice-Bourgoin L, Martinez MJ, Grélaud J, Filizolaand N, Boaventura GR (2005) The role of flood plains in the hydrology and sediment dynamics of the Amazon river, Brazil. In: Walling DE, Horowitz AJ (eds) Sediment budgets1 and 2, Foz do Iguaço (BRA). IAHS Publication 291, Foz do Iguaçu, Rio Grande do Sul Brazil, pp 310–322
Maurice-Bourgoin L, Bonnet MP, Martinez JM, Kosuth P, Cochonneau G, Moreira Turcq P, Guyot JL, Vauchel P, Filizolaand N, Seyler P (2007) Temporal dynamics of water and sediment exchanges between the Curuaí floodplain and the Amazon River mainstream, Brazil. J Hydrol 335:140–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2006.11.023
Moreira-Turcq P, Jouanneau JM, Turcq B, Seyler P, Weber O, Guyot JL (2004) Carbon sedimentation at Lago Grande do Curuai, a floodplain Lake in the low Amazon region: insights into sedimentation rates. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 214:27–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2004.06.013
Moreira-Turcq P, Bonnet MP, Amorim M, Bernardes M, Lagane C, Maurice L, Perez M, Seyler P (2013) Seasonal variability in concentration, composition, age, and fluxes of particulate organic carbon exchanged between the floodplain and Amazon river. Global Biogeochem Cycles 27:119–130. https://doi.org/10.1002/gbc.20022,2013
Naselli-Flores L, Barone R (2012) Phytoplankton dynamics in permanent and temporary Mediterranean waters: is the game hard to play because of hydrological disturbance? Hydrobiologia 698:147–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-012-1059-3
Neiff JJ (1990) Ideas for the ecological interpretation of Paraná (Spanish). Interciencia 5(6):424–441
Neiff JJ, Poi de Neiff ASG (2003) Connectivity processes as a basis for the management of aquatic plants. In: Thomaz SM, Bini LM, (eds) Ecologia e manejo de macrófitas aquáticas. Maringá, pp 39–58.
Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Kindt R, Legendre P, Minchin PR, O'Hara RB (2013). Vegan: community ecology package. R package version 2.0–8. http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan. Accessed 28 Jun 2019
Padisák J (1997) Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Woloszynnska) Seenayya et Subba Raju, an expanding, highly adaptive cyanobacterium: worldwide distribution and review of its ecology. Arch Hydrobiol Suppl 107:563–593
Phlips EJ, Havens KE, Lopes MRM (2008) Seasonal dynamics of phytoplankton in two Amazon flood plain lakes of varying hydrologic connectivity to the main river channel. Fundam Appl Limnol 172v2:99–109. https://doi.org/10.1127/1863-9135/2008/0172-0099
Reynolds CS (1998) What factors influence the species composition of phytoplankton in lakes of different trophic status? Hydrobiologia 369:11–26. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017062213207
Reynolds CS (2006) The ecology of phytoplankton. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Reynolds CS (2007) Variability in the provision and function of mucilage in phytoplankton: facultative responses to the environment. Hydrobiologia 578:37–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-006-0431-6
Reynolds CS, Oliver RL, Walsby AE (1987) Cyanobacteria dominance: the role of buoyancy regulation in dynamic lake environments. N Z J Mar Freshwater Res 21:379–390. https://doi.org/10.1080/00288330.1987.9516234
Reynolds CS, Huszar VLM, Kruk C, Naselli-Flores L, Melo S (2002) Towards a functional classification of the freshwater phytoplankton. J Plank Res 24(5):417–428. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/24.5.417
Robarts RD, Zohary T (1987) Temperature effects on photosynthetic capacity, respiration, and growth rates of bloom-forming cyanobacteria. N Z J Mar Freshwater Res 21:391–399. https://doi.org/10.1080/00288330.1987.9516235
Rodríguez MA, Lewis WM (1994) Regulation and stability in fish assemblages of neotropical floodplain lakes. Oecologia 99:166–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00317098
Ryabov AB, Rudolf L, Blasius B (2010) Vertical distribution and composition of phytoplankton under the influence of an upper mixed layer. J Theor Biol 263(1):120–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtbi.2009.10.034
Scheffer M, Rinaldi S, Gragnani A, Mur LR, Van Nes EH (1997) On the dominance of filamentous cyanobacteria in shallow turbid lakes. Ecology 78:272–282
Simões NR, Lansac-Tôha FA, Bonecker CC (2013) Drought disturbances increase temporal variability of zooplankton community structure in floodplains. Hydrobiology 98:24–33. https://doi.org/10.1002/iroh.201201473
Sioli H (1985) Amazônia: fundamentals of ecology of the largest rainforest region (in Portuguese). Vozes, Rio de Janeiro
Sosik HM, Mitchell BG (1995) Light absorption by phytoplankton, photosynthetic pigments, and detritus in the California current system. Deep Sea Res Part I 42:1717–1748. https://doi.org/10.1016/0967-0637(95)00081-G
Team RC (2018) R: A language and environment for statistical computing, R foundation for statistical computing, Austria, 2015. ISBN 3-900051-07-0: URL: http://www.R-project.Org. Accessed 28 Jun 2019
Thomas MK, Litchman E (2016) Effects of temperature and nitrogen availability on the growth of invasive and native cyanobacteria. Hydrobiologia 763(1):357–369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-015-2390-2
Uhelinger V (1964) Statistical study of plankton counting methods (in French). Arch Sci 17:121–223
Utermöhl H (1958) To perfect the quantitative phytoplankton methodology. Negotiat Int Assoc Theor Appl Limnol (in German) 9:1–38
Veech JA, Crist TO (2007) Habitat and climate heterogeneity maintain beta-diversity of birds among landscapes within ecoregions. Global Ecol Biogeogr 16(5):650–656. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1466-8238.2007.00315.x
Yamaguchi T, Tsuchiya T, Nakahara S, Fukui A, Nagamoto Y, Murotani K (2016) Efficacy of left atrial voltage-based catheter ablation of persistent atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 27:1055–1063. https://doi.org/10.1111/jce.13019
Yoshiyama K, Mellard JP, Litchman E, Klausmeier CA (2009) Phytoplankton competition for nutrients and light in a stratified water column. Am Nat 174(2):190–203. https://doi.org/10.1086/600113
Zar JH (2010) Biostatistical analysis. 5th Edn, Prentice-Hall/Pearson, Upper Saddle River, xiii, 944 p
Zehr JP, Ward BB (2002) Nitrogen cycling in the ocean: new perspectives on processes and paradigms. Am Societ Microb 68:1015–1024. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.68.3.1015-1024.2002
Zhang M, Shi X, Chen F, Yang Z, Yu Y (2021) The underlying causes and effects of phytoplankton seasonal turnover on resource use efficiency in freshwater lakes. Ecol Evol 11:8897–8909. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.7724
Acknowledgements
This study was sponsored by CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico) (fellowship to D.A.S), CAPES (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior, Brazil) grant number 1224656/2013-6, grant number 2019/15984-2, São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) and CLIM-FABIAM program (Climate changes and Amazonian Floodplain Biodiversity), which was funded by FRB (Fondation Pour la Recherche sur la Biodiversité). We are grateful to Dra. Lúcia Helena Sampaio da Silva for assistance in the identification of phytoplankton and biovolume metrics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by DAdS, ALB, CK, DdMM, SdM, SC, KD-S, NRS and TB. The first draft of the manuscript was written by DAdS and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
This study was funded by CLIM-FABIAM program (Climate changes and Amazonian Floodplain Biodiversity), which was funded by FRB (Fondation pour la Recherche sur la Biodiversité).
Additional information
Handling Editor: Camilla Capelli.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Souza, D.A., Kraus, C.N., Burliga, A.L. et al. Understanding the effects of environmental heterogeneity on the morphofunctional structure of the phytoplankton community during the hydrological year in an Amazon floodplain lake, Brazil. Limnology 23, 275–286 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10201-021-00685-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10201-021-00685-9