Abstract
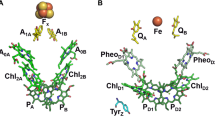
For billions of years, nature has optimized the photosynthetic machinery that converts light energy into chemical energy. Key primary reactions of photosynthesis occur in large membrane protein–cofactor complexes. The light-induced sequential electron transfer reactions occur through a chain of donor/acceptor cofactors embedded in the protein matrix resulting in a long-lived transmembrane charge-separated state. EPR is the method of choice to study electron transfer and the interaction of protein environment with redox-active cofactors. However, the spectra of organic cofactor radicals typically are not fully resolved and severely overlap at conventional X-band EPR. Even at Q-band EPR, this overlap is present and often a serious problem. As a result, there is a large variation of the reported EPR data and limited understanding of electronic structures of several redox-active cofactors. These serious problems can often be overcome by the excellent spectral resolution provided by high-frequency EPR (HF EPR). Here, we study the electronic structure of the primary electron donor P700 and the secondary electron acceptor A1 of Photosystem I (PSI) using 130 GHz (D-band) EPR and Electron–Nuclear-Double-Resonance (ENDOR) spectroscopy. PSI was isotopically labeled with 15N (I = ½) to avoid quadrupolar interactions in the most abundant nitrogen isotope 14N (I = 1) and simplify the ENDOR spectra. ENDOR spectroscopy is central for determining the hyperfine coupling of nitrogen atoms of the two chlorophyll molecules comprising oxidized P700 and the involvement of protein nitrogen atoms with reduced A1. While HF ENDOR of A1− allows identification of two nitrogen atoms, HF ENDOR of P700+ still does not permit unique assignment of the recorded hyperfine couplings.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.E. Blankenship, Molecular Mechanisms of Photosynthesis (Blackwell Science Limited, Oxford, 2002)
D.W. Lawlor, Photosynthesis (BIOS Scientific Publishers Limited, New York, 2001)
D. Shevela, L.O. Björn, Govindjee, Photosynthesis: Solar Energy for Life (World Scientific Publishing, Singapore, 2019)
R.E. Blankenship et al., Comparing photosynthetic and photovoltaic efficiencies and recognizing the potential for improvement. Science 332, 805–809 (2011)
T.J. Wydrzynski, K. Satoh, Photosystem II - the Light-Driven Water: Plastoquinone Oxidoreductase, vol. 22 (Springer, Dordrecht, 2005)
J.H. Golbeck, Photosystem I: The Light-Driven Plastocyanin: Ferredoxin Oxidoreductase, vol. 24 (Springer, Dordrecht, 2006)
A.J. Hoff, J. Deisenhofer, Photophysics of photosynthesis. Structure and spectroscopy of reaction centers of purple bacteria. Phys. Rep. 287, 1–247 (1997)
P. Jordan, P. Fromme, H.T. Witt, O. Klukas, W. Saenger, N. Krauss, Three-dimensional structure of cyanobacterial photosystem I at 2.5 Å resolution. Nature 411, 909–917 (2001)
P. Fromme, P. Jordan, N. Krauss, Structure of photosystem I. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Bioenerg. 1507, 5–31 (2001)
U. Ermler, G. Fritzsch, S.K. Buchanan, H. Michel, Structure of the photosynthetic reaction center from Rhodobacter sphaeroides at 2.65 Å resolution—cofactors and protein–cofactor interactions. Structure 2, 925–936 (1994)
M.H.B. Stowell, T.M. McPhillips, D.C. Rees, S.M. Soltis, E. Abresch, G. Feher, Light-induced structural changes in photosynthetic reaction center: implications for mechanism of electron-proton transfer. Science 276, 812–816 (1997)
A. Zouni, H.T. Witt, J. Kern, P. Fromme, N. Krauss, W. Saenger, P. Orth, Crystal structure of photosystem II from Synechococcus elongatus at 3.8 Ångstrom resolution. Nature 409, 739–743 (2001)
Y. Umena, K. Kawakami, J.R. Shen, N. Kamiya, Crystal structure of oxygen-evolving photosystem II at a resolution of 1.9 Ångstrom. Nature 473, 55-U65 (2011)
M. Suga et al., Native structure of photosystem II at 1.95 Ångstrom resolution viewed by femtosecond X-ray pulses. Nature 517, 99-U265 (2015)
M.G. Müller, C. Slavov, R. Luthra, K.E. Redding, A.R. Holzwarth, Independent Initiation of primary electron transfer in the two branches of the photosystem I reaction center. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 4123–4128 (2010)
A.R. Holzwarth, M.G. Müller, J. Niklas, W. Lubitz, Ultrafast transient absorption studies on photosystem I reaction centers from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii 2: mutations near the P700 reaction center chlorophylls provide new insight into the nature of the primary electron donor. Biophys. J. 90, 552–565 (2006)
A.R. Holzwarth, M.G. Müller, J. Niklas, W. Lubitz, Charge recombination fluorescence in photosystem I reaction centers from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 5903–5911 (2005)
M.G. Müller, J. Niklas, W. Lubitz, A.R. Holzwarth, Ultrafast transient absorption studies on photosystem I reaction centers from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. 1. A new interpretation of the energy trapping and early electron transfer steps in photosystem I. Biophys. J. 85, 3899–3922 (2003)
K. Brettel, Electron transfer and arrangement of the redox cofactors in photosystem I. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Bioenerg. 1318, 322–373 (1997)
N. Srinivasan, J.H. Golbeck, Protein–cofactor interactions in bioenergetic complexes: the role of the A1A and A1B phylloquinones in photosystem I. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Bioenerg. 1787, 1057–1088 (2009)
J.A. Bautista, F. Rappaport, M. Guergova-Kuras, R.O. Cohen, J.H. Golbeck, J.Y. Wang, D. Beal, B.A. Diner, Biochemical and biophysical characterization of photosystem I from phytoene desaturase and Xi-carotene desaturase deletion mutants of Synechocystis Sp. Pcc 6803. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 20030–20041 (2005)
M. Guergova-Kuras, B. Boudreaux, A. Joliot, P. Joliot, K. Redding, Evidence for two active branches for electron transfer in photosystem I. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 4437–4442 (2001)
P. Joliot, A. Joliot, In vivo analysis of the electron transfer within photosystem I: Are the two phylloquinones involved? Biochemistry 38, 11130–11136 (1999)
N. Dashdorj, W. Xu, R.O. Cohen, J.H. Golbeck, S. Savikhin, Asymmetric electron transfer in cyanobacterial photosystem I: charge separation and secondary electron transfer dynamics of mutations near the primary electron acceptor A0. Biophys. J. 88, 1238–1249 (2005)
O.G. Poluektov, J. Niklas, L.M. Utschig, Spin-correlated radical pairs as quantum sensors of bidirectional ET mechanisms in photosystem I. J. Phys. Chem. B 123, 7536–7544 (2019)
O.G. Poluektov, L.M. Utschig, Directionality of electron transfer in type I reaction center proteins: high-frequency EPR study of PSI with removed iron-sulfur centers. J. Phys. Chem. B 119, 13771–13776 (2015)
O.G. Poluektov, S.V. Paschenko, L.M. Utschig, K.V. Lakshmi, M.C. Thurnauer, Bidirectional electron transfer in photosystem I: direct evidence from high-frequency time-resolved EPR spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 11910–11911 (2005)
I.R. Vassiliev, M.L. Antonkine, J.H. Golbeck, Iron-sulfur clusters in type I reaction centers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Bioenerg. 1507, 139–160 (2001)
A.N. Webber, W. Lubitz, P700: the primary electron donor of photosystem I. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1507, 61–79 (2001)
W. Lubitz, EPR studies of the primary electron donor P700 in Photosystem I, in Photosystem I: The Light-Driven Plastocyanin:Ferredoxin Oxidoreductase. ed. by J.H. Golbeck (Springer, Dordrecht, 2006), pp. 245–269
K. Möbius, W. Lubitz, N. Cox, A. Savitsky, Biomolecular EPR meets NMR at high magnetic fields. Magnetochemistry 4, 85 (2018)
M.C. Thurnauer, O.G. Poluektov, G. Kothe, Time-resolved high-frequency and multifrequency EPR studies of spin-correlated radical pairs in photosynthetic reaction center proteins, in Very high frequency (Vhf) ESR/EPR, vol. 22, ed. by O. Grinberg, L.J. Berliner (Springer, New York, 2004), pp. 166–206
O.G. Poluektov, L.M. Utschig, S.L. Schlesselman, K.V. Lakshmi, G.W. Brudvig, G. Kothe, M.C. Thurnauer, Electronic structure of the P700 special pair from high-frequency electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B 106, 8911–8916 (2002)
K. Möbius, A. Savitsky, High-Field EPR Spectroscopy on Proteins and Their Model Systems: Characterization of Transient Paramagnetic States (The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, 2009)
P.J. Bratt, O.G. Poluektov, M.C. Thurnauer, J. Krzystek, L.C. Brunel, J. Schrier, Y.W. Hsiao, M. Zerner, A. Angerhofer, The G-factor anisotropy of plant chlorophyll A. J. Phys. Chem. B 104, 6973–6977 (2000)
A. van der Est, T. Prisner, R. Bittl, P. Fromme, W. Lubitz, K. Mobius, D. Stehlik, Time-resolved X-, K-, and W-band EPR of the radical pair state P700•+A1•- of photosystem I in comparison with P865•+Qa•- in bacterial reaction centers. J. Phys. Chem. B 101, 1437–1443 (1997)
O. Burghaus, M. Plato, M. Rohrer, K. Möbius, F. Macmillan, W. Lubitz, 3 mm high-field EPR on semiquinone radical anions Q•- related to photosynthesis and on the primary donor P•+ and acceptor Qa•- in reaction centers of Rhodobacter sphaeroides R-26. J. Phys. Chem. 97, 7639–7647 (1993)
R. Klette, J.T. Torring, M. Plato, K. Möbius, B. Bonigk, W. Lubitz, Determination of the G-tensor of the primary donor cation radical in single-crystals of Rhodobacter sphaeroides R-26 reaction centers by 3 mm high-field EPR. J. Phys. Chem. 97, 2015–2020 (1993)
J. Bonnerjea, M.C.W. Evans, Identification of multiple components in the intermediary electron carrier complex of photosystem I. FEBS Lett. 148, 313–316 (1982)
P. Gast, T. Swarthoff, F.C.R. Ebskamp, A.J. Hoff, Evidence for a new early acceptor in photosystem-I of plants—an electron-spin-resonance investigation of reaction center triplet yield and of the reduced intermediary acceptors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 722, 163–175 (1983)
S.E.J. Rigby, M.C.W. Evans, P. Heathcote, ENDOR and special triple resonance spectroscopy of A1•- of photosystem. Biochemistry 35, 6651–6656 (1996)
F. MacMillan, J. Hanley, L. van der Weerd, M. Knupling, S. Un, A.W. Rutherford, Orientation of the phylloquinone electron acceptor anion radical in photosystem I. Biochemistry 36, 9297–9303 (1997)
J. Hanley, Y. Deligiannakis, F. MacMillan, H. Bottin, A.W. Rutherford, ESEEM study of the phyllosemiquinone radical A1•- in 14N- and 15N-labeled photosystem I. Biochemistry 36, 11543–11549 (1997)
N. Srinivasan, R. Chatterjee, S. Milikisiyants, J.H. Golbeck, K.V. Lakshmi, Effect of hydrogen bond strength on the redox properties of phylloquinones: a two-dimensional hyperfine sublevel correlation spectroscopy study of photosystem I. Biochemistry 50, 3495–3501 (2011)
J. Niklas, B. Epel, M.L. Antonkine, S. Sinnecker, M.E. Pandelia, W. Lubitz, Electronic structure of the quinone radical anion A1•- of photosystem I investigated by advanced pulse EPR and ENDOR techniques. J. Phys. Chem. B 113, 10367–10379 (2009)
J. Niklas, O. Gopta, B. Epel, W. Lubitz, M.L. Antonkine, Investigation of the stationary and transient A1•- radical in Trp -> Phe mutants of photosystem I. Appl. Magn. Reson. 38, 187–203 (2010)
H.F. Daboll, H.L. Crespi, J.J. Katz, Mass cultivation of algae in pure heavy water. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 4, 281–297 (1962)
L.M. Utschig, L.X. Chen, O.G. Poluektov, Discovery of native metal ion sites located on the ferredoxin docking side of photosystem I. Biochemistry 47, 3671–3676 (2008)
A.Y. Bresgunov, A.A. Dubinskii, V.N. Krimov, Y.G. Petrov, O.G. Poluektov, Y.S. Lebedev, Pulsed EPR in 2-mm band. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2, 715–728 (1991)
W.B. Mims, Pulsed endor experiments. Proc. R. Soc. A 283, 452–457 (1965)
D. Goldfarb, S. Stoll, EPR Spectroscopy: Fundamentals and Methods (Wiley, New Jersey, 2018)
C. Gemperle, A. Schweiger, Pulsed electron-nuclear double resonance methodology. Chem. Rev. 91, 1481–1505 (1991)
A. Schweiger, G. Jeschke, Principles of Pulse Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (Oxford University Press, New York, 2001)
S. Stoll, A. Schweiger, EasySpin, a comprehensive software package for spectral simulation and analysis in EPR. J. Magn. Reson. 178, 42–55 (2006)
P.J. Bratt, M. Rohrer, J. Krzystek, M.C.W. Evans, L.C. Brunel, A. Angerhofer, Submillimeter high-field EPR studies of the primary donor in plant photosystem I P700+. J. Phys. Chem. 101, 9686–9689 (1997)
A. Petrenko, A.L. Maniero, J. van Tol, F. MacMillan, Y. Li, L.C. Brunel, K. Redding, A High-field EPR study of P700+ in wild-type and mutant photosystem I from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Biochemistry 43, 1781–1786 (2004)
T.F. Prisner, A.E. McDermott, S. Un, J.R. Norris, M.C. Thurnauer, R.G. Griffin, Measurement of the g-tensor of the P700+. signal from deuterated cyanobacterial photosystem I particles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 9485–9488 (1993)
S.G. Zech, W. Hofbauer, A. Kamlowski, P. Fromme, D. Stehlik, W. Lubitz, R. Bittl, A structural model for the charge separated state P700•+A1•- in photosystem I from the orientation of the magnetic interaction tensors. J. Phys. Chem. B 104, 9728–9739 (2000)
C. Teutloff, W. Hofbauer, S.G. Zech, M. Stein, R. Bittl, W. Lubitz, High-frequency EPR studies on cofactor radicals in photosystem I. Appl. Magn. Reson. 21, 363–379 (2001)
A.J. Stone, Gauge invariance of g-tensor. Proc. R. Soc. A 271, 424–424 (1963)
A.J. Stone, g-factors of aromatic free radicals. Mol. Phys. 6, 509–515 (1963)
M. Plato, N. Krauss, P. Fromme, W. Lubitz, Molecular orbital study of the primary electron donor P700 of photosystem I based on a recent X-ray single crystal structure analysis. Chem. Phys. 294, 483–499 (2003)
R. Angstl, Contribution of the relativistic mass correction to the g-tensor of molecules. Chem. Phys. 132, 435–442 (1989)
J. Telser, Electron-Nuclear Double Resonance (ENDOR) Spectroscopy. Encyclopedia of Inorganic Chemistry (Wiley, Chichester, 2005)
H. Käss, W. Lubitz, Evaluation of 2D-ESEEM data of 15N-labeled radical cations of the primary donor P700 in photosystem I and chlorophyll a. Chem. Phys. Lett. 251, 193–203 (1996)
H. Käss, E. Bittersmann-Weidlich, L.E. Andreasson, B. Bönigk, W. Lubitz, ENDOR and ESEEM of the 15N labelled radical cations of chlorophyll a and the primary donor P700 in photosystem I. Chem. Phys. Lett. 194, 419–432 (1995)
M. Mac, N.R. Bowlby, G.T. Babcock, J. McCracken, Monomeric spin density distribution in the primary donor of photosystem I as determined by electron magnetic resonance: functional and thermodynamic implications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 120, 13215–13223 (1998)
M.M. Chestnut, S. Milikisiyants, R. Chatterjee, J. Kern, A.I. Smirnov, Electronic structure of the primary electron donor P700+• in photosystem I studied by multifrequency HYSCORE spectroscopy at X- and Q-band. J. Phys. Chem. B 125, 36–48 (2021)
M. Mac, X.S. Tang, B.A. Diner, J. McCracken, G.T. Babcock, Identification of histidine as an axial ligand to P700+. Biochemistry 35, 13288–13293 (1996)
L. Krabben, E. Schlodder, R. Jordan, D. Carbonera, G. Giacometti, H. Lee, A.N. Webber, W. Lubitz, Influence of the axial ligands on the spectral properties of P700 of photosystem I: a study of site-directed mutants. Biochemistry 39, 13012–13025 (2000)
H. Käss, P. Fromme, H.T. Witt, W. Lubitz, Orientation and electronic structure of the primary donor radical cation P700+ in photosystem I: a single crystals EPR and ENDOR study. J. Phys. Chem. B 105, 1225–1239 (2001)
H. Witt, E. Schlodder, C. Teutloff, J. Niklas, E. Bordignon, D. Carbonera, S. Kohler, A. Labahn, W. Lubitz, Hydrogen bonding to P700: site-directed mutagenesis of threonine A739 of photosystem I in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Biochemistry 41, 8557–8569 (2002)
D.G. Artiukhin, P. Eschenbach, J. Neugebauer, Computational investigation of the spin-density asymmetry in photosynthetic reaction center models from first principles. J. Phys. Chem. B 124, 4873–4888 (2020)
D. Goldfarb, B. Epel, H. Zimmermann, G. Jeschke, 2D Triple in orientationally disordered samples—a means to resolve and determine relative orientation of hyperfine tensors. J. Magn. Reson. 168, 75–87 (2004)
E. Schlodder, K. Falkenberg, M. Gergeleit, K. Brettel, Temperature dependence of forward and reverse electron transfer from A1-, the reduced secondary electron acceptor in photosystem I. Biochemistry 37, 9466–9476 (1998)
M.C. Thurnauer, P. Gast, Q-band (35 GHz) electron-paramagnetic resonance results on the nature of A1 and the electron-spin polarization in photosystem I particles. Photobiochem. Photobiophys. 9, 29–38 (1985)
M.A. Yu, T. Egawa, S.R. Yeh, D.L. Rousseau, G.J. Gerfen, EPR characterization of ascorbyl and sulfur dioxide anion radicals trapped during the reaction of bovine cytochrome C oxidase with molecular oxygen. J. Magn. Reson. 203, 213–219 (2010)
J. Niklas, O.G. Poluektov, High-frequency EPR of the sulfur dioxide radical—unpublished results
G. Link et al., Structure of the P700+A1- radical pair intermediate in photosystem I by high time resolution multifrequency electron paramagnetic resonance: analysis of quantum beat oscillations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123, 4211–4222 (2001)
B. Epel, J. Niklas, S. Sinnecker, H. Zimmermann, W. Lubitz, Phylloquinone and related radical anions studied by pulse electron nuclear double resonance spectroscopy at 34 GHz and density functional theory. J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 11549–11560 (2006)
S. Sinnecker, E. Reijerse, F. Neese, W. Lubitz, Hydrogen bond geometries from electron paramagnetic resonance and electron-nuclear double resonance parameters: density functional study of quinone radical anion-solvent interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 3280–3290 (2004)
T.J. Lin, P.J. O’Malley, Binding site influence on the electronic structure and electron paramagnetic resonance properties of the phyllosemiquinone free radical of photosystem I. J. Phys. Chem. B 115, 9311–9319 (2011)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge support by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, Division of Chemical Sciences, Geosciences, and Biosciences, through Argonne National Laboratory under Contract No. DE-AC02-06CH11357. The authors acknowledge Arlene Wagner for growth of perdeuterated and 15N-labeled cyanobacteria.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niklas, J., Brahmachari, U., Utschig, L.M. et al. D‐Band EPR and ENDOR Spectroscopy of 15N‐Labeled Photosystem I. Appl Magn Reson 53, 1175–1193 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-021-01438-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-021-01438-8