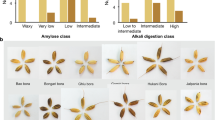
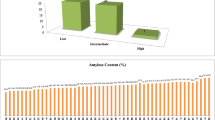
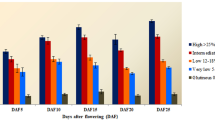
Abstract
Starch is the main component of cereals like rice. It is mainly composed of amylose and amylopectin. Apparent amylose content (AAC) in rice grain controlled by granule bound starch synthase enzyme (GBSS) is the key factor determining cooking and processing quality. The present study has been attempted to decipher the genetic variability among 36 cultivars of rice for agro-morphological parameters along with AAC and amylopectin content, to determine the extent of association among yield and its contributing characters and to detect the sequence variations among the cultivars having differential AAC. Results revealed the presence of adequate genetic variability among the tested rice cultivars for yield attributing traits, as well as their AAC and amylopectin content. Most of the yield attributing traits was under control of additive genes. Genetic diversity study of the tested rice cultivars grouped them into four clusters. The nucleotide sequence and derived amino acid sequence variations among the region spanning between the intron 7 and exon 10 of GBSSI allele from the rice cultivars differing in AAC detected the presence of several SNPs, deletions and insertions within the tested exon and intron regions. Presence of methionine (M) or isoleucine (I) at 308 aa position and presence of phenylalanine (F) at 425 or 434 aa position of GBSSI protein across the tested rice cultivars can be exploited in marker-assisted breeding programme for developing high yielding rice cultivars with proper grain quality as per consumer’s preference.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adjah KL, Abe A, Adetimirin VO, Asante MD (2020) Genetic variability, heritability and correlations for milling and grain appearance qualities in some accessions of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Physiol Mol Biol Plants 26:1309–1317
Ahuja S, Malhotra PK, Bhatia VK, Prasad R (2008) Statistical package for agricultural research (SPAR 2). J Ind Soc Agric Stat 62:65–74
Akinwale MG, Gregorio G, Nwilene F, Akinyele BO, Ogunbayo SA, Odiyi AC (2011) Heritability and correlation coefficient analysis for yield and its components in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Afr J Plant Sci 5(3):207–212
Ayres NM, McClung AM, Larkin PD, Bligh HFJ, Jones CA, Park WD (1997) Microsatellites and a single-nucleotide polymorphism differentiate apparent amylose classes in an extended pedigree of US rice germ plasm. Theor Appl Genet 94(6–7):773–781
Biselli C, Daniela C, Rosaria P, Alberto G, Paolo B, Simona U, Gabriele O et al (2014) Improvement of marker-based predictability of apparent amylose content in japonica rice through GBSSI allele mining. Rice. https://doi.org/10.1186/1939-8433-7-1
Biswas T, Das A, Bhattacharyya S (2012) Microsatellite marker-based diversity analysis for submergence tolerance in some Bengal landraces of rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Trop Agril 50(1):67–71
Carrijo DR, Lundy ME, Linquist BA (2017) Rice yields and water use under alternate wetting and drying irrigation: a meta-analysis. Field Crops Res 203:173–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2016.12.002
Chen MH, Bergman C, Pinson S, Fjellstrom R (2008) Waxy gene haplotypes: associations with apparent amylose content and the effect by the environment in an international rice germplasm collection. J Cereal Sci 47(3):536–545
Choudhury B, Khan ML, Dayanandan S (2013) Genetic structure and diversity of indigenous rice (Oryza sativa) varieties in the Eastern Himalayan region of Northeast India. Springer plus 2(1):228
Das A, Pramanik K, Sharma R, Gantait S, Banerjee J (2019) In-silico study of biotic and abiotic stress-related transcription factor binding sites in the promoter regions of rice germin-like protein genes. PLoS ONE 14(2):e0211887
Deng N, Ling X, Sun Y, Zhang C, Fahad S, Peng S et al (2015) Influence of temperature and solar radiation on grain yield and quality in irrigated rice system. Eur J Agron 64:37–46
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem Bull 19:11–15
FAO (2018) FAOSTAT database. Rome: FAO. http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QC/
Hanashiro I, Itoh K, Kuratomi Y, Yamazaki M, Igarashi T, Matsugasako JI, Takeda Y (2008) Granule-bound starch synthase I is responsible for biosynthesis of extra-long unit chains of amylopectin in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 49(6):925–933
Hirose T, Terao T (2004) A comprehensive expression analysis of the starch synthase gene family in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Planta 220(1):9–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-004-1314-6 (Epub 2004 Jun 30 PMID: 15232694)
Hizukuri S, Abe JI, Hanashiro I (2006) Starch: analytical aspects. Food Sci Technol 159:305
Jennings PR (1979) Rice improvement, International Rice Research Institute, Los Baños, Laguna, Philippines
Johnson HW, Robinson HF, Comstock RE (1955) Estimates of genetic and environmental variability in soybeans. Agron J 47(7):314–318
Juliano BO, Perez CM, Blakeney AB, Castillo T, Kongseree N, Laignelet B et al (1981) International cooperative testing on the amylose content of milled rice. Starch Stärke 33(5):157–162
Kong X, Zhu P, Sui Z, Bao J (2015) Physicochemical properties of starches from diverse rice cultivars varying in apparent amylose content and gelatinisation temperature combinations. Food Chem 172:433–440
Kumar S, Chauhan MP, Tomar A, Kasana RK, Kumar N (2018) Correlation and path coefficient analysis in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Pharma Innov J 7(6):20–26
Mahalanobis PC (1963) On the generalized distance in statistics. Proc Natl Acad Sci (india) 2:49–55
Nakamura Y, Ono M, Ozaki N (2019) Structural features of α-glucans in the very early developmental stage of rice endosperm. J Cereal Sci 89:102778
Nirmaladevi G, Padmavathi G, Kota S, Babu VR (2015) Genetic variability, heritability and correlation coefficients of grain quality characters in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Sabrao J Breed Genet 47(4):424–433
Okagaki RJ (1992) Nucleotide sequence of a long cDNA from the rice waxy gene. Plant Mol Biol 19:513. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00023402
Pandey MK, Rani NS, Madhav MS, Sundaram RM, Varaprasad GS, Sivaranjani AK, Bohra A, Kumar GR, Kumar A (2012) Different isoforms of starch-synthesizing enzymes controlling amylose and amylopectin content in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Biotechnol Adv 30(6):1697–1706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2012.08.011
PPV & FRA, Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmer’s Rights Authority (PPV&FRA) (2007) Specific DUS test guidelines for twelve notified crops – rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Var J India 1:151–169
Raigond P, Ezekiel R, Raigond B (2015) Resistant starch in food: A review. J Sci Food Agric 95(10):1968–1978
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Sarawgi AK, Subba Rao LV, Parikh M, Sharma B, Ojha GC (2013) Assessment of variability of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) germplasm using agro-morphological characterization. J Rice Res 6(1):14–19
Singh RK, Chaudhary BD (1979) Biometrical methods in quantitative genetic analysis. Kalyani Publishers, Dudhiano
Tian Z, Qian Q, Liu Q, Yan M, Liu X, Yan C et al (2009) Allelic diversities in rice starch biosynthesis leadled to a diverse array of rice eating and cooking qualities. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106(51):21760–21765
Veni B, Krishna D, Sandeep R, Rama Rao CV, Sridevi P (2020) Characterization of colored rice genotypes for nutritional traits and functional properties. Extended Summ 2020:63
Vrinten PL, Nakamura T (2000) Wheat granule-bound starch synthase I and II are encoded by separate genes that are expressed in different tissues. Plant Physiol 122:255–264
Wang W, Wei X, Jiao G, Chen W, Wu Y, Sheng Z, Hu S, Xie L, Wang J, Tang S, Hu P (2020) GBSS-binding protein, encoding a CBM48 domain-containing protein, affects rice quality and yield. J Integr Plant Biol 62(7):948–966. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12866 (Epub 2019 Oct 18 PMID: 31449354)
Zhao C, Zhao L, Zhao Q et al (2020) Genetic dissection of eating and cooking qualities in different subpopulations of cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.) through association mapping. BMC Genet 21:119. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-020-00922-7
Zhou H, Wang L, Liu G, Meng X, Jing Y, Shu X, Kong X, Sun J, Yu H, Smith SM, Wu D (2016) Critical roles of soluble starch synthase SSIIIa and granule-bound starch synthase Waxy in synthesizing resistant starch in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci 113(45):12844–12849
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by A. Das.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghosh, M., Banerjee, J., Bhattacharya, S. et al. Studies on genetic variability and identification of sequence variations among cultivars and landraces of rice (Oryza sativa L.) for apparent amylose and amylopectin contents. CEREAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS 50, 1085–1094 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42976-021-00231-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42976-021-00231-4