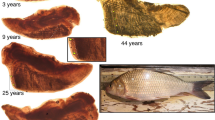
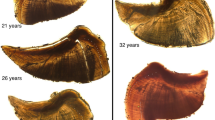
Abstract
Otoliths can record growth information of fishes. This information is valuable in reconstructing growth history and evaluating environmental changes on marine resources. Small yellow croaker (Larimichthys polyactis) is a commercially and ecologically important species in the East China Sea. Yet, continuous long-term growth patterns and the environmental factors that affect growth remain unknown. In this study, 17 years of otolith growth pattern of small yellow croaker was reconstructed using chronology analysis. Mixed modeling was applied to identify the effects of physical and biological processes on growth patterns, as well as the key climate driver that influences the species. The optimal model was built by a random slope and intercept for FishID, random intercept for Year and Cohort, and Age as an intrinsic factor. Reconstructed otolith growth demonstrated significant variability among years and cohorts, with a short-term pattern observed in periods of 3–5 years. The growth of small yellow croaker negatively responded to rising summer temperature, and such response coincides with recent population dynamic that shifts northwards. Kuroshio intrusions during winter promoted the otolith growth of small yellow croaker for the following year. The result helps better understand and predict population dynamic of small yellow croaker, but the revealed situation of resource is not encouraging and makes management challenging. Active fishery management measures for biological characters of fish populations should be considered.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Some or all data, models, or code generated or used during the study are proprietary or confidential in nature and may only be provided with restrictions.
References
Alongi DM (1998) Coastal ecosystem processes. CRC Press
Audzijonyte A, Kuparinen A, Gorton R, Fulton EA (2013) Ecological consequences of body size decline in harvested fish species: positive feedback loops in trophic interactions amplify human impact. Biol Let 9(2):20121103. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsbl.2012.1103
Bakun A, Black BA, Bograd SJ, García-Reyes M, Miller AJ, Rykaczewski RR, Sydeman WJ (2015) Anticipated effects of climate change on coastal upwelling ecosystems. Current Climate Change Reports 1(2):85–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40641-015-0008-4
Barton BA, Morgan JD, Vijayan MM (2002) Physiological and condition-related indicators of environmental stress in fish. American Fisheries Society, 111–148, Bethesda
Belkin IM (2009) Rapid warming of Large Marine Ecosystems. Prog Oceanogr 81(1):207–213
Chang NN, Shiao JC, Gong GC (2012) Diversity of demersal fish in the East China Sea: implication of eutrophication and fishery. Cont Shelf Res 47(15):42–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2012.06.011
Cheunge WWL, Watson R, Pauly D (2013) Signature of ocean warming in global fisheries catch. Nature 497(7449):365–368. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12156
Christie GC, Regier HA (1988) Measures of optimal thermal habitat and their relationship to yields for four commercial fish species. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 45(2):301–314
Doubleday ZA, Izzo C, Haddy JA, Lyle JM, Ye Q, Gillanders BM (2015) Long-term patterns in estuarine fish growth across two climatically divergent regions. Oecologia 179(4):1079–1090. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-015-3411-6
García-Comas C, Chang CY, Ye L, Sastri AR, Lee YC, Gong GC, Hsieh CH (2014) Mesozooplankton size structure in response to environmental conditions in the East China Sea: how much does size spectra theory fit empirical data of a dynamic coastal area? Prog Oceanogr 121:141–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pocean.2013.10.010
Gong GC, Wen YH, Wang BW, Liu GJ (2003) Seasonal variation of chlorophyll a concentration, primary production and environmental conditions in the subtropical East China Sea. Deep Sea Res Part II Top Stud Oceanogr 50(6–7):1219–1236. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0967-0645(03)00019-5
Hoegh-Guldberg O, Bruno JF (2010) The impact of climate change on the world’s marine ecosystems. Science 328(5985):1523–1528. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1189930
Hung JJ, Chen CH, Gong GC, Sheu DD, Shiah FK (2003) Distributions, stoichiometric patterns and cross-shelf exports of dissolved organic matter in the East China Sea. Deep Sea Res Part II Top Stud Oceanogr 50(6–7):1127–1145. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0967-0645(03)00014-6
Johnson RH, Toy MD (2017) SST gradients and the East Asian early-summer monsoon. The Global Monsoon System: Research and Forecast(3rd edition), 3–12
Jung S, Pang IC, Lee Jh, Choi I, Cha HK (2013) Latitudinal shifts in the distribution of exploited fishes in Korean waters during the last 30 years: a consequence of climate change. Rev Fish Biol Fisheries 24(2):443–462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11160-013-9310-1
Keeling RE, Kortzinger A, Gruber N (2010) Ocean deoxygenation in a warming world. Ann Rev Mar Sci 2:463–493. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.marine.010908.163855
Kilduff DP, Lorenzo ED, Botsford LW, Teo SLH (2015) Changing central Pacific El Niños reduce stability of North American salmon survival rates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112(35):10962–10966. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1503190112
Kim S, Jung S, Zhang CI (1997) The effect of seasonal anomalies of seawater temperature and salinity on the fluctuation in yields of small yellow croaker, Pseudosciaena polyactis, in the Yellow Sea. Fish Oceanogr 6(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2419.1997.00025.x
Kim YS, Jang CJ, Yeh SW (2018) Recent surface cooling in the Yellow and East China Seas and the associated North Pacific climate regime shift. Cont Shelf Res 156(15):43–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2018.01.009
Li ZL, Shan XJ, Jin XS, Dai FQ (2011) Long-term variations in body length and age at maturity of the small yellow croaker (Larimichthys polyactis Bleeker, 1877) in the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea, China. Fish Res 110(1):67–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fishres.2011.03.013
Liu QH, Ma L, Li XZ (2020) The communities of meiofauna in the northern East China Sea and their responses to runoff and the intrusion of Kuroshio Current. Haiyang Xuebao 42(2):52–64. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0253−4193.2020.02.006
Liu XS, Yang CH, Ye JX (1964) The primary research of annuli characteristics and formation patterns of scale and otolith for small yellow croaker in Northern Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea. China Agriculture Press, Beijing
Liu XY, Liu YG, Guo L, Rong ZR, Gu YZ, Liu YH (2010) Interannual changes of sea level in the two regions of East China Sea and different responses to ENSO. Global Planet Change 72(3):215–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2010.04.009
Ma QY, Jiao Y, Ren YP (2017) Linear mixed-effects models to describe length-weight relationships for yellow croaker (Larimichthys polyactis) along the north coast of China. PLoS One 12(2):e0171811. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0171811
Ma SY, Cheng JH, Li JC, Liu Y, Wan R, Tian YJ (2019) Interannual to decadal variability in the catches of small pelagic fishes from China Seas and its responses to climatic regime shifts. Deep Sea Res Part II 159:112–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr2.2018.10.005
Matsuno T, Lee JS, Yanao S (2009) Influence of the Kuroshio on the water properties in the shelf. Ocean Sci Discuss 6(1):741–764
McLaughlin JF, Hellmann JJ, Boggs CL, Ehrlich PR (2002) The route to extinction: population dynamics of a threatened butterfly. Oecologia 132(4):538–548. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-002-0997-2
Morrongiello JR, Ronald ET (2016) A statistical framework to explore ontogenetic growth variation among individuals and populations: a marine fish example. Ecol Monogr 85(1):93–115. https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.c.3309903.v1
Morrongiello JR, Sweetman PC, Thresher RE (2019) Fishing constrains phenotypic responses of marine fish to climate variability. J Anim Ecol 88(11):1645–1656. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2656.12999
Morrongiello JR, Thresher RE, Smith DC (2012) Aquatic biochronologies and climate change. Nat Clim Chang 2(12):849–857. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate1616
Neuheimer AB, Thresher RE, Lyle JM, Semmens JM (2011) Tolerance limit for fish growth exceeded by warming waters. Nat Clim Chang 1(2):110–113. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate1084
Ning X, Lin C, Su J, Liu C, Hao Q, Le F (2011) Long-term changes of dissolved oxygen, hypoxia, and the responses of the ecosystems in the East China Sea from 1975 to 1995. J Oceanogr 67(1):59–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10872-011-0006-7
Ong JJL et al (2018) A boundary current drives synchronous growth of marine fishes across tropical and temperate latitudes. Glob Change Biol 24(5):1894–1903. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.14083
Pang YM et al (2018) Variability of coastal cephalopods in overexploited China Seas under climate change with implications on fisheries management. Fish Res 208:22–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fishres.2018.07.004
Park T, Jang CJ, Jungclaus JH, Haak H, Park W, Sang OhI (2011) Effects of the Changjiang river discharge on sea surface warming in the Yellow and East China Seas in summer. Cont Shelf Res 31(1):15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2010.10.012
Pei YH, Liu XH, He HL (2017) Interpreting the sea surface temperature warming trend in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Sci China Earth Sci 60(8):1558–1568. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-017-9054-5
Pol M et al (2016) Identifying the best climatic predictors in ecology and evolution. Methods Ecol Evol 7(10):1246–1257. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210x.12590
Qu TD, Kim YY, Yaremchuk M, Tozuka T, Ishida A, Yamagata T (2004) Can Luzon Strait transport play a role in conveying the impact of ENSO to the South China Sea? J Clim 17(18):3644–3657. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(2004)017%3c3644:clstpa%3e2.0.co;2
Roessig JM, Woodley CM, Cech JJ, Hansen LJ (2004) Effects of global climate change on marine and estuarine fishes and fisheries. Rev Fish Biol Fisheries 14(2):251–275
Shan XJ, Li XS, Yang T, Sharifuzzaman SM, Zhang GZ, Jin XS, Dai FQ (2017) Biological responses of small yellow croaker (Larimichthyspolyactis) to multiple stressors: a case study in the Yellow Sea. China. Acta Oceanologica Sinica 36(10):39–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-017-1091-2
Siswanto E, Nakata H, Matsuoka Y, Tanaka K, Kiyomoto Y, Okamura K, Zhu JR, Ishizaka J (2008) The long-term freshening and nutrient increases in summer surface water in the northern East China Sea in relation to Changjiang discharge variation. Journal of Geophysical Research 113(C10030) https://doi.org/10.1029/2008jc004812
Smoliński S (2019) Incorporation of optimal environmental signals in the prediction of fish recruitment using random forest algorithms. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 76(1):15–27. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjfas-2017-0554
Tang QS, Sherman K (1999) The large marine ecosystems of the Pacific Rim: assessment, sustainability,and management: a report of a symposium held in Qingdao, People’s Republic of China, 8–11 October 1994. IUCN
van der Sleen P, Dzaugis MP, Gentry C, Hall WP, Hamilton V, Helser TE, Matta ME, Underwood CA, Zuercher R, Black BA (2016) Long-term Bering Sea environmental variability revealed by a centennial-length biochronology of Pacific ocean perch Sebastes alutus. Climate Res 71(1):33–45. https://doi.org/10.3354/cr01425
Vélez-Belchí P, Centurioni LR, Lee DK, Jan S, Niiler PP (2013) Eddy induced Kuroshio intrusions onto the continental shelf of the East China Sea. J Mar Res 71(1):83–108
Wang ZZ, Zuo JC, Chen MX, Xu Q, Yang YQ (2012) Relationship between El Niño and sea surface temperature variation in coastal region of Yellow Sea and East China Sea. J Hohai Univ (Natural Sciences) 40(4):461–468. https://doi.org/10.3876/j.issn.1000-1980.2012.04.018
Wu CR, Hsin YC, Chiang TL, Lin YF, Tsui IF (2015) Seasonal and interannual changes of the Kuroshio intrusion onto the East China Sea Shelf. J Geophys Res Oceans 119(8):5039–5051. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013JC009748
Wu RH, Li CY, Lin JM (2017) Enhanced winter warming in the Eastern China Coastal Waters and its relationship with ENSO. Atmos Sci Lett 18(1):11–18. https://doi.org/10.1002/asl.718
Yang DZ et al (2017) Advance in research on Kuroshio intrusion and its ecological influence on the continental shelf of East China Sea. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica 48(6):1196–1207. https://doi.org/10.11693/hyhz20170900223
Zhang C, Ye ZJ, Wan R, Ma QY, Li ZG (2014) Investigating the population structure of small yellow croaker (Larimichthys polyactis) using internal and external features of otoliths. Fish Res 153:41–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fishres.2013.12.012
Zhang S, Yu F, Diao XY, Guo JS (2009) The characteristic analysis on sea surface temperature inter-annual variatio in the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Marine Science 33(8):76–81
Zuur AF, Ieno EN, Walker NJ, Saveliev AA, Smith GM (2009) Mixed effects models and extensions in ecology with R. J Roy Stat Soc 173(4):938–939. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-985x.2010.00663_9.x
Acknowledgements
We thank Captain Shifang Liu for his assistance in sample collection.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Key R and D Program of China (2018YFD0900903).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and conflict of interest statement
All authors certify that this manuscript is original and has not been published and will not be submitted elsewhere for publication while being considered by Environmental Biology of Fishes. No data have been fabricated or manipulated (including images) to support the conclusion. No data, text, or theories by others are presented as if they were our own. And authors whose names appear on the submission have contributed sufficiently to the scientific work and therefore share collective responsibility and accountability for the results. All authors have no competing interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Ye, Z. Inter-annual otolith growth pattern of adult small yellow croaker in the East China Sea and its response to environmental changes. Environ Biol Fish 104, 1643–1653 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-021-01192-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-021-01192-7