Abstract
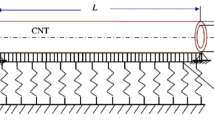
The present paper investigated nonlinear free and forced vibration of carbon nanotubes conveying magnetic nanoflow and subjected to a longitudinal magnetic field resting on a viscoelastic foundation. The nonlinear equations of motion were established using Hamilton's principle and solved by employing the Galerkin method. Stress-driven nonlocal integral model has been used to model small-scale effects, its results are compared with Eringen differential model. The instability of divergence and flutter are investigated for different boundary conditions. The primary and secondary resonance of carbon nanotubes is addressed for four boundary conditions. In addition, the effects of length small scale parameters, longitudinal magnetic field, magnetic nanofluid, and boundary conditions on nonlinear free and forced vibration of carbon nanotubes are discussed in detail. As the most important result, it can be seen that Eringen differential model shows an increasing trend by increasing the nonlocal parameter for a cantilever carbon nanotube and in other boundary conditions shows a decreasing trend in free and forced vibrations. While stress-driven nonlocal integral model, by increasing the length scale parameter, always shows increasing behavior, both in free and forced vibrations for all boundary conditions.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Salehi MG, Rostamzadeh A, Gharib A, Masoumi H (2016) Role of magnetic nanoparticles in targeted drug delivery for central nervous system. J Chem Pharm Sci 9(3):1419–1423
Mody VV, Cox A, Shah S, Singh A, Bevins W, Parihar H (2014) Magnetic nanoparticle drug delivery systems for targeting tumor. Appl Nanosci 4(4):385–392
Sanadgol N, Wackerlig J (2020) Developments of smart drug-delivery systems based on magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for targeted cancer therapy: a short review. Pharmaceutics 12(9):831
Madasu KP, Bucha T (2019) Impact of magnetic field on flow past cylindrical shell using cell model. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 41(8):1–2
Moradicheghamahi J, Jahangiri M, Mousaviraad M, Sadeghi MR (2020) Computational studies of comparative and cumulative effects of turbulence, fluid–structure interactions, and uniform magnetic fields on pulsatile non-Newtonian flow in a patient-specific carotid artery. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 42(10):1–22
Mitra P, Dutta S, Hens A (2020) Separation of particles in spiral micro-channel using Dean’s flow fractionation. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 42(8):1–2
Ali N, Asghar Z, Sajid M, Bég OA (2019) Biological interactions between Carreau fluid and microswimmers in a complex wavy canal with MHD effects. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 41(10):1–3
SafarPour H, Ghadiri M (2017) Critical rotational speed, critical velocity of fluid flow and free vibration analysis of a spinning SWCNT conveying viscous fluid. Microfluid Nanofluid 21(2):22
Rahmati M, Khodaei S (2018) Nonlocal vibration and instability analysis of carbon nanotubes conveying fluid considering the influences of nanoflow and non-uniform velocity profile. Microfluid Nanofluid 22(10):1–4
Pashaki PV, Ji JC (2020) Nonlocal nonlinear vibration of an embedded carbon nanotube conveying viscous fluid by introducing a modified variational iteration method. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 42(4):1–3
Mohammadi K, Barouti MM, Safarpour H, Ghadiri M (2019) Effect of distributed axial loading on dynamic stability and buckling analysis of a viscoelastic DWCNT conveying viscous fluid flow. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 41(2):93
Azarboni HR, Rahimzadeh M, Heidari H, Keshavarzpour H, Edalatpanah SA (2019) Chaotic dynamics and primary resonance analysis of a curved carbon nanotube considering influence of thermal and magnetic fields. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 41(7):1–4
Ponte PJ, Ritto TG, Deü JF (2020) Dynamic analysis of a pipe conveying a two-phase fluid considering uncertainties in the flow parameters. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 42(12):1–5
Li F, An C, Duan M, Su J (2019) In-plane and out-of-plane dynamics of curved pipes conveying fluid by integral transform method. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 41(12):1–6
Zhang X, Gou R, Yang W, Chang X (2018) Vortex-induced vibration dynamics of a flexible fluid-conveying marine riser subjected to axial harmonic tension. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 40(8):1–2
Rashidi H, Rahimi Z, Sumelka W (2018) Effects of the slip boundary condition on dynamics and pull-in instability of carbon nanotubes conveying fluid. Microfluid Nanofluid 22(11):1–9
Sahmani S, Safaei B (2019) Nonlinear free vibrations of bi-directional functionally graded micro/nano-beams including nonlocal stress and microstructural strain gradient size effects. Thin-Walled Struct 140:342–356
Parsa A, Mahmoudpour E (2019) Nonlinear free vibration analysis of embedded flexoelectric curved nanobeams conveying fluid and submerged in fluid via nonlocal strain gradient elasticity theory. Microsyst Technol 25(11):4323–4339
Farajpour A, Ghayesh MH, Farokhi H (2019) A coupled nonlinear continuum model for bifurcation behaviour of fluid-conveying nanotubes incorporating internal energy loss. Microfluid Nanofluid 23(3):1–8
Kochupillai JA (2020) new formulation for fluid–structure interaction in pipes conveying fluids using Mindlin shell element and 3-D acoustic fluid element. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 42(7):1–23
Orsino RM, Pesce CP (2018) Modular methodology applied to the nonlinear modeling of a pipe conveying fluid. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 40(2):1–2
Xia W, Wang L (2010) Microfluid-induced vibration and stability of structures modeled as microscale pipes conveying fluid based on non-classical Timoshenko beam theory. Microfluid Nanofluid 9(4–5):955–962
Rezapour B, Araghi MF (2019) Semi-analytical investigation on dynamic response of viscoelastic single-walled carbon nanotube in nanoparticle delivery. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 41(3):117
Bahaadini R, Saidi AR, Hosseini M (2019) Flow-induced vibration and stability analysis of carbon nanotubes based on the nonlocal strain gradient Timoshenko beam theory. J Vib Control 25(1):203–218
Hosseini M, Sadeghi-Goughari M (2016) Vibration and instability analysis of nanotubes conveying fluid subjected to a longitudinal magnetic field. Appl Math Model 40(4):2560–2576
Salehipour H, Shahidi AR, Nahvi H (2015) Modified nonlocal elasticity theory for functionally graded materials. Int J Eng Sci 90:44–57
Faraji Oskouie M, Ansari R, Rouhi H (2020) Investigating vibrations of viscoelastic fluid-conveying carbon nanotubes resting on viscoelastic foundation using a nonlocal fractional Timoshenko beam model. In: Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part N: Journal of Nanomaterials, Nanoengineering and Nanosystems, 2397791420931701
Mahmoudpour E, Esmaeili M (2021) Nonlinear free and forced vibration of carbon nanotubes conveying magnetic nanoflow and subjected to a longitudinal magnetic field using stress-driven nonlocal integral model. Thin-Walled Struct 166:108134
Sedighi HM, Ouakad HM, Dimitri R, Tornabene F (2020) Stress-driven nonlocal elasticity for the instability analysis of fluid-conveying C-BN hybrid-nanotube in a magneto-thermal environment. Phys Scr 95(6):065204
Zeighampour H, Beni YT, Dehkordi MB (2018) Wave propagation in viscoelastic thin cylindrical nanoshell resting on a visco-Pasternak foundation based on nonlocal strain gradient theory. Thin-Walled Struct 122:378–386
Ghayesh MH, Farajpour A (2018) Nonlinear mechanics of nanoscale tubes via nonlocal strain gradient theory. Int J Eng Sci 129:84–95
Li L, Hu Y, Li X, Ling L (2016) Size-dependent effects on critical flow velocity of fluid-conveying microtubes via nonlocal strain gradient theory. Microfluid Nanofluid 20(5):1–2
Mahmoudpour E, Hosseini-Hashemi SH, Faghidian SA (2018) A nonlocal strain gradient theory for nonlinear free and forced vibration of embedded thick FG double layered nanoplates. Struct Eng Mech Int J 68(1):103–119
Mahmoudpour E, Hosseini-Hashemi SH, Faghidian SA (2019) Nonlinear resonant behaviors of embedded thick FG double layered nanoplates via nonlocal strain gradient theory. Microsyst Technol 25(3):951–964
Mahmoudpour E (2020) Nonlinear resonant behavior of thick multilayered nanoplates via nonlocal strain gradient elasticity theory. Acta Mech 231(6):2651–2667
Fernández-Sáez J, Zaera R, Loya JA, Reddy JN (2016) Bending of Euler-Bernoulli beams using Eringen’s integral formulation: a paradox resolved. Int J Eng Sci 99:107–116
Romano G, Barretta R (2017) Stress-driven versus strain-driven nonlocal integral model for elastic nano-beams. Compos B Eng 114:184–188
Romano G, Barretta R (2017) Nonlocal elasticity in nanobeams: the stress-driven integral model. Int J Eng Sci 115:14–27
Barretta R, Faghidian SA, Luciano R (2019) Longitudinal vibrations of nano-rods by stress-driven integral elasticity. Mech Adv Mater Struct 26(15):1307–1315
Barretta R, Caporale A, Faghidian SA, Luciano R, de Sciarra FM, Medaglia CM (2019) A stress-driven local-nonlocal mixture model for Timoshenko nano-beams. Compos B Eng 164:590–598
Bian PL, Qing H, Gao CF (2021) One-dimensional stress-driven nonlocal integral model with bi-Helmholtz kernel: close form solution and consistent size effect. Appl Math Model 89:400–412
Barretta R, Faghidian SA, Luciano R, Medaglia CM, Penna R (2018) Free vibrations of FG elastic Timoshenko nano-beams by strain gradient and stress-driven nonlocal models. Compos B Eng 154:20–32
Apuzzo A, Barretta R, Luciano R, de Sciarra FM, Penna R (2017) Free vibrations of Bernoulli-Euler nano-beams by the stress-driven nonlocal integral model. Compos B Eng 123:105–111
Mahmoudpour E, Hosseini-Hashemi SH, Faghidian SA (2018) Nonlinear vibration analysis of FG nano-beams resting on elastic foundation in thermal environment using stress-driven nonlocal integral model. Appl Math Model 57:302–315
Barretta R, Faghidian SA, De Sciarra FM (2019) Stress-driven nonlocal integral elasticity for axisymmetric nano-plates. Int J Eng Sci 136:38–52
Faraji Oskouie M, Ansari R, Rouhi H (2018) A numerical study on the buckling and vibration of nanobeams based on the strain and stress-driven nonlocal integral models. Int J Comput Mater Sci Eng 7(03):1850016
Oskouie MF, Ansari R, Rouhi H (2018) Bending of Euler-Bernoulli nanobeams based on the strain-driven and stress-driven nonlocal integral models: a numerical approach. Acta Mech Sin 34(5):871–882
Oskouie MF, Ansari R, Rouhi H (2018) Stress-driven nonlocal and strain gradient formulations of Timoshenko nanobeams. Eur Phys J Plus 133(8):1–2
Ansari R, Oskouie MF, Roghani M, Rouhi H (2021) Nonlinear analysis of laminated FG-GPLRC beams resting on an elastic foundation based on the two-phase stress-driven nonlocal model. Acta Mech 1:1–7
Oskouie MF, Ansari R, Rouhi H (2021) Bending analysis of nanoscopic beams based upon the strain-driven and stress-driven integral nonlocal strain gradient theories. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 43(3):1–4
Ansari R, Nesarhosseini S, Faraji Oskouie M, Rouhi H (2021) Size-dependent buckling analysis of piezoelectric nanobeams resting on elastic foundation considering flexoelectricity effect using the stress-driven nonlocal model. Eur Phys J Plus 136(8):1–3
Oskouie MF, Rouhi H (2021) Hybrid strain-and stress-driven integral non-local model. Eur Phys J Plus 136(8):1–9
Oskouie MF, Ansari R, Rouhi H (2018) Vibration analysis of FG nanobeams on the basis of fractional nonlocal model: a variational approach. Microsyst Technol 24(6):2775–2782
Oskouie MF, Ansari R, Rouhi H (2019) Nonlinear bending and postbuckling analysis of FG nanoscale beams using the two-phase fractional nonlocal continuum mechanics. Eur Phys J Plus 134(10):1–5
Oskouie MF, Ansari R, Rouhi H (2018) Bending analysis of functionally graded nanobeams based on the fractional nonlocal continuum theory by the variational Legendre spectral collocation method. Meccanica 53(4):1115–1130
Sadeghi-Goughari M, Jeon S, Kwon HJ (2017) Effects of magnetic-fluid flow on structural instability of a carbon nanotube conveying nanoflow under a longitudinal magnetic field. Phys Lett A 381(35):2898–2905
Choulaie M, Bagheri A, Khademifar A (2017) Nonlinear vibration and stability analysis of beam on the variable viscoelastic foundation. J Comput Appl Mech 48(1):99–110
Vatankhah R, Kahrobaiyan MH, Alasty A, Ahmadian MT (2013) Nonlinear forced vibration of strain gradient microbeams. Appl Math Model 37(18–19):8363–8382
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Technical Editor: Aurelio Araujo.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahmoudpour, E. Differences between stress-driven nonlocal integral model and Eringen differential model in the vibrations analysis of carbon nanotubes conveying magnetic nanoflow. J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 43, 555 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-021-03273-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-021-03273-1