Abstract
Background or purpose
We report our single-center experience with percutaneous left atrial appendage closure (LAAC) in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation (NVAF) and primary hemostasis disorders (HD).
Methods
Consecutive patients with primary HD who underwent a percutaneous LAAC were included. Baseline characteristics, procedural data, and clinical outcomes were prospectively collected and compared with the overall LAAC cohort without HD.
Results
Since 2013, among 229 LAAC, 17 patients (7%) had a primary HD: thrombocytopenia (n = 5), myelodysplastic syndrome (n = 6), von Willebrand syndrome (n = 4), type A hemophilia (n = 1), and dysfibrinogenemia (n = 1). The HD population’s age ranged from 61 to 87 years, and the median CHA2DS2VASc was 5. Periprocedural plasmatic management was required in 47% of patients. The immediate LAAC implantation success rate was 100%. Patients received a direct oral anticoagulant (DOA) (n = 9), dual antiplatelet (n = 6), aspirin (n = 1), or no therapy (n = 1) during the first six postoperative weeks, followed with single antiplatelet (n = 16) or no therapy (n = 1) during lifelong. After 20 months, the technical success rate and procedural success rate were 100% and 94%. Zero device-/procedure-related complication and only one life-threatening bleeding occurred. Compared to patients without HD (n = 212), a baseline history of bleeding was less frequent (53% vs 91%, p < 0.001), and more patients received a perioperative blood transfusion (47% vs 4%, p < 0.001) in the HD group. The efficacy and safety outcomes did not differ between HD and non-HD cohorts.
Conclusions
Percutaneous LAAC in primary HD carriers appeared as safe and as effective as in overall LAAC population for stroke and bleeding prevention at midterm follow-up.
Graphical abstract
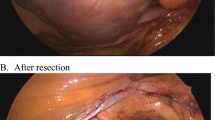
Percutaneous left atrial appendage closure in patients with atrial fibrillation and primary hemostasis disorders. The percutaneous LAAC in primary hemostasis disorders and AF carriers requires a multidisciplinary approach. Cardiologist, anesthesiologist, and hematologist discussion is a cornerstone to assess anticoagulant contraindication, LAAC feasibility, periprocedural management, and follow-up (high). This multidisciplinary care is illustrated by the case of a 61-year-old male with hemophilia type A and recurrent hemarthrosis. Pre-LAAC assessment confirmed procedural indication and cactus LAA anatomy (left). After plasmatic management with factor VIII infusion, a WATCHMAN™ no. 21 was successfully implanted (middle). During follow-up, without antithrombotic regime, no ischemic or hemorrhagic complication occurred (right). LAA, left atrial appendage; LAAC, left atrial appendage closure; TEE, transesophageal echocardiography. Percutaneous LAAC in primary HD carriers appeared as safe and as effective as in overall LAAC population for stroke and bleeding prevention at midterm follow-up.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data and material are available.
Abbreviations
- AC:
-
Anticoagulant
- DOA:
-
Direct oral anticoagulant
- DRT:
-
Device-related thrombus
- ECG:
-
Electrocardiogram
- FA:
-
Atrial fibrillation
- HD:
-
Hemostasis disorders
- LAA:
-
Left atrial appendage
- LAAC:
-
Left atrial appendage closure
- NVAF:
-
Non-valvular atrial fibrillation
- PASS:
-
Position, anchor, size, and seal
- TEE:
-
Transesophageal echocardiography
- TTE:
-
Transthoracic echocardiography
- VKA:
-
Vitamin K antagonist
References
Lip GYH, Nieuwlaat R, Pisters R, Lane DA, Crijns HJGM. Refining clinical risk stratification for predicting stroke and thromboembolism in atrial fibrillation using a novel risk factor-based approach: the Euro Heart Survey on Atrial Fibrillation. Chest. 2010;137(2):263–72. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.09-1584.
Takashima N, Arima H, Kita Y, Fujii T, Miyamatsu N, Komori M, … Nozaki K. Incidence, management and short-term outcome of stroke in a general population of 1.4 million Japanese- Shiga Stroke Registry. Circ J. 2017; 81 (11):1636–1646. https://doi.org/10.1253/circj.CJ-17-0177
Lip GYH, Collet JP, de Caterina R, Fauchier L, Lane DA, Larsen TB, … Scott-Millar R. Antithrombotic therapy in atrial fibrillation associated with valvular heart disease: a joint consensus document from the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) and European Society of Cardiology Working Group on Thrombosis, endorsed by the ESC Working Group on Valvular Heart Disease, Cardiac Arrhythmia Society of Southern Africa (CASSA), Heart Rhythm Society (HRS), Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS), South African Heart (SA Heart) Association and Sociedad Latinoamericana de Estimulación Cardíaca y Electrofisiología (SOLEACE). EP Europace. 2017;19(11):1757–1758. https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/eux240
Holmes DR, Reddy VY, Turi ZG, Doshi SK, Sievert H, Buchbinder M, … Sick P. Percutaneous closure of the left atrial appendage versus warfarin therapy for prevention of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation: a randomised non-inferiority trial. 2009;374:9.
Holmes DR, Kar S, Price MJ, Whisenant B, Sievert H, Doshi SK, … Reddy VY. Prospective randomized evaluation of the Watchman left atrial appendage closure device in patients with atrial fibrillation versus long-term warfarin therapy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;64(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2014.04.029
Reddy VY, Möbius-Winkler S, Miller MA, Neuzil P, Schuler G, Wiebe J, … Sievert H. Left atrial appendage closure with the Watchman device in patients with a contraindication for oral anticoagulation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;61(25):2551–2556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2013.03.035
Boersma LVA, Schmidt B, Betts TR, Sievert H, Tamburino C, Teiger E, … Bergmann MW. Implant success and safety of left atrial appendage closure with the WATCHMAN device: peri-procedural outcomes from the EWOLUTION registry. Eur Heart J. 2016;37(31):2465–2474. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehv730
January CT, Wann LS, Calkins H, Chen LY, Cigarroa JE, Cleveland JC, … Yancy CW. 2019 AHA/ACC/HRS focused update of the 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74(1):104–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2019.01.011
Hindricks G, Potpara T, Dagres N, Arbelo E, Bax JJ, Blomström-Lundqvist C, … Zakirov NU. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). European Heart Journal. 2020;ehaa612. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa612
Shokr M, Adegbala O, Elmoghrabi A, Saleh M, Ajam M, Ali A, … Afonso L. Impact of chronic thrombocytopenia on outcomes after transcatheter valvular intervention and cardiac devices implantation (from a national inpatient sample). Am J Cardiol. 2019;124(10):1601–1607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2019.08.012
Pastori D, Antonucci E, Violi F, Palareti G, Pignatelli P, Testa S, Liberato NL. Thrombocytopenia and Mortality Risk in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: An Analysis From the START Registry. Journal of the American Heart Association. 2019;8(21).https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.119.012596
Janion-Sadowska A, Papuga-Szela E, Łukaszuk R, Chrapek M, Undas A. Non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants in patients with atrial fibrillation and thrombocytopenia. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2018;72(3):153–60. https://doi.org/10.1097/FJC.0000000000000607.
Wang C-L, Wu VC-C, Lee C-H, Kuo C-F, Chen Y-L, Chu P-H, … Chang S-H. Effectiveness and safety of non-vitamin-K antagonist oral anticoagulants versus warfarin in atrial fibrillation patients with thrombocytopenia. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2019;47(4): 512–519. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-018-1792-1
Horváth-Puhó E, Suttorp MM, Frederiksen H, Hoekstra T, Dekkers OM, Pedersen L, … Sørensen HT. Erythropoiesis-stimulating agents and cardiovascular events in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome and multiple myeloma. Clin Epidemiol. 2018;10: 1371–1380. https://doi.org/10.2147/CLEP.S172306
Adelborg K, Corraini P, Darvalics B, Frederiksen H, Ording A, Horváth-Puhó E, … Sørensen HT. Risk of thromboembolic and bleeding outcomes following hematological cancers: a Danish population-based cohort study. J Thromb Haemost: JTH. (2019);17(8):1305–1318. https://doi.org/10.1111/jth.14475
Sorigue M, Nieto J, Santos-Gomez M, Sarrate E, Jiménez M-J, Morales-Indiano C, … Xicoy B. Indications and use of, and incidence of major bleeding with, antithrombotic agents in myelodysplastic syndrome. Leuk Res. 2018;73:24–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2018.08.017
Schutgens REG, Klamroth R, Pabinger I, Malerba M, Dolan G, ADVANCE working group. Atrial fibrillation in patients with haemophilia: a cross-sectional evaluation in Europe. Haemophilia. 2014;20(5):682–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/hae.12445.
Toselli M, Bosi D, Benatti G, Solinas E, Cattabiani MA, Vignali L. Left atrial appendage closure: a balanced management of the thromboembolic risk in patients with hemophilia and atrial fibrillation. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-020-02097-5.
Cheung VTF, Hunter RJ, Ginks MR, Schilling RJ, Earley MJ, Bowles L. Management of thromboembolic risk in persons with haemophilia and atrial fibrillation: is left atrial appendage occlusion the answer for those at high risk? Haemophilia. 2013;19(2):e84–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/hae.12055.
Güray Ü, Korkmaz A, Gürsoy HT, Elalmış ÖU. Percutaneous left atrial appendage closure in a patient with haemophilia and atrial fibrillation: a case report. Eur Heart J Case Rep. 2019; 3(3). https://doi.org/10.1093/ehjcr/ytz124
Bhatti Z, Goldbarg S. Combined left atrial appendage closure and ablation in a patient with hemophilia B, paroxysmal atrial fibrillation, and transient ischemic attack. HeartRhythm Case Reports. 2019;5(5):266–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrcr.2019.01.014.
Ancedy Y, Berthelot E, Lang S, Ederhy S, Boyer-Chatenet L, Di Angelantonio E, … Cohen A. Is von Willebrand factor associated with stroke and death at mid-term in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation? Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2018;111(5):357–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acvd.2017.08.004
Castaman G, Giacomelli SH, Biasoli C, Contino L, Radossi P. Risk of bleeding and thrombosis in inherited qualitative fibrinogen disorders. Eur J Haematol. 2019;103(4):379–84. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejh.13296.
Chan AK, deVeber G. Prothrombotic disorders and ischemic stroke in children. Seminars in Pediatric Neurology. 2000;7(4):301–8. https://doi.org/10.1053/spen.2000.20075.
Neunert C, Terrell DR, Arnold DM, Buchanan G, Cines DB, Cooper N, … Vesely SK. American Society of Hematology 2019 guidelines for immune thrombocytopenia. Blood Adv. 2019;3(23): 3829–3866. https://doi.org/10.1182/bloodadvances.2019000966
Malcovati L, Hellström-Lindberg E, Bowen D, Adès L, Cermak J, Del Cañizo C, … European Leukemia Net. Diagnosis and treatment of primary myelodysplastic syndromes in adults: recommendations from the European LeukemiaNet. Blood. 2013;122(17): 2943–2964. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2013-03-492884
Nichols WL, Hultin MB, James AH, Manco-Johnson MJ, Montgomery RR, Ortel TL, … Yawn BP. von Willebrand disease (VWD): evidence-based diagnosis and management guidelines, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) Expert Panel report (USA). Haemophilia. 2008;14(2): 171–232. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2516.2007.01643.x
Srivastava A, Brewer AK, Mauser‐Bunschoten EP, Key NS, Kitchen S, Llinas A, … Street A. Guidelines for the management of hemophilia. Haemophilia. 2013;19(1):e1–e47. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2516.2012.02909.x
Casini A, Neerman-Arbez M, Ariëns RA, de Moerloose P. Dysfibrinogenemia: from molecular anomalies to clinical manifestations and management. Journal of thrombosis and haemostasis: JTH. 2015;13(6):909–19. https://doi.org/10.1111/jth.12916.
Sacco RL, Kasner SE, Broderick JP, Caplan LR, Connors JJB, Culebras A, … Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity and Metabolism. An updated definition of stroke for the 21st century: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2013; 44(7): 2064–2089. https://doi.org/10.1161/STR.0b013e318296aeca
Schulman S, Kearon C. Definition of major bleeding in clinical investigations of antihemostatic medicinal products in non-surgical patients. J Thromb Haemost. 2005;3(4):692–4. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1538-7836.2005.01204.x.
Schulman S, Angerås U, Bergqvist D, Eriksson B, Lassen MR, Fisher W, Subcommittee on Control of Anticoagulation of the Scientific and Standardization Committee of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis. Definition of major bleeding in clinical investigations of antihemostatic medicinal products in surgical patients. J Thromb Haemost: JTH. 2010;8(1):202–4. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1538-7836.2009.03678.x.
Kaufman RM, Djulbegovic B, Gernsheimer T, Kleinman S, Tinmouth AT, Capocelli KE, … Tobian AAR. Platelet transfusion: a clinical practice guideline from the AABB. Ann Intern Med. 2015;162(3): 205. https://doi.org/10.7326/M14-1589
Cooper N, Ghanima W. Immune thrombocytopenia. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(10):945–55. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMcp1810479.
Tzikas A, Holmes DR, Gafoor S, Ruiz CE, Blomström-Lundqvist C, Diener H-C, … Lewalter T. Percutaneous left atrial appendage occlusion: the Munich consensus document on definitions, endpoints, and data collection requirements for clinical studies. Europace. 2017;19(1); 4–15. https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/euw141
Reddy VY, Sievert H, Halperin J, Doshi SK, Buchbinder M, Neuzil P, … PROTECT AF Steering Committee and Investigators.Percutaneous left atrial appendage closure vs warfarin for atrial fibrillation: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2014;312(19):1988–1998. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2014.15192
Mehran R, Rao SV, Bhatt DL, Gibson CM, Caixeta A, Eikelboom J, … White H. Standardized bleeding definitions for cardiovascular clinical trials: a consensus report from the Bleeding Academic Research Consortium. Circulation. 2011;123(23): 2736–2747. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.009449
Oliva EN, Dimitrov BD, Benedetto F, D’Angelo A, Nobile F. Hemoglobin level threshold for cardiac remodeling and quality of life in myelodysplastic syndrome. Leuk Res. 2005;29(10):1217–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2005.03.004.
Greenberg P, Cox C, LeBeau MM, Fenaux P, Morel P, Sanz G, … Bennett J. International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 1997;89(6): 2079–2088.
van der Valk PR, Mauser-Bunschoten EP, van der Heijden JF, Schutgens REG. Catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation in patients with hemophilia or von Willebrand disease. TH Open. 2019;3(4):e335–9. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0039-1698756.
Rodés-Cabau J, O’Hara G, Paradis J-M, Bernier M, Rodriguez-Gabella T, Regueiro A, … Champagne J. Changes in coagulation and platelet activation markers following transcatheter left atrial appendage closure. Am J Cardiol. 2017;120(1):87–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2017.03.253
Sherwood M, Bliden KP, Ilkhanoff L, Venkataraman G, Strickberger A, Yazdani S, … Gurbel PA. Detailed thrombogenicity phenotyping and 1 year outcomes in patients undergoing WATCHMAN implantation: (TARGET-WATCHMAN) a case–control study. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2020;50(3): 484–498. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-020-02205-5
Dukkipati Srinivas R, Kar Saibal, Holmes David R, Doshi Shephal K, Swarup Vijendra, Gibson Douglas N, … Reddy Vivek Y. Device-related thrombus after left atrial appendage closure. Circulation. 2018;138(9): 874–885. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.035090
Fauchier L, Cinaud A, Brigadeau F, Lepillier A, Pierre B, Gras D, … Defaye P. Left atrial appendage closure in atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;72(22), 2806–2807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2018.08.2196
Asmarats L, O’Hara G, Champagne J, Paradis J-M, Bernier M, O’Connor K, … Rodés-Cabau J. Short-term oral anticoagulation versus antiplatelet therapy following transcatheter left atrial appendage closure. Circulation. Cardiovascular Interventions. 2020;13(8):e009039. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.120.009039
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ND, ES, CC, GD, and JC made substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work, or the acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data.
ND, ES, CC, GD, GO, FP, JMP, LF, JB, KO, MB, JRC, and JC drafted the work or revised it critically for important intellectual content, approved the version to be published, and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The study received ethics committee approval.
Consent to participate and for publication
All of the patients expressed a consent to participate and for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
ND is the first author; ES is the second author; and JC is the senior author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dognin, N., Salaun, E., Champagne, C. et al. Percutaneous left atrial appendage closure in patients with primary hemostasis disorders and atrial fibrillation. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 64, 497–509 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-021-01073-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-021-01073-0