Abstract
Purpose
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is characterized by insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction. Elevated free fatty acids-induced lipotoxicity may play a vital role in the pathogenesis of β-cell insulin resistance. Exercise-stimulated myokine irisin has been reported to be closely related to T2DM. However, its function on β-cell insulin signaling and the underlying mechanisms are only partially elucidated as yet.
Methods
High-fat diet-fed C57BL/6J mice and palmitic acid-treated MIN6 cell models were utilized as lipotoxic models. Factors associated with β-cell insulin signaling transduction and inflammatory responses were assessed in these models. Furthermore, the role of irisin in β-cells and the underlying mechanisms were also explored.
Results
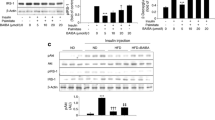
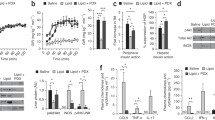
Irisin effectively decreased lipid levels in HFD mice, enhanced glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and nullified the expressions of inflammatory cytokines in vivo and in vitro experiments. Moreover, irisin improved PI3K/AKT insulin signaling pathway and inhibited TLR4/NF-κB inflammatory signaling pathway in both islets of HFD mice and PA-treated MIN6 cells. Mechanistic analysis indicated that FOXO1 might serve as a bridge between the two pathways.
Conclusion
Irisin alleviates lipotoxicity-induced β-cell insulin resistance and inflammatory response through the activation of PI3K/AKT/FOXO1 signaling pathways and the inhibition of TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathways. Irisin might provide a novel therapeutic strategy for T2DM.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
D. Accili, Insulin Action Research and the Future of Diabetes Treatment: The 2017 Banting Medal for Scientific Achievement Lecture. Diabetes 67(9), 1701–1709 (2018)
R.N. Kulkarni, J.C. Bruning, J.N. Winnay, C. Postic, M.A. Magnuson, C.R. Kahn, Tissue-specific knockout of the insulin receptor in pancreatic beta cells creates an insulin secretory defect similar to that in type 2 diabetes. Cell 96(3), 329–339 (1999)
M.I. McCarthy, Genomics, type 2 diabetes, and obesity. N. Engl. J. Med 363(24), 2339–2350 (2010)
T. Kubota, N. Kubota, T. Kadowaki, Imbalanced insulin actions in obesity and type 2 diabetes: key mouse models of insulin signaling pathway. Cell Metab. 25(4), 797–810 (2017)
Y.X. Li, T.T. Han, Y. Liu, S. Zheng, Y. Zhang, W. Liu, Y.M. Hu, Insulin resistance caused by lipotoxicity is related to oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress in LPL gene knockout heterozygous mice. Atherosclerosis 239(1), 276–282 (2015)
S. Zheng, X. Ren, T. Han, Y. Chen, H. Qiu, W. Liu, Y. Hu, Fenofibrate attenuates fatty acid-induced islet beta-cell dysfunction and apoptosis via inhibiting the NF-kappaB/MIF dependent inflammatory pathway. Metabolism 77, 23–38 (2017)
A. Sampath Kumar, A.G. Maiya, B.A. Shastry, K. Vaishali, N. Ravishankar, A. Hazari, S. Gundmi, R. Jadhav, Exercise and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med 62(2), 98–103 (2019)
P. Bostrom, J. Wu, M.P. Jedrychowski, A. Korde, L. Ye, J.C. Lo, K.A. Rasbach, E.A. Bostrom, J.H. Choi, J.Z. Long, S. Kajimura, M.C. Zingaretti, B.F. Vind, H. Tu, S. Cinti, K. Hojlund, S.P. Gygi, B.M. Spiegelman, A PGC1-alpha-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature 481(7382), 463–468 (2012)
T. Kurdiova, M. Balaz, M. Vician, D. Maderova, M. Vlcek, L. Valkovic, M. Srbecky, R. Imrich, O. Kyselovicova, V. Belan, I. Jelok, C. Wolfrum, I. Klimes, M. Krssak, E. Zemkova, D. Gasperikova, J. Ukropec, B. Ukropcova, Effects of obesity, diabetes and exercise on Fndc5 gene expression and irisin release in human skeletal muscle and adipose tissue: in vivo and in vitro studies. J. Physiol. 592(5), 1091–1107 (2014)
J.J. Liu, M.D. Wong, W.C. Toy, C.S. Tan, S. Liu, X.W. Ng, S. Tavintharan, C.F. Sum, S.C. Lim, Lower circulating irisin is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Complications 27(4), 365–369 (2013)
C. Zhang, Z. Ding, G. Lv, J. Li, P. Zhou, J. Zhang, Lower irisin level in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a case-control study and meta-analysis. J. Diabetes 8(1), 56–62 (2016)
B. Garcia-Fontana, R. Reyes-Garcia, S. Morales-Santana, V. Avila-Rubio, A. Munoz-Garach, P. Rozas-Moreno, M. Munoz-Torres, Relationship between myostatin and irisin in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a compensatory mechanism to an unfavourable metabolic state? Endocrine 52(1), 54–62 (2016)
B.L. Guilford, J.C. Parson, C.W. Grote, S.N. Vick, J.M. Ryals, D.E. Wright, Increased FNDC5 is associated with insulin resistance in high fat-fed mice. Physiol. Rep. 5, 13 (2017)
A. Natalicchio, N. Marrano, G. Biondi, R. Spagnuolo, R. Labarbuta, I. Porreca, A. Cignarelli, M. Bugliani, P. Marchetti, S. Perrini, L. Laviola, F. Giorgino, The Myokine Irisin Is Released in Response to Saturated Fatty Acids and Promotes Pancreatic beta-Cell Survival and Insulin Secretion. Diabetes 66(11), 2849–2856 (2017)
Y. Zhang, R. Li, Y. Meng, S. Li, W. Donelan, Y. Zhao, L. Qi, M. Zhang, X. Wang, T. Cui, L.J. Yang, D. Tang, Irisin stimulates browning of white adipocytes through mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 MAP kinase and ERK MAP kinase signaling. Diabetes 63(2), 514–525 (2014)
J.E. Dominy, P. Puigserver, Nuclear FoxO1 inflames insulin resistance. EMBO J. 29(24), 4068–4069 (2010)
Y. Mirdamadi, A. Thielitz, A. Wiede, A. Goihl, E. Papakonstantinou, R. Hartig, C.C. Zouboulis, D. Reinhold, L. Simeoni, U. Bommhardt, S. Quist, H. Gollnick, Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 can modulate the phosphoinositide-3-kinase/Akt/FoxO1 pathway in SZ95 sebocytes in vitro. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 415, 32–44 (2015)
J.C. Ansarullah, F.F. Far, S. Homberg, K. Wissmiller, F.G. von Hahn, A. Raducanu, S. Schirge, M. Sterr, S. Bilekova, J. Siehler, J. Wiener, L. Oppenlander, A. Morshedi, A. Bastidas-Ponce, G. Collden, M. Irmler, J. Beckers, A. Feuchtinger, M. Grzybek, C. Ahlbrecht, R. Feederle, O. Plettenburg, T.D. Muller, M. Meier, M.H. Tschop, U. Coskun, H. Lickert, Inceptor counteracts insulin signalling in beta-cells to control glycaemia. Nature 590(7845), 326–331 (2021)
J. Bai, S. Zheng, D. Jiang, T. Han, Y. Li, Y. Zhang, W. Liu, Y. Cao, Y. Hu, Oxidative stress contributes to abnormal glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity in two hyperlipidemia models. Int J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 8(10), 13193–13200 (2015)
K. Eguchi, I. Manabe, Y. Oishi-Tanaka, M. Ohsugi, N. Kono, F. Ogata, N. Yagi, U. Ohto, M. Kimoto, K. Miyake, K. Tobe, H. Arai, T. Kadowaki, R. Nagai, Saturated fatty acid and TLR signaling link beta cell dysfunction and islet inflammation. Cell Metab. 15(4), 518–533 (2012)
L. Marselli, M. Bugliani, M. Suleiman, F. Olimpico, M. Masini, M. Petrini, U. Boggi, F. Filipponi, F. Syed, P. Marchetti, beta-Cell inflammation in human type 2 diabetes and the role of autophagy. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 15(Suppl 3), 130–136 (2013)
J.A. Ehses, A. Perren, E. Eppler, P. Ribaux, J.A. Pospisilik, R. Maor-Cahn, X. Gueripel, H. Ellingsgaard, M.K. Schneider, G. Biollaz, A. Fontana, M. Reinecke, F. Homo-Delarche, M.Y. Donath, Increased number of islet-associated macrophages in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 56(9), 2356–2370 (2007)
M.J. Butcher, D. Hallinger, E. Garcia, Y. Machida, S. Chakrabarti, J. Nadler, E.V. Galkina, Y. Imai, Association of proinflammatory cytokines and islet resident leucocytes with islet dysfunction in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 57(3), 491–501 (2014)
J.J. Kim, D.D. Sears. TLR4. and Insulin Resistance. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2010, 212563 (2010)
W. Link, Introduction to FOXO Biology. Methods Mol. Biol. 1890, 1–9 (2019)
T. Kitamura, J. Nakae, Y. Kitamura, Y. Kido, W.H. Biggs III, C.V. Wright, M.F. White, K.C. Arden, D. Accili, The forkhead transcription factor Foxo1 links insulin signaling to Pdx1 regulation of pancreatic beta cell growth. J. Clin. Investig. 110(12), 1839–1847 (2002)
S.J. Mutt, G.S. Raza, M.J. Makinen, S. Keinanen-Kiukaanniemi, M.R. Jarvelin, K.H. Herzig, Vitamin D deficiency induces insulin resistance and re-supplementation attenuates hepatic glucose output via the PI3K-AKT-FOXO1 mediated pathway. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 64(1), e1900728 (2020)
A. Clark, M.R. Nilsson, Islet amyloid: a complication of islet dysfunction or an aetiological factor in Type 2 diabetes? Diabetologia 47(2), 157–169 (2004)
L. Chen, B. Gao, Y. Zhang, H. Lu, X. Li, L. Pan, L. Yin, X. Zhi, PAR2 promotes M1 macrophage polarization and inflammation via FOXO1 pathway. J. Cell Biochem. 120(6), 9799–9809 (2019)
Y. Akgul Balaban, N. Yilmaz, M. Kalayci, M. Unal, T. Turhan, Irisin and Chemerin Levels in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Acta Endocrinol. 15(4), 442–446 (2019)
M.P. Jedrychowski, C.D. Wrann, J.A. Paulo, K.K. Gerber, J. Szpyt, M.M. Robinson, K.S. Nair, S.P. Gygi, B.M. Spiegelman, Detection and Quantitation of Circulating Human Irisin by Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Cell Metab. 22(4), 734–740 (2015)
M. Yang, P. Chen, H. Jin, X. Xie, T. Gao, L. Yang, X. Yu, Circulating levels of irisin in middle-aged first-degree relatives of type 2 diabetes mellitus—correlation with pancreatic beta-cell function. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 6(1), 133 (2014)
X.Q. Xiong, D. Chen, H.J. Sun, L. Ding, J.J. Wang, Q. Chen, Y.H. Li, Y.B. Zhou, Y. Han, F. Zhang, X.Y. Gao, Y.M. Kang, G.Q. Zhu, FNDC5 overexpression and irisin ameliorate glucose/lipid metabolic derangements and enhance lipolysis in obesity. Biochim Biophys. Acta. 1852(9), 1867–1875 (2015)
M.J. Park, D.I. Kim, J.H. Choi, Y.R. Heo, S.H. Park, New role of irisin in hepatocytes: the protective effect of hepatic steatosis in vitro. Cell Signal 27(9), 1831–1839 (2015)
D. Zhu, H. Wang, J. Zhang, X. Zhang, C. Xin, F. Zhang, Y. Lee, L. Zhang, K. Lian, W. Yan, X. Ma, Y. Liu, L. Tao, Irisin improves endothelial function in type 2 diabetes through reducing oxidative/nitrative stresses. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 87, 138–147 (2015)
J.Y. Huh, F. Dincer, E. Mesfum, C.S. Mantzoros, Irisin stimulates muscle growth-related genes and regulates adipocyte differentiation and metabolism in humans. Int J. Obes. 38(12), 1538–1544 (2014)
N. Marrano, G. Biondi, A. Borrelli, A. Cignarelli, S. Perrini, L. Laviola, F. Giorgino, A. Natalicchio, Irisin and incretin hormones: similarities, differences, and implications in type 2 diabetes and obesity. Biomolecules 11, 2 (2021)
Funding
This study was supported by Shanghai Sailing Program (19YF1428600), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2019M651588) and Cultivation Program for the National Natural Science Foundation of China from Shanghai Tenth People’s Hospital (04. 03. 18. 081).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SZ and SS contributed to the conception and design of the study; SZ, NC and XK contributed to perform the experiments and analyzed data. YH edited the manuscript. SZ, NC and SS contributed to the analysis and interpretation of the data. All authors revised and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
All experiments were approved by the Ethics Committee of Shanghai University (ECSHU).
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, S., Chen, N., Kang, X. et al. Irisin alleviates FFA induced β-cell insulin resistance and inflammatory response through activating PI3K/AKT/FOXO1 signaling pathway. Endocrine 75, 740–751 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-021-02875-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-021-02875-y