Abstract
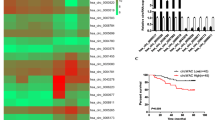
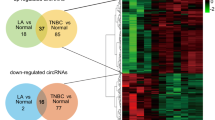
Approximately 25% of breast cancer (BC) patients are HER2-positive. Trastuzumab is used as a targeted therapy drug to treat HER2-positive BC patients; however, the drug resistance remains a big challenge. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are reported to be involved in drug resistance, but the role of circ_0001598 has never been studied in BC. First, we identified the expression of circ_0001598 by RT-qPCR in BC. The gain-of-function and loss-of-function studies were applied to study the functional roles of circ_0001598 and its target gene. We observed upregulation of circ_0001598 in BC tissues, especially in trastuzumab-resistant BC samples. We further identified that miR-1184 is a functional target of circ_0001598. Moreover, it was found that programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) was a direct target of miR-1184. The oncogenic effects of circ_0001598 in promoting BC cell growth, trastuzumab-resistance, PD-L1 expression, and escaping of CD8 T cell killing were abolished after the restoration of miR-1184. In conclusion, we demonstrate that circ_0001598/miR-1184/PD-L1 signaling plays a crucial role in the regulation of BC progression and trastuzumab-resistance phonotypes, which suggests that circ_0001598 may be a molecular target to treat HER2-positive BC patients.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The data to generate the figures could be obtained upon reasonable request to the authors.
References
Harbeck N, Penault-Llorca F, Cortes J, Gnant M, Houssami N, Poortmans P, et al. Breast cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019;5(1):66. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-019-0111-2.
Akram M, Iqbal M, Daniyal M, Khan AU. Awareness and current knowledge of breast cancer. Biol Res. 2017;50(1):33. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40659-017-0140-9.
Yersal O, Barutca S. Biological subtypes of breast cancer: prognostic and therapeutic implications. World J Clin Oncol. 2014;5(3):412–24. https://doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v5.i3.412.
Dai X, Li T, Bai Z, Yang Y, Liu X, Zhan J, et al. Breast cancer intrinsic subtype classification, clinical use and future trends. Am J Cancer Res. 2015;5(10):2929–43.
Pernas S, Tolaney SM. HER2-positive breast cancer: new therapeutic frontiers and overcoming resistance. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2019;11:1758835919833519. https://doi.org/10.1177/1758835919833519.
Goutsouliak K, Veeraraghavan J, Sethunath V, De Angelis C, Osborne CK, Rimawi MF, et al. Towards personalized treatment for early stage HER2-positive breast cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2020;17(4):233–50. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41571-019-0299-9.
Cho HS, Mason K, Ramyar KX, Stanley AM, Gabelli SB, Denney DW Jr, et al. Structure of the extracellular region of HER2 alone and in complex with the Herceptin Fab. Nature. 2003;421(6924):756–60. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01392.
Han Y, Wang J, Liu W, Yuan P, Li Q, Zhang P, et al. Trastuzumab treatment after progression in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer following relapse of trastuzumab-based regimens: a meta-analysis. Cancer Manag Res. 2019;11:4699–706. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S198962.
Wang YC, Morrison G, Gillihan R, Guo J, Ward RM, Fu X, et al. Different mechanisms for resistance to trastuzumab versus lapatinib in HER2-positive breast cancers—role of estrogen receptor and HER2 reactivation. Breast Cancer Res. 2011;13(6):R121. https://doi.org/10.1186/bcr3067.
Fiszman GL, Jasnis MA. Molecular mechanisms of trastuzumab resistance in HER2 overexpressing breast cancer. Int J Breast Cancer. 2011;2011: 352182. https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/352182.
Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, Torti F, Krueger J, Rybak A, et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature. 2013;495(7441):333–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11928.
Zhao Z, Wang K, Wu F, Wang W, Zhang K, Hu H, et al. circRNA disease: a manually curated database of experimentally supported circRNA-disease associations. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(5):475. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0503-3.
Wang L, Tong X, Zhou Z, Wang S, Lei Z, Zhang T, et al. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0008305 (circPTK2) inhibits TGF-beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis by controlling TIF1gamma in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer. 2018;17(1):140. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0889-7.
Li J, Ma M, Yang X, Zhang M, Luo J, Zhou H, et al. Circular HER2 RNA positive triple negative breast cancer is sensitive to Pertuzumab. Mol Cancer. 2020;19(1):142. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-01259-6.
Zhao M, Xu J, Zhong S, Liu Y, Xiao H, Geng L, et al. Expression profiles and potential functions of circular RNAs in extracellular vesicles isolated from radioresistant glioma cells. Oncol Rep. 2019;41(3):1893–900. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2019.6972.
Zhang H, Yan J, Lang X, Zhuang Y. Expression of circ_001569 is upregulated in osteosarcoma and promotes cell proliferation and cisplatin resistance by activating the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Oncol Lett. 2018;16(5):5856–62. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.9410.
Nigro JM, Cho KR, Fearon ER, Kern SE, Ruppert JM, Oliner JD, et al. Scrambled exons. Cell. 1991;64(3):607–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(91)90244-s.
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK, et al. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 2013;495(7441):384–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11993.
Baumann K. CircRNAs in lifespan. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(8):420. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-020-0269-1.
Lu L, Sun J, Shi P, Kong W, Xu K, He B, et al. Identification of circular RNAs as a promising new class of diagnostic biomarkers for human breast cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8(27):44096–107. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.17307.
Wang H, Xiao Y, Wu L, Ma D. Comprehensive circular RNA profiling reveals the regulatory role of the circRNA-000911/miR-449a pathway in breast carcinogenesis. Int J Oncol. 2018;52(3):743–54. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2018.4265.
Wu J, Jiang Z, Chen C, Hu Q, Fu Z, Chen J, et al. CircIRAK3 sponges miR-3607 to facilitate breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2018;430:179–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2018.05.033.
Housman G, Byler S, Heerboth S, Lapinska K, Longacre M, Snyder N, et al. Drug resistance in cancer: an overview. Cancers (Basel). 2014;6(3):1769–92. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers6031769.
Mansoori B, Mohammadi A, Davudian S, Shirjang S, Baradaran B. The different mechanisms of cancer drug resistance: a brief review. Adv Pharm Bull. 2017;7(3):339–48. https://doi.org/10.15171/apb.2017.041.
Nikolaou M, Pavlopoulou A, Georgakilas AG, Kyrodimos E. The challenge of drug resistance in cancer treatment: a current overview. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2018;35(4):309–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-018-9903-0.
Hua X, Sun Y, Chen J, Wu Y, Sha J, Han S, et al. Circular RNAs in drug resistant tumors. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;118:109233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109233.
Xu T, Wang M, Jiang L, Ma L, Wan L, Chen Q, et al. CircRNAs in anticancer drug resistance: recent advances and future potential. Mol Cancer. 2020;19(1):127. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-01240-3.
Liang Y, Song X, Li Y, Su P, Han D, Ma T, et al. circKDM4C suppresses tumor progression and attenuates doxorubicin resistance by regulating miR-548p/PBLD axis in breast cancer. Oncogene. 2019;38(42):6850–66. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-019-0926-z.
Chen J, Yang J, Fei X, Wang X, Wang K. CircRNA ciRS-7: a novel oncogene in multiple cancers. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17(1):379–89. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.54292.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participant
Ethics committee of Zibo Central Hospital has approved this study. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All participants in this study were informed and gave a written consent.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, L., Ma, J. & Cui, M. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0001598 promotes programmed death-ligand-1-mediated immune escape and trastuzumab resistance via sponging miR-1184 in breast cancer cells. Immunol Res 69, 558–567 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-021-09237-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-021-09237-w