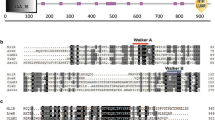
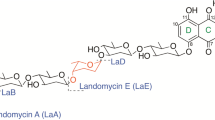
Abstract
Milbemycins, a group of 16-membered macrocylic lactones with excellent acaricidal, insecticidal and anthelmintic activities, can be produced by several Streptomyces species. For the reason that they have low toxicity in mammals, milbemycins and their derivatives are widely used in agricultural, medical and veterinary industries. Streptomyces bingchenggensis, one of milbemycin-producing strains, has been sequenced and intensively investigated in the past decades. In this mini-review, we comprehensively revisit the progress that has been made in research efforts to elucidate the biosynthetic pathways and regulatory networks for the cellular production of milbemycins. The advances in the development of production strains for milbemycin and its derivatives are discussed along the strain-generation technical approaches of random mutagenesis, metabolic engineering and combinatorial biosynthesis. The research progress made so far indicates that strain improvement and generation of novel milbemycin derivatives will greatly benefit from future development of enabling technologies and deeper understanding of the fundamentals of biosynthesis of milbemycin and the regulation of its production in S. bingchenggensis. This mini-review also proposes that the overproduction of milbemycins could be greatly enhanced by genome minimization, systematical metabolic engineering and synthetic biology approaches in the future.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker GH, Blanchflower SE, Dorgen RJ, Everett JR, Manger BR, Reading CR, Readshaw SA, Shelley P (1996) Further novel milbemycin antibiotics from Streptomyces sp. E225: fermentation, isolation and structure elucidation. J Antibiot 27(35):272–280. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.49.272
Baltz RH (2014) Combinatorial biosynthesis of cyclic lipopeptide antibiotics: a model for synthetic biology to accelerate the evolution of secondary metabolite biosynthetic pathways. ACS Synth Biol 3(10):748–758. https://doi.org/10.1021/sb3000673
Bertram R, Schlicht M, Mahr K, Nothaft H, Saier MH Jr, Titgemeyer F (2004) In silico and transcriptional analysis of carbohydrate uptake systems of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Bacteriol 186(5):1362–1373. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.186.5.1362-1373.2004
Bienhoff SE, Kok DJ, Roycroft LM, Roberts ES (2013) Efficacy of a single oral administration of milbemycin oxime against natural infections of Ancylostoma braziliense in dogs. Vet Parasitol 195(1–2):102–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2013.01.004
Breitling R, Avbelj M, Bilyk O, Carratore FD, Filisetti A, Hanko EKR, Iorio M, Redondo RP, Reyes F, Rudden M, Severi E, Slemc L, Schmidt K, Whittall DR, Donadio S, García AR, Genilloud O, Kosec G, De Lucrezia D, Petković H, Thomas G, Takano, (2021) Synthetic biology approaches to actinomycete strain improvement. FEMS Microbiol Lett 368(10):fnab060. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fnab060
Burg JM, Cooper CB, Ye ZX, Reed BR, Moreb EA, Lynch MD (2016) Large-scale bioprocess competitiveness: the potential of dynamic metabolic control in two-stage fermentations. Curr Opin Chem Eng 14:121–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coche.2016.09.008
Carter GT, Nietsche JA, Hertz MR, William DR, Siegel MM, Morton GO, James JC, Borders DB (1988) LL-F28249 antibiotic complex: a new family of antiparastic macrocyclic lactones. J Antibiot 41(4):519–529. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.41.519
Chae TU, Choi SY, Kim JW, Ko YS, Lee SY (2017) Recent advances in systems metabolic engineering tools and strategies. Curr Opin Biotechnol 47:67–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2017.06.007
Chen JS, Liu M, Liu XT, Miao J, Fu CZ, Gao HY, Müller R, Zhang Q, Zhang LX (2016) Interrogation of Streptomyces avermitilis for efficient production of avermectins. Synth Syst Biotechnol 1(1):7–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synbio.2016.03.002
Danaher M, Radeck W, Kolar L, Keegan J, Cerkvenik-Flajs V (2012) Recent developments in the analysis of avermectin and milbemycin residues in food safety and the environment. Curr Pharm Biotehnol 13(6):936–995. https://doi.org/10.2174/138920112800399068
Gao H, Liu M, Zhuo Y, Zhou XL, Liu JT, Chen DF, Zhang WQ, Guo ZX, Peng S, Zhang LX (2010) Assessing the potential of an induced-mutation strategy for avermectin overproducers. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(13):4583–4586. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01682-09
Getsin I, Nalbandian GH, Yee DC, Vastermark A, Paparoditis PCG, Reddy VS, Saier MH Jr (2013) Comparative genomics of transport proteins in developmental bacteria: Myxococcus xanthus and Streptomyces coelicolor. BMC Microbiol 13(1):279–279. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-13-279
Gomez-Escribano JP, Bibb MJ (2011) Engineering Streptomyces coelicolor for heterologous expression of secondary metabolite gene clusters. Microb Biotechnol 4(2):207–215. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-7915.2010.00219.x
He YL, Sun YH, Liu TG, Zhou XF, Bai LQ, Deng ZX (2010) Cloning of separate meilingmycin biosynthesis gene clusters by use of acyltransferase-ketoreductase didomain PCR amplification. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(10):3283–3292. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02262-09
Huang H, Zheng GS, Jiang WH, Hu HF, Lu YH (2015a) One-step high-efficiency CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing in Streptomyces. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 47(4):231–243. https://doi.org/10.1093/abbs/gmv007
Huang J, Chen AL, Zhang H, Yu Z, Li MH, Li N, Lin JT, Bai H, Wang JD, Zheng YG (2015b) Gene replacement for the generation of designed novel avermectin derivatives with enhanced acaricidal and nematicidal activities. Appl Environ Microbiol 81(16):5326–5334. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01025-15
Ikeda H, Kazuo SY, Omura S (2014) Genome mining of the Streptomyces avermitilis genome and development of genome-minimized hosts for heterologous expression of biosynthetic gene clusters. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 41(2):233–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-013-1327-x
Jacobs CT, Scholtz CH (2015) A review on the effect of macrocyclic lactones on dung-dwelling insects: toxicity of macrocyclic lactones to dung beetles. Onderstepoort J Vet Res 82(1):858. https://doi.org/10.4102/ojvr.v82i1.858
Jin PJ, Li SS, Zhang YY, Chu LY, He HR, Dong ZX, Xiang WS (2020) Mining and fine-tuning sugar uptake system for titer improvement of milbemycins in Streptomyces bingchenggensis. Synth Syst Biotechnol 5(3):214–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synbio.2020.07.001
Kim SW, Rahman M, Abd El-Aty AM, Truong TBL, Choi JH, Park JS, Kim MR, Shin HC, Shim JH (2016) Residue level and dissipation pattern of lepimectin in shallots using high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with photodiode array detection. Biomed Chromatogr 30(11):1835–1842. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.3759
Kim MS, Cho WJ, Song MC, Park SW, Kim K, Kim E, Lee N, Nam SJ, Oh KH, Yoon YJ (2017) Engineered biosynthesis of milbemycins in the avermectin high-producing strain Streptomyces avermitilis. Microb Cell Fact 16(1):9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-017-0626-8
Ko YS, Kim JW, Lee JA, Han T, Kim GB, Park JE, Lee SY (2020) Tools and strategies of systems metabolic engineering for the development of microbial cell factories for chemical production. Chem Soc Rev 49(14):4615–4636. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0cs00155d
Komatsu M, Uchiyama T, Omura S, Cane DE, Ikeda H (2010) Genome-minimized Streptomyces host for the heterologous expression of secondary metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(6):2646–2651. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0914833107
Lee N, Hwang S, Lee Y, Cho S, Palsson B, Cho BK (2019) Synthetic biology tools for novel secondary metabolite discovery in Streptomyces. J Microbiol Biotechnol 29(5):667–686. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1904.04015
Li M, Chen Z, Zhang X, Song Y, Wen Y, Li JL (2010) Enhancement of avermectin and ivermectin production by overexpression of the maltose ATP-binding cassette transporter in Streptomyces avermitilis. Bioresour Technol 101(23):9228–9235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.06.132
Li L, Jiang WH, Lu YH (2017a) New strategies and approaches for engineering biosynthetic gene clusters of microbial natural products. Biotechnol Adv 35(8):936–946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2017.03.007
Li JS, Zhang SY, Zhang H, Wang HY, Zhang J, Chen AL, Wang JD, Xiang WS (2017b) Isolation and identification of new macrocyclic lactones from a genetically engineered strain Streptomyces bingchenggensis BCJ60. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 70(3):297–300. https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2016.130
Li L, Wei KK, Zheng GS, Liu XC, Chen SX, Jiang WH, Lu YY (2018) CRISPR-Cpf1 assisted multiplex genome editing and transcriptional repression in Streptomyces. Appl Environ Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00827-18
Liu YQ, Wang HY, Li SS, Zhang YY, Cheng X, Xiang WS, Wang XJ (2021) Engineering of primary metabolic pathways for titer improvement of milbemycins in Streptomyces bingchenggensis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105(5):1875–1887. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11164-7
Lu CY, Zhang XJ, Jiang M, Bai LQ (2016) Enhanced salinomycin production by adjusting the supply of polyketide extender units in Streptomyces albus. Metab Eng 35:129–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2016.02.012
Lu FJ, Hou YY, Li XG, He LL, Chu YW, Xia HY, Tian YQ (2018) Breeding of high milbemycin-producing strain by ribosomal engineering. Chin J Antibiot 43(7):811–816. https://doi.org/10.13461/j.cnki.cja.006299
Meng L, Xiong Z, Chu J, Wang Y (2016) Enhanced production of avermectin by deletion of type III polyketide synthases biosynthetic cluster rpp in Streptomyces avermitilis. Lett Appl Microbiol 63(5):384–390. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.12635
Nicastro RL, Sato ME, Silva MZ (2011) Fitness costs associated with milbemectin resistance in the two-spotted spider mite Tetranychus urticae. Int J Pest Manag 57(3):223–228. https://doi.org/10.1080/09670874.2011.574745
Nonaka K, Kumasaka C, Okamoto Y, Maruyama F, Yoshikawa H (1999a) Bioconversion of milbemycin-related compounds: biosynthetic pathway of milbemycins. J Antibiot 52(2):109–116. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.52.109
Nonaka K, Tsukiyama T, Sato K, Kumasaka C, Maruyama F, Yoshikawa H (1999b) Bioconversion of milbemycin-related compounds: isolation and utilization of non-producer, strain RNBC-5-51. J Antibiot 52(7):620–627. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.52.620
Nonaka K, Tsukiyama T, Okamoto Y, Sato K, Kumasaka C, Yammoto T, Maruyama F, Yoshikawa H (2010) New milbemycins from Streptomyces hygroscopicus subsp. aureolacrimosus: fermantation, isolation and strucutre elucidation. J Antibiot 31(47):694–704. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.53.694
Ono M, Mishima H, Takiguchi Y, Terao M (1983a) Milbemycins, a new family of macrolide antibiotics. Fermentation, isolation and physico-chemical properties of milbemycins D, E, F, G, and H. J Antibiot 36(5):509–515. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.36.509
Ono M, Mishima H, Takiguchi Y, Terao M, Kobayashi H, Iwasaki S, Okuda S (1983b) Milbemycins, a new family of macrolide antibiotics. Studies on the biosynthesis of milbemycins alpha 2, alpha 4 and D using 13C labeled precursors. J Antibiot 36(8):991–1000. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.36.991
O’rourke S, Wietzorrek A, Fowler K, Corre C, Challis GL, Chater KF (2009) Extracellular signalling, translational control, two repressors and an activator all contribute to the regulation of methylenomycin production in Streptomyces coelicolor. Mol Microbiol 71(3):763–778. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06560.x
Palazzotto E, Weber T (2018) Omics and multi-omics approaches to study the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites in microorganisms. Curr Opin Microbiol 45:109–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2018.03.004
Park JW, Yoon YJ (2019) Recent advances in the discovery and combinatorial biosynthesis of microbial 14-membered macrolides and macrolactones. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 46(3–4):445–458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-018-2095-4
Phelan RM, Sachs D, Petkiewicz SJ, Barajas JF, Blake-Hedges JM, Thompson MG, Reider Apel A, Rasor BJ, Katz L, Keasling DJ (2017) Development of next generation synthetic biology tools for use in Streptomyces venezuelae. ACS Synth Biol 6(1):159–166. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.6b00202
Pluschkell U, Horowitz AR, Ishaaya I (1999) Effect of milbemectin on the sweetpotato whitefly, Bemisia tabad. Phytoparasitica 27(3):183–191. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02981457
Robertsen HL, Weber T, Kim HU, Lee SY (2018) Toward systems metabolic engineering of Streptomycetes for secondary metabolites production. Biotechnol J. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.201700465
Romero-Rodríguez A, Robledo-Casados I, Sánchez S (2015) An overview on transcriptional regulators in Streptomyces. Biochim Biophys Acta 1849(8):1017–1039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2015.06.007
Sultan SP, Kitani S, Miyamoto KT, lguchi H, Atago T, lkeda H, Nihira T (2016) Characterization of AvaR1, a butenolide-autoregulator receptor for biosynthesis of a Streptomyces hormone in Streptomyces avermitilis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(22):9581–9591. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7781-4
Sun P, Zhao QF, Yu FT, Zhang H, Wu ZH, Wang YY, Wang Y, Zhang QL, Liu W (2013) Spiroketal formation and modification in avermectin biosynthesis involves a dual activity of AveC. J Am Chem Soc 135(4):1540–1548. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja311339u
Takano E (2006) Gamma-butyrolactones: Streptomyces signaling molecules regulating antibiotic production and differentiation. Curr Opin Microbiol 9(3):287–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2006.04.003
Tan GY, Deng KH, Liu XH, Tao H, Chang YY, Chen J, Chen K, Sheng Z, Deng ZX, Liu TG (2017) Heterologous biosynthesis of spinosad: an omics-guided large polyketide synthase gene cluster reconstitution in Streptomyces. ACS Synth Biol 6(6):995–1005. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.6b00330
Teng Y, Xu MD, Zhu JW, Zheng LH, Ying XX, Bai H (2019) The rational breeding of high-yield strains for producing the single A3 and A4 components of milbemycin. Chin J Antibiot 44(2):197–202. https://doi.org/10.13461/j.cnki.cja.006553
Tian JZ, Yang GH, Gu Y, Sun XQ, Lu YY, Jiang WH (2020) Developing an endogenous quorum-sensing based CRISPRi circuit for autonomous and tunabledynamic regulation of multiple targets in Streptomyces. Nucleic Acids Res 48(14):8188–8202. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa602
Wang XJ, Guo SL, Guo WQ, Xiang WS (2006) Role of nsdA in negative regulation of antibiotic production and morphological differentiation in Streptomyces bingchenggensis. J Antibiot 62:309–313. https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2009.33
Wang XJ, Wang XC, Xiang WS (2009) Improvement of milbemycin-producingStreptomyces bingchenggensis by rational screening of ultraviolet- and chemically induced mutants. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25(6):1051–1056. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-009-9986-5
Wang XJ, Wang CQ, Sun XL, Xiang WS (2010a) 5-ketoreductase from Streptomyces bingchenggensis: overexpression and preliminary characterization. Biotechnol Lett 32(10):1497–1502. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-010-0320-y
Wang XJ, Yan YJ, Zhang B, An J, Wang JJ, Tian J, Jiang L, Chen YH, Huang SX, Yin M, Zhang J, Gao AL, Liu CX, Zhu ZX, Xiang WS (2010b) Genome sequence of the milbemycin-producing bacterium Streptomyces bingchenggensis. J Bacteriol 192(17):4526–4527. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00596-10
Wang XJ, Zhang B, Yan YJ, An J, Zhang J, Liu CX, Xiang WS (2013) Characterization and analysis of an industrial strain of Streptomyces bingchenggensis by genome sequencing and gene microarray. Genome 56(11):677–689. https://doi.org/10.1139/gen-2013-0098
Wang HY, Zhang J, Zhang YJ, Zhang B, Liu CX, He HR, Wang XJ, Xiang WS (2014) Combined application of plasma mutagenesis and gene engineering leads to 5-oxomilbemycins A3/A4 as main components from Streptomyces bingchenggensis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(23):9703–9712. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5970-6
Wang HY, Cheng X, Liu YQ, Li SS, Zhang YY, Wang XJ, Xiang WS (2020) Improved milbemycin production by engineering two Cytochromes P450 in Streptomyces bingchenggensis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104(7):2935–2946. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10410-8
Warr SRC, Box SJ, Burbidge C, Edwards H, Jones JJ (1994) Milbemycin production by Streptomyces sp.: the effect of carbohydrates. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 13(1):43–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01569661
Wei KK, Wu YJ, Li L, Jiang WH, Hu JF, Lu YH, Chen SX (2018) MilR2, a novel TetR family regulator involved in 5-oxomilbemycin A3/A4 biosynthesis in Streptomyces hygroscopicus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:8841–8853. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9280-2
Yu Z, Wang Q, Deng ZX, Tao MF (2006) Activation of silent antibiotic synthesis in Streptomyces lividans by disruption of a negative regulator nsdA, a gene conserved in Streptomyces. Chin J Biotechnol 22(5):757–762
Zhang BX, Wang XJ, Xiang WS (2011) Optimization of fermentation medium for enhanced production of milbemycin by a mutant of Streptomyces bingchenggensis BC-X-1 using response surface methodology. Afr J Biotechnol 10(37):7225–7235. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB11.077
Zhang J, An J, Wang JJ, Yan YJ, He HR, Wang XJ, Xiang WS (2013) Genetic engineering of Streptomyces bingchenggensis to produce milbemycins A3/A4 as main components and eliminate the biosynthesis of nanchangmycin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(23):10091–10101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5255-5
Zhang J, Yan YJ, An J, Huang SX, Wang XJ, Xiang WS (2015) Designed biosynthesis of 25-methyl and 25-ethyl ivermectin with enhanced insecticidal activity by domain swap of avermectin polyketide synthase. Microb Cell Fact 14:152. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-015-0337-y
Zhang YY, He HR, Liu H, Wang HY, Wang XJ, Xiang WS (2016) Characterization of a pathway-specific activator of milbemycin biosynthesis and improved milbemycin production by its overexpression in Streptomyces bingchenggensis. Microb Cell Fact 15(1):152. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-016-0552-1
Zhao JH, Xu XJ, Ji MH, Cheng JL, Zhu GN (2011) Design, synthesis, and biological activities of milbemycin analogues. J Agric Food Chem 59(9):4836–4850. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf2001926
Acknowledgements
We thank the members of Institute of Biopharmaceuticals, Taizhou University for many fruitful discussions. Many thanks to Dr. Alexander Zawaira (formerly of Taizhou University and now of Beijing Open University, Haidian District, Beijing) for editing and suggestion.
Funding
This study was funded the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province to HX (LY19C010002) and the Scientific Research Foundation of Taizhou to HX (No. 2001xg07).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical statement
This manuscript is in compliance with ethical standards. This manuscript does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, YS., Xia, HY. Recent advances in the research of milbemycin biosynthesis and regulation as well as strategies for strain improvement. Arch Microbiol 203, 5849–5857 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-021-02575-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-021-02575-1