Abstract
Purpose
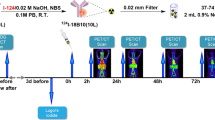
A novel cystine-knot peptide–based PET radiopharmaceutical, 18F-FP-R01-MG-F2 (knottin), was developed to selectively bind to human integrin αvβ6 which is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the safety, biodistribution, dosimetry, and lesion uptake of 18F-FP-R01-MG-F2 in patients with pancreatic cancer.
Methods
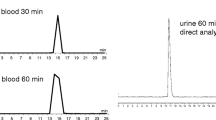
Fifteen patients (6 men, 9 women) with histologically confirmed pancreatic cancer were prospectively enrolled and underwent knottin PET/CT between March 2017 and February 2021 (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier NCT02683824). Vital signs and laboratory results were collected before and after the imaging scans. Maximum standardized uptake values (SUVmax) and mean SUV (SUVmean) were measured in 24 normal tissues and pancreatic cancer lesions for each patient. From the biodistribution data, the organ doses and whole-body effective dose were calculated using OLINDA/EXM software.
Results
There were no significant changes in vital signs or laboratory values that qualified as adverse events or serious adverse events. At 1 h post-injection, areas of high 18F-FP-R01-MG-F2 uptake included the pituitary gland, stomach, duodenum, kidneys, and bladder (average SUVmean: 9.7–14.5). Intermediate uptake was found in the normal pancreas (average SUVmean: 4.5). Mild uptake was found in the lungs and liver (average SUVmean < 1.0). The effective dose was calculated to be 2.538 × 10−2 mSv/MBq. Knottin PET/CT detected all known pancreatic tumors in the 15 patients, although it did not detect small peri-pancreatic lymph nodes of less than 1 cm in short diameter in two of three patients who had lymph node metastases at surgery. Knottin PET/CT detected distant metastases in the lungs (n = 5), liver (n = 4), and peritoneum (n = 2), confirmed by biopsy and/or contrast-enhanced CT.
Conclusion
18F-FP-R01-MG-F2 is a safe PET radiopharmaceutical with an effective dose comparable to other diagnostic agents. Evaluation of the primary pancreatic cancer and distant metastases with 18F-FP-R01-MG-F2 PET is feasible, but larger studies are required to define the role of this approach.
Trial registration
NCT02683824.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material (data transparency)
Yes.
Code availability (software application or custom code)
Yes.
References
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–49. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660.
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2021. CA: Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:7–33. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21654.
Allen PJ, Kuk D, Castillo CF, Basturk O, Wolfgang CL, Cameron JL, et al. Multi-institutional validation study of the American Joint Commission on Cancer (8th edition) changes for T and N staging in patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg. 2017;265:185–91. https://doi.org/10.1097/sla.0000000000001763.
Breuss J, Gallo J, DeLisser H, Klimanskaya I, Folkesson H, Pittet J, et al. Expression of the beta 6 integrin subunit in development, neoplasia and tissue repair suggests a role in epithelial remodeling. J Cell Sci. 1995;108:2241–51.
Sipos B, Hahn D, Carceller A, Piulats J, Hedderich J, Kalthoff H, et al. Immunohistochemical screening for beta6-integrin subunit expression in adenocarcinomas using a novel monoclonal antibody reveals strong up-regulation in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas in vivo and in vitro. Histopathology. 2004;45:226–36. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2559.2004.01919.x.
Maubant S, Cruet-Hennequart S, Dutoit S, Denoux Y, Crouet H, Henry-Amar M, et al. Expression of alpha V-associated integrin beta subunits in epithelial ovarian cancer and its relation to prognosis in patients treated with platinum-based regimens. J Mol Histol. 2005;36:119–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-004-4273-0.
Orimoto AM, Neto CF, Pimentel ER, Sanches JA, Sotto MN, Akaishi E, et al. High numbers of human skin cancers express MMP2 and several integrin genes. J Cutan Pathol. 2008;35:285–91.
Bates RC, Bellovin DI, Brown C, Maynard E, Wu B, Kawakatsu H, et al. Transcriptional activation of integrin β6 during the epithelial-mesenchymal transition defines a novel prognostic indicator of aggressive colon carcinoma. J Clin Investig. 2005;115:339–47.
Elayadi AN, Samli KN, Prudkin L, Liu YH, Bian A, Xie XJ, et al. A peptide selected by biopanning identifies the integrin alphavbeta6 as a prognostic biomarker for nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2007;67:5889–95. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-07-0245.
Hazelbag S, Kenter GG, Gorter A, Dreef EJ, Koopman LA, Violette SM, et al. Overexpression of the alpha v beta 6 integrin in cervical squamous cell carcinoma is a prognostic factor for decreased survival. J Pathol. 2007;212:316–24. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.2168.
Zhang ZY, Xu KS, Wang JS, Yang GY, Wang W, Wang JY, et al. Integrin alphanvbeta6 acts as a prognostic indicator in gastric carcinoma. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2008;20:61–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clon.2007.09.008.
Kimura RH, Wang L, Shen B, Huo L, Tummers W, Filipp FV, et al. Evaluation of integrin alphavbeta6 cystine knot PET tracers to detect cancer and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Nat Commun. 2019;10:4673. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-11863-w.
Stabin MG, Sparks RB, Crowe E. OLINDA/EXM: the second-generation personal computer software for internal dose assessment in nuclear medicine. J Nucl Med. 2005;46:1023–7.
Nordhausen K, Oja H. Multivariate L1 methods: the package MNM. J Stat Softw. 2011;43:1–28.
Yeh R, Dercle L, Garg I, Wang ZJ, Hough DM, Goenka AH. The role of 18F-FDG PET/CT and PET/MRI in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2018;43:415–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-017-1374-2.
Niu J, Li Z. The roles of integrin αvβ6 in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2017;403:128–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2017.06.012.
Koivisto L, Bi J, Häkkinen L, Larjava H. Integrin αvβ6: structure, function and role in health and disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2018;99:186–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2018.04.013.
Färber SF, Wurzer A, Reichart F, Beck R, Kessler H, Wester HJ, et al. Therapeutic radiopharmaceuticals targeting integrin αvβ6. ACS Omega. 2018;3:2428–36. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b00035.
Hausner SH, Bauer N, Hu LY, Knight LM, Sutcliffe JL. The effect of bi-terminal PEGylation of an integrin αvβ6-targeted 18F peptide on pharmacokinetics and tumor uptake. J Nucl Med. 2015;56:784–90. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.114.150680.
Nothelfer EM, Zitzmann-Kolbe S, Garcia-Boy R, Krämer S, Herold-Mende C, Altmann A, et al. Identification and characterization of a peptide with affinity to head and neck cancer. J Nucl Med. 2009;50:426–34. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.108.058123.
Kraft S, Diefenbach B, Mehta R, Jonczyk A, Luckenbach GA, Goodman SL. Definition of an unexpected ligand recognition motif for alphav beta6 integrin. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:1979–85. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.4.1979.
Altmann A, Sauter M, Roesch S, Mier W, Warta R, Debus J, et al. Identification of a novel ITGalphavbeta6-binding peptide using protein separation and phage display. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23:4170–80. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-3217.
Flechsig P, Lindner T, Loktev A, Roesch S, Mier W, Sauter M, et al. PET/CT Imaging of NSCLC with a alphavbeta6 integrin-targeting peptide. Mol Imaging Biol. 2019;21:973–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-018-1296-6.
Acknowledgements
We thank the radiochemistry staff and the nuclear medicine technologists. Special thanks to the participants and their families.
Funding
The study was supported by the National Cancer Institute (1U01CA21002001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RN: content planning, data analyses, manuscript writing and editing; VF: data analyses, manuscript editing; HD: data analyses, manuscript editing; NH: data collection; MG: data collection; JR: statistical analyses; RK: content planning, data analyses; MW: data analyses; TH: data collection; RK: data collection; BS: data collection; WP: data analyses, manuscript editing, AI content planning, data analyses, manuscript editing; SS: content planning, manuscript editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Yes.
Consent to participate
Yes.
Consent for publication
Yes.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Oncology—Digestive tract
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakamoto, R., Ferri, V., Duan, H. et al. Pilot-phase PET/CT study targeting integrin αvβ6 in pancreatic cancer patients using the cystine-knot peptide–based 18F-FP-R01-MG-F2. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 50, 184–193 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-021-05595-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-021-05595-7