Abstract
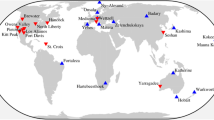
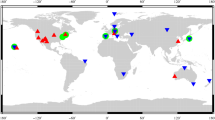
CONT17 is an observation campaign of continuous Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) sessions for a period of 15 days, carried out by the International VLBI Service for Geodesy and Astrometry (IVS). This campaign represents an interesting opportunity for the inter-comparison of space geodetic techniques given that they share the same observability conditions in co-located sites. In this work, VLBI estimates of Earth orientation parameters (EOP), station coordinates and troposphere—zenith total delays (ZTD) and gradients—are compared to those estimated by means of Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) observations. We considered solutions from different software packages and processing techniques for this analysis, including all the available IVS and IGS (International GNSS Service) solutions and two VLBI series obtained by the authors. This extensive analysis provides a representative view of the inter-technique differences under the same observation conditions. We considered in the analysis the two VLBI legacy S/X networks that took part in the CONT17 campaign. We found that the EOP WRMS with respect to IGS final products is similar to previous CONT campaigns, even using global VLBI solutions that assimilate the data from both CONT17 legacy-1 and legacy-2 networks. Repeatabilities of estimated VLBI antenna coordinates of the legacy-1 network have a similar behaviour than GNSS-based repeatabilities in east and north components and slightly worse in up component whereas the repeatabilities of the legacy-2 network are smaller than legacy-1 network and similar to the IGS combined solution. Finally, troposphere inter-technique differences in terms of ZTD and gradients also show a similar agreement to different sources of GNSS-based troposphere estimates.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
The datasets analysed in this study are freely available at IVS and IGS servers. VLBI series estimated by the authors and results of the analysis carried out can be made available by the corresponding author on request.
References
Altamimi Z, Rebischung P, Métivier L, Collilieux X (2016) ITRF2014: a new release of the international terrestrial reference frame modeling nonlinear station motions. J Geophys Res: Solid Earth 8(121):6109–6131. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016JB013098
Bachmann S, Thaller D, Roggenbuck O et al (2016) IVS contribution to ITRF2014. J Geod 90:631–654. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-016-0899-4
Böhm J, Werl B, Schuh H (2006) Troposphere mapping functions for GPS and very long baseline interferometry from European centre for medium-range weather forecasts operational analysis data. J Geophys Res 111(B02):406. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JB003629
Böhm J, Böhm S, Boisits J, Girdiuk A, Gruber J, Hellerschmied A, Krásná H, Landskron D, Madzak M, Mayer D, McCallum J, McCallum L, Schartner M, Teke K (2018) Vienna VLBI and satellite software (VieVS) for geodesy and astrometry. Publ Astron Soc Pac 130(986):044503. https://doi.org/10.1088/1538-3873/aaa22b
Brunner FK, Rüeger JM (1992) Theory of the local scale parameter method for EDM. Bull Géodésique 66:355–364
Charlot P, Jacobs CS, Gordon D, Lambert S, de Witt A, Böhm J, Fey AL, Heinkelmann R, Skurikhina E, Titov O, Arias EF, Bolotin S, Bourda G, Ma C, Malkin Z, Nothnagel A, Mayer D, MacMillan DS, Nilsson T, Gaume R (2020) The third realization of the international celestial reference frame by very long baseline interferometry. Astron Astrophys. https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/202038368
Conventions IERS (2010) Petit G, Luzum, B (eds) IERS Technical Note 36. Verlag des Bundesamts für Kartographie und Geodäsie, Frankfurt a. M
Hobiger T, Otsubo T (2014) Combination of GPS and VLBI on the observation level during CONT11-common parameters, ties and inter-technique biases. J Geod 88:1017. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-014-0740-x
Johnston G, Riddell A, Hausler G (2017) The international GNSS service. In: Teunissen PJG, Montenbruck O (eds) Springer handbook of global navigation satellite systems, 1st edn. Springer, Cham, pp 967–982. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-42928-1
Karbon M, Soja N, Nilsson T, Deng Z, Heinkelmann R, Schuh H (2017) Earth orientation parameters from VLBI determined with a Kalman filter. Geod Geodyn 8(6):396–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geog.2017.05.006
Kirkvik AS, Hjelle GA, Dähnn M, Fausk I, Mysen E (2017) Where—a new software for geodetic analysis. In: 23th EVGA working meeting and 18th IVS analysis workshop
MacMillan DS (2017) EOP and scale from continuous VLBI observing: CONT campaigns to future VGOS networks. J Geod 91:819–829. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-017-1003-4
Malkin Z (2009) On comparison of the earth orientation parameters obtained from different VLBI networks and observing programs. J Geod 83:547–556. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-008-0265-2
Nilsson T, Heinkelmann R, Karbon M et al (2014) Earth orientation parameters estimated from VLBI during the CONT11 campaign. J Geod 88:491–502. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-014-0700-5
Nilsson T, Balidakis K, Heinkelmann R, Schuh H (2019) Earth orientation parameters from the CONT17 campaign. Geophysica 54(1):19–25
Nothnagel A, Artz T, Behrend D, Malkin Z (2017) International VLBI service for geodesy and astrometry–delivering high-quality products and embarking on observations of the next generation. J Geod 91:711–721. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-016-0950-5
Pacione R, Pace B, de Haan S, Vedel H, Lanotte R, Vespe F (2011) Combination methods of tropospheric time series. Adv Space Res 47(2):323–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2010.07.021
Ray J, Rebischung P, Griffiths J (2017) IGS polar motion measurement accuracy. Geod Geodyn 8(6):413–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geog.2017.01.008
Rothacher M, Beutler G, Herring TA, Weber R (1999) Estimation of nutation using the global positioning system. J Geophys Res 104:4835–4860
Teke K, Böhm J, Nilsson T, Schuh H, Steigenberger P, Dach R, Heinkelmann R, Willis P, Haas R, Garcia-Espada S, Hobiger T, Ichikawa R, Shimizu S (2011) Multi-technique comparison of troposphere zenith delays and gradients during CONT08. J Geod 85(7):395–413. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-010-0434-y
Teke K, Nilsson T, Böhm J et al (2013) Troposphere delays from space geodetic techniques, water vapor radiometers, and numerical weather models over a series of continuous VLBI campaigns. J Geod 87:981–1001. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-013-0662-z
Zumberge JF, Heflin MB, Jefferson DC, Watkins MM, Webb FH (1997) Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J Geophys Res 102(B3):5005–17
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to all parties that contributed to the success of the CONT17 campaign, in particular to the IVS Coordinating Center at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) for taking the bulk of the organizational load, to the GSFC VLBI group for preparing the legacy S/X observing schedules and MIT Haystack Observatory for the VGOS observing schedules, to the IVS observing stations at Badary and Zelenchukskaya (both Institute for Applied Astronomy, IAA, St. Petersburg, Russia), Fortaleza (Rádio Observatório Espacial do Nordeste, ROEN; Center of Radio Astronomy and Astrophysics, Engineering School, Mackenzie Presbyterian University, Sao Paulo and Brazilian Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas Espaciais, INPE, Brazil), GGAO (MIT Haystack Observatory and NASA GSFC, USA), Hartebeesthoek (Hartebeesthoek Radio Astronomy Observatory, National Research Foundation, South Africa), the AuScope stations of Hobart, Katherine and Yarragadee (Geoscience Australia, University of Tasmania), Ishioka (Geospatial Information Authority of Japan), Kashima (National Institute of Information and Communications Technology, Japan), Kokee Park (U.S. Naval Observatory and NASA GSFC, USA), Matera (Agencia Spatiale Italiana, Italy), Medicina (Istituto di Radioastronomia, Italy), Ny Ålesund (Kartverket, Norway), Onsala (Onsala Space Observatory, Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden), Seshan (Shanghai Astronomical Observatory, China), Warkworth (Auckland University of Technology, New Zealand), Westford (MIT Haystack Observatory), Wettzell (Bundesamt für Kartographie und Geodäsie and Technische Universität München, Germany) and Yebes (Instituto Geográfico Nacional, Spain) plus the Very Long Baseline Array (VLBA) stations of the Long Baseline Observatory (LBO) for carrying out the observations under the US Naval Observatory’s time allocation, to the staff at the MPIfR/BKG Correlator Center, the VLBA Correlator at Socorro and the MIT Haystack Observatory Correlator for performing the correlations and the fringe fitting of the data, and to the IVS Data Centers at BKG (Leipzig, Germany), Observatoire de Paris (France) and NASA CDDIS (Greenbelt, MD, USA) for the central data holds. We wish to also thank the hard work of IGS contributors for providing high-quality data and products and the very valuable feedback provided by the three anonymous reviewers of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
VP designed the study, collected IVS and IGS series, performed the different comparisons and wrote the manuscript. EA and YGE participated in the analysis of VLBI series using VieVS and Where software packages. SGE provided support and reviewed the manuscript. All authors provided critical feedback and helped to shape the research and the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Puente, V., Azcue, E., Gomez-Espada, Y. et al. Comparison of common VLBI and GNSS estimates in CONT17 campaign. J Geod 95, 120 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-021-01565-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-021-01565-x