Abstract
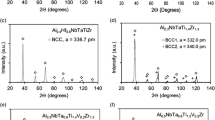
Refractory high-entropy alloys are a new type of alloy exhibiting good properties at high temperatures. In this study, AlxCrTiMo refractory high-entropy alloys were prepared by spark plasma sintering, and the mechanical and tribological properties of the alloys were investigated. The three-dimensional morphology and SEM image of the worn surface showed variation of wear marks, wherein the wear rate of the alloy decreased with increasing temperature, and the main wear mechanism changed from abrasive to adhesive wear. The results of Raman and x-ray diffraction spectroscopies of the phase structure of the oxidized glazed layer on the wear marks showed that the oxide layer on the surface of the Al0.25CrTiMo wear mark at 800°C contained oxides of MoO3 and MoO2. It can be concluded from these results that reduction of the aluminum content of the alloy will promote the formation of Cr and Mo oxides, which is important in the development of high-temperature wear resistance of AlxCrTiMo alloys.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.-W. Yeh, S.-K. Chen, S.-J. Lin, J.-Y. Gan, T.-S. Chin, T.-T. Shun, C.-H. Tsau and S.-Y. Chang, Nanostructured High-Entropy Alloys with Multi-Principal Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts and Outcomes, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2004, 6(299), p 303. https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.200300567
J.M. Torralba, P. Alvaredo and A. García-Junceda, High-Entropy Alloys Fabricated via Powder Metallurgy. A Critical Review, Powder Metall., 2019, 62, p 84–114. https://doi.org/10.1080/00325899.2019.1584454
Y. Zhang, T.T. Zuo, Z. Tang, M.C. Gao, K.A. Dahmen, P.K. Liaw and Lu. Zhao Ping, Microstructures and Properties of Highentropy Alloys, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2014, 61, p 1–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2013.10.001
O.N. Senkov, D.B. Miracle, K.J. Chaput and J.-P. Couzinie, Development and Exploration of Refractory High Entropy Alloys—A Review, J. Mater. Res., 2018, 19, p 3092–3128. https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2018.153
O.N. Senkov, G.B. Wilks, D.B. Miracle, C.P. Chuang and P.K. Liaw, Refractory High-Entropy Alloys, Intermetallics, 2010, 18, p 1758–1765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2010.05.014
O.N. Senkov, G.B. Wilks, J.M. Scott and D.B. Miracle, Mechanical Properties of Nb25Mo25Ta25W25 and V20Nb20Mo20Ta20W20 Refractory High Entropy Alloys, Intermetallics, 2011, 19, p 698–706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2011.01.004
B. Gorr, F. Müller, M. Azim, H.-J. Christ, T. Müller, H. Chen, A. Kauffmann and M. Heilmaier, High-Temperature Oxidation Behavior of Refractory High-Entropy Alloys: Effect of Alloy Composition, Oxid. Met., 2017, 88, p 339–349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-016-9696-y
F. Müller, B. Gorr, H.-J. Christ, J. Müller, B. Butz, H. Chen, A. Kauffmann and M. Heilmaier, On the Oxidation Mechanism of Refractory High Entropy Alloys, Corros. Sci., 2019, 159, p 108161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2019.108161
B. Gorr, F. Müller, S. Schellert, H.-J. Christ, H. Chen, A. Kauffmann and M. Heilmaier, A New Strategy to Intrinsically Protect Refractory Metal Based Alloys at Ultra High Temperatures, Corros. Sci., 2020, 166, p 108475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2020.108475
A. Poulia, E. Georgatis, A. Lekatou and A.E. Karantzalis, Microstructure and Wear Behavior of a Refractory High Entropy Alloy, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 2016, 57, p 50–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2016.02.006
C. Mathiou, A. Poulia, E. Georgatis and A.E. Karantzalis, Microstructural Features and Dry-Sliding Wear Response of MoTaNbZrTi High Entropy Alloy, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2018, 210, p 126–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2017.08.036
W. Steurer, Single-Phase High-Entropy Alloys – A Critical Update, Mater. Charact., 2020, 162, p 110179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2020.110179
J. Menghani, A. Vyas, P. Patel, H. Natu and S. More, Wear, Erosion and Corrosion Behavior of Laser Cladded High Entropy Alloy Coatings – A Review, Mater. Today Proc., 2020 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.08.763
D.B. Miracle and O.N. Senkov, A Critical Review of High Entropy Alloys and Related Concepts, Acta Mater., 2017, 122, p 448–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2016.08.081
J. Chen, X. Zhou, W. Wang, B. Liu, Y. Lv, W. Yang, D. Xu and Y. Liu, A Review on Fundamental of High Entropy Alloys with Promising High temperature Properties, J. Alloy. Compd., 2018, 760, p 15–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.05.067
S. Alvi and F. Akhtar, High Temperature Tribology of CuMoTaWV High Entropy Alloy, Wear, 2019, 426, p 412–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2018.12.085
Y. Guo, H. Wang and Q. Liu, Microstructure Evolution and Strengthening Mechanism of Laser-Cladding MoFexCrTiWAlNby Refractory High-Entropy Alloy Coatings, J. Alloy Compd., 2020, 834, 155147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155147
G. Deng, A.K. Tieu, L. Su, P. Wang, L. Wang, X. Lan, S. Cui and H. Zhu, Investigation into Reciprocating Dry Sliding Friction and Wear Properties of bulk CoCrFeNiMo High Entropy Alloys Fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering and Subsequent Cold Rolling Processes: Role of Mo Element Concentration, Wear, 2020, 460, p 203440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2020.203440
S. Yadav, K. Biswas and A. Kumar, Spark Plasma Sintering of High Entropy Alloys, Spark Plasma Sinter. Mater., 2019 https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-05327-7_19
J. Han, B. Su, J. Lu, J. Meng, A. Zhang and Y. Wu, Preparation of MoNbTaW Refractory High Entropy Alloy Powders by Pressureless Spark Plasma Sintering: Crystal Structure and Phase Evolution, Intermetallics, 2020, 123, 106832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2020.106832
C. Zhu, Z. Li, C. Hong, P. Dai and J. Chen, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the TiZrNbMoTa Refractory High-Entropy Alloy Produced by Mechanical Alloying and Spark PLASMA sintering, Int. J. Refract Met. Hard Mater., 2020, 93, 105357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2020.105357
Z. Guo, A. Zhang, J. Han and J. Meng, Effect of Si Additions on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Refractory NbTaWMo High-Entropy Alloys, J. Mater. Sci., 2019, 54, p 5844–5851. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-03280-z
R. Zhang, J. Meng, J. Han, T. Kelimu and R. Zhang, Oxidation Resistance Properties of Refractory High-Entropy Alloys with Varied AlxCrTiMo Content, J. Mater. Sci., 2021, 56, p 3551–3561. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-05480-y
C.-M. Lin, C.-C. Juan, C.-H. Chang, C.-W. Tsai and J.-W. Yeh, Effect of Al Addition on Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Refractory AlxHfNbTaTiZr Alloys, J. Alloy Compd., 2015, 624, p 100–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.11.064
A.J. Zhang, J.S. Han, J.H. Meng, B. Su and P.D. Li, Rapid Preparation of AlCoCrFeNi High Entropy Alloy by Spark Plasma Sintering from Elemental Powder Mixture, Mater. Lett., 2016, 181, p 82–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2016.06.014
J. Joseph, N. Haghdadi, K. Shamlaye, P. Hodgson, M. Barnett and D. Fabijanic, The Sliding Wear Behaviour of CoCrFeMnNi and AlxCoCrFeNi High Entropy Alloys at Elevated Temperatures, Wear, 2019, 428, p 32–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2019.03.002
K. Dohda, C. Boher, F. Rezai-Aria and N. Mahayotsanun, Tribology in Metal Forming at Elevated Temperatures, Friction, 2015, 3, p 1–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40544-015-0077-3
F.A. Essa, Q.X. Zhang, X.J. Huang, M.K.A. Ali, A. Elagouz and M.A.A. Abdelkareem, Effects of ZnO and MoS2 Solid Lubricants on Mechanical and Tribological Properties of M50-Steel-Based Composites at High Temperatures: Experimental and Simulation Study, Tribol. Lett., 2017, 65, p 97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-017-0880-2
C. Huang, B. Zou, P. Guo, Y. Liu, C. Huang and J. Wang, Sliding Behavior and Wear Mechanism of Iron and Cobalt-Based High-Temperature Alloys Against WC and SiC Balls, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 2016, 59, p 40–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2016.05.007
A. Zhang, J. Han, B. Su, P. Li and J. Meng, Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Tribological Performance of CoCrFeNi High Entropy Alloy Matrix Self-Lubricating Composite, Mater. Des., 2017, 114, p 253–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.11.072
M. Pole, M. Sadeghilaridjani, J. Shittu, A. Ayyagari and S. Mukherjee, High Temperature Wear Behavior of Refractory High Entropy Alloys Based on 4-5-6 Elemental Palette, J. Alloy Compd., 2020, 843, 156004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156004
F. Müller, B. Bronislava Gorr, H.-J. Christ, J. Müller, B. Butz, H. Chen, A. Kauffmann and M. Heilmaier, On the Oxidation Mechanism of Refractory High Entropy Alloys, Corros. Sci., 2019, 159, 108161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2019.108161
N. Becker and R. Dronskowski, A First-Principles Study on New High-Pressure Metastable Polymorphs of MoO2, J. Solid State Chem., 2016, 237, p 404–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2016.03.002
X. Yang, S. Dong, J. Zeng, X. Zhou, J. Jiang, L. Deng and X. Cao, Sliding Wear Characteristics of Plasma-Sprayed Cr2O3 Coatings with Incorporation of Metals and Ceramics, Ceram. Int., 2019, 45, p 20243–20250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.06.297
Z. Guo, A. Zhang, J. Han and J. Meng, Microstructure, Mechanical and Tribological Properties of CoCrFeNiMn High Entropy Alloy Matrix Composites with Addition of Cr3C2, Tribol. Int., 2020, 151, 106436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2020.106436
E.A. Gulbransen, K.F. Andrew and F.A. Brassart, Oxidation of Molybdenum 550°C to 1700°C, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1963, 110, p 952–959. https://doi.org/10.1016/0042-207X(64)91551-9
X.F. Lu and H.M. Wang, Microstructural Characterization and Dry Sliding Wear Resistance of MoO2-Strengthened γ/NiMo Alloys with Different Primary Phases, Mater. Charact., 2009, 60, p 834–842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2009.01.016
H.-S. Ahn, I.-W. Lyo and D.-S. Lim, Influence of Molybdenum Composition in Chromium Oxide-Based Coatings on their Tribological Behavior, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2000, 133, p 351–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0257-8972(00)00892-6
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province, China (Grant No. 20JR5RA560) and the Project National United Engineering Laboratory for Advanced Bearing Tribology, Henan University of Science and Technology, China (Grant No. 201907).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RZ involved in conceptualization, formal analysis, data curation, investigation, writing—original draft, and writing—review & editing. KT participated in writing—review & editing and formal analysis. AZ involved in funding acquisition, investigation, and methodology. JM participated in formal analysis, methodology, and project administration. J H: participated in software, supervision, and validation.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors of this manuscript have directly participated in planning, execution, and analysis of this study. The contents of this manuscript have not been copyrighted or published previously. The contents of this manuscript are not now under consideration for publication elsewhere. The contents of this manuscript will not be copyrighted, submitted, or published elsewhere while acceptance by Journal of Materials Science is under consideration. There are no directly related manuscripts or abstracts, published or unpublished, by any authors of this manuscript. We declare that we do not have any commercial or associative interest that represents a conflict of interest in connection with the work submitted.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, R., Tulugan, K., Zhang, A. et al. Effect of Aluminum Content on the Tribological Properties of AlxCrTiMo Refractory High-Entropy Alloys. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 31, 984–993 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06243-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06243-9