Abstract
Aim/hypothesis
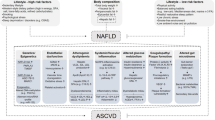
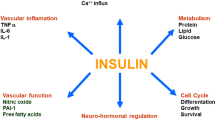
Hepatic insulin resistance (HIR) is considered to be an independent predictor of metabolic disorders and plays an important role in systemic inflammation, which contributes to abnormalities in cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors. The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship between HIR and new markers of cardiovascular risks, including leptin/adiponectin ratio (L/A), lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)], and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), at comparable whole body insulin sensitivity in non-diabetic individuals with or without CVD and at high risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Methods
The HIR index, L/A, Lp(a), and TNF-α were measured in 50 participants with CVD and in 200 without CVD (1:4 ratio). These were also matched for the homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) and Matsuda-insulin sensitivity index (ISI) in an observational study design.
Results
The HIR index (1.52 ± 0.14 vs. 1.45 ± 0.17, p < 0.02), L/A (3.22 ± 3.10 vs. 2.09 ± 2.27, p < 0.004), and levels of Lp(a) (66.6 ± 49.5 vs. 37.9 ± 3 6.8 mg/dL, p < 0.0001) and TNF-α (18.9 ± 21.8 vs. 5.4 ± 7.1 pg/mL, p < 0.0001) were higher in those with CVD than those without CVD. HOMA-IR and ISI were not significantly different (p = 0.88 and p = 0.35, respectively). The HIR index was directly correlated with L/A (r = 0.41, p < 0.0001), Lp(a) (r = 0.20, p < 0.002), TNF- α (r = 0.14, p < 0.03), and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) (r = 0.13, p < 0.03). The stepwise model analysis showed that L/A, Lp(a), and TNF-α explained about 20% of the variation in the HIR indices of all the participants (p < 0.02).
Conclusions/Interpretations
Our results suggest a positive association between HIR and new markers of cardiovascular risk [L/A, Lp(a), and TNF- α] at comparable whole body insulin sensitivity in those with or without CVD and at high risk of developing type 2 diabetes.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AUC:
-
area under the curve
- BMI:
-
body mass index
- CVD:
-
cardiovascular disease
- FFM:
-
free fat mass
- FM:
-
fat mass
- HDL:
-
high density lipoprotein
- HIR:
-
hepatic insulin resistance
- HIR index:
-
hepatic insulin resistance index
- HOMA-IR:
-
homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance
- IR:
-
insulin resistance
- L/A:
-
leptin/adiponectin ratio
- LDL:
-
low density lipoprotein
- Matsuda-ISI::
-
Matsuda insulin sensitivity index
- MS:
-
metabolic syndrome
- OGTT:
-
oral glucose tolerance test
- TNF-α:
-
tumor necrosis factor alpha
References
G. Reaven, Insulin resistance and coronary heart disease in nondiabetic individuals. Arterioscler Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 32, 1754–9 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.241885
K.B. Gast, N. Tjeerdema, T. Stijnen, J.W. Smit, O.M. Dekkers, Insulin resistance and risk of incident cardiovascular events in adults without diabetes: meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 7, e52036 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0052036
M. Stumvoll, S. Jacob, H.G. Wahl, B. Hauer, K. Loblein, P. Grauer, R. Becker, M. Nielsen, W. Renn, H. haring, Suppression of systemic, intramuscular, and subcutaneous adipose tissue lipolysis by insulin in human. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 85, 3740–3745 (2000)
S. Zhao, C.M. Kusminski, P.E. Scherer, Adiponectin, leptin and cardiovascular disorders. Circ. Res 128, 136–149 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA
J. Zaletel, D.P. Barlovic, J. Prezelj, Adiponectin-leptin ratio: a useful estimate of insulin resistance in patients with Type 2 diabetes. J. Endocrinol. Invest 33, 514–8 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03346639
M. Inoue, M. Yano, M. Yamakado, Relationship between the adiponectin-leptin ratio and parameters of insulin resistance in subjects without hyperglycemia. Metabolism 55, 1248–54 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2006.05.010
P. Finneran, A. Pampana, S.A. Khetarpal, M. Trinder, A.P. Patel, K. Paruchuri, K. Aragam, G.M. Peloso, P. Natarajan, Lipoprotein (a) and coronary artery disease risk without a family history of heart disease. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 10, e017470 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.120.017470
B.G. Nordestgaard, M.J. Chapman, K. Ray, J. Borén, F. Andreotti, G.F. Watts et al. European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel. Lipoprotein (a) as a cardiovascular risk factor: current status. Eur. Heart J. 31, 2844–53 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehq386
Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration, S. Erqou, S. Kaptoge, P.L. Perry, E. Di Angelantonio, A. Thompson, I.R. White et al. Lipoprotein(a) concentration and the risk of coronary heart disease, stroke, and nonvascular mortality. JAMA 302, 412–23 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2009.1063
R. Clarke, J.F. Peden, J.C. Hopewell, T. Kyriakou, A. Goel, S.C. Heath et al. PROCARDIS Consortium. Genetic variants associated with Lp (a) lipoprotein level and coronary disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 361, 2518–28 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0902604
J.L. Jin, Y.X. Cao, H.W. Zhang, D. Sun, Q. Hua, Y.F. Li et al. Lipoprotein(a) and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Coronary Artery Disease in patients with prediabetes and diabetes. Diabetes Care 42, 1312–8 (2019). https://doi.org/10.2337/dc19-0274
R. Huang, S.-R. Zhao, Y. Li, F. Liu, Y. Gong, J. Xing, Z.-S. Xu, Association of tumor necrosis factor-α gene polymorphisms and coronary artery disease susceptibility: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. Genet. 21, 29 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12881-020-0952-2
D. Gupta, S. Varma, R.L. Khandelwal, Long-term effects of tumor necrosis factor-alpha treatment on insulin signaling pathway in HepG2 cells and HepG2 cells overexpressing constitutively active Akt/PKB. J. Cell Biochem 100, 593–607 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.21080
H. Zhao, X. Huang, J. Jiao, H. Zhang, J. Liu, W. Qin et al. Protein phosphatase 4 (PP4) functions as a critical regulator in tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α-induced hepatic insulin resistance. Sci. Rep. 5, 18093 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep18093
M.S.H. Akash, K. Rehman, A. Liaqat, Tumor necrosis factor-alpha: role in development of insulin resistance and pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Cell Biochem 119, 105–10 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.26174
K.G. Alberti, P. Zimmet, J. Shaw; IDF epidemiology task force consensus group, The metabolic syndrome–a new worldwide definition. Lancet 366, 1059–62 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67402-8
T.D. Topolski, J. LoGerfo, D.L. Patrick, B. Williams, J. Walwick, M.B. Patrick, The rapid assessment of physical activity (RAPA) among older adults. Prev. Chronic Dis. 3, 1–8 (2006)
J. Vangipurapu, A. Stančáková, T. Kuulasmaa, J. Paananen, J. Kuusisto, E. Ferrannini et al. A novel surrogate index for hepatic insulin resistance. Diabetologia 54, 540–3 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-010-1966-7. & the EGIR-RISC Study Group
R.A. DeFronzo, J.D. Tobin, R. Andres, Glucose clamp technique: a method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. Am. J. Physiol. 237, E214–E23 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.1979.237.3.E214
J. Vangipurapu, A. Stančáková, T. Kuulasmaa, P. Soininen, A.J. Kangas, M. Ala-Korpela, J. Kuusisto, M. Laakso, Association between liver insulin resistance and cardiovascular risk factors. J. Intern Med. 272, 402–408 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2796.2012.02540.x
D.R. Matthews, J.P. Hosker, A.S. Rudenski, B.A. Naylor, D.F. Treacher, R.C. Turner, Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28, 412–9 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00280883
M. Matsuda, R.A. DeFronzo, Insulin sensitivity indices obtained from oral glucose tolerance testing: comparison with the euglycemic insulin clamp. Diabetes Care 22, 1462–70 (1999). https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.22.9.1462
L.D. Monti, E. Setola, P.C. Lucotti, M.M. Marrocco-Trischitta, M. Comola, E. Galluccio, A. Poggi, S. Mammì, A.L. Catapano, G. Comi, R. Chiesa, E. Bosi, P.M. Piatti, Effect of a long-term oral l-arginine supplementation on glucose metabolism: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 14, 893–900 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1463-1326.2012.01615.x
E. Galluccio, P. Piatti, L. Citterio, P.C. Lucotti, E. Setola, L. Cassina et al. Hyperinsulinemia and impaired leptin-adiponectin ratio associate with endothelial nitric oxide synthase polymorphisms in subjects with in-stent restenosis. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 294, E978–E86 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00003.2008
P. Piatti, C. Di Mario, L.D. Monti, G. Fragasso, F. Sgura, A. Caumo et al. Association of insulin resistance, hyperleptinemia, and impaired nitric oxide release with in-stent restenosis in patients undergoing coronary stenting. Circulation 108, 2074–81 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000095272.67948.17
M. Matsuda, I. Shimomura, Roles of adiponectin and oxidative stress in obesity-associated metabolic and cardiovascular diseases. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 15, 1–10 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11154-013-9271-7
Y. Li, L. Ding, W. Hassan, D. Abdelkader, J. Shang, Adipokines and hepatic insulin resistance. J. Diabetes Res 2013, 170532 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/170532
A. Baranova, S.I. Gowder, K. Schlauch, H. Elariny, R. Collantes, A. Afendy, J.P. Ong, Z. Goodman, V. Chandhoke, Z.M. Younossi, Gene expression of leptin, resistin, and adiponectin in the white adipose tissue of obese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance. Obes. Surg. 16, 1118–1125 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1381/096089206778392149
N. Vrachnis, P. Belitsos, S. Sifakis, K. Dafopoulos, C. Siristatidis, K.I. Pappa, Z. Iliodromiti, Role of adipokines and other inflammatory mediators in gestational diabetes mellitus and previous gestational diabetes mellitus. Int J. Endocrinol. 2012, 549748 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/549748
A. Gastaldelli, S.A. Harrison, R. Belfort-Aguilar, L.J. Hardies, B. Balas, S. Schenker, K. Cusi, Importance of changes in adipose tissue insulin resistance to histological response during thiazolidinedione treatment of patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 50, 1087–93 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.23116
H. Oku, F. Matsuura, M. Koseki, J.C. Sandoval, M. Yuasa-Kawase, K. Tsubakio-Yamamoto, D. Masuda, N. Maeda, T. Ohama, M. Ishigami, M. Nishida, K. Hirano, S. Kihara, M. Hori, I. Shimomura, S. Yamashita, Adiponectin deficiency suppresses ABCA1 expression and ApoA-I synthesis in the liver. Febs. Lett. 581, 5029–5033 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.08.009
F. Matsuura, H. Oku, M. Koseki, J.C. Sandoval, M. Yuasa-Kawase, K. Tsubakio-Yamamoto, D. Masuda, N. Maeda, K. Tsujii, M. Ishigami, M. Nishida, K. Hirano, S. Kihara, M. Hori, I. Shimomura, S. Yamashita, Adiponectin accelerates reverse cholesterol transport by increasing high density lipoprotein assembly in the liver. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 358, 1091–1095 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.05.040
D.L. Rainwater, S.M. Haffner, Insulin and 2-hour glucose levels are inversely related to Lp (a) concentrations controlled for LPA genotype. Arterioscler Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 18, 1335–1341 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1161/01.atv.18.8.1335
S.M. Haffner, P. Karhapaa, D.L. Rainwater, L. Mykkanen, G. Aldrete Jr, M. Laakso, Insulin sensitivity and Lp (a) concentrations in normoglycemic men. Diabetes Care 18, 193–189 (1995). https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.18.2.193
H. Vaverková, D. Karásek, M. Halenka, L. Cibíčková, V. Kubíčková, Inverse association of lipoprotein (a) with markers of insulin resistance in dyslipidemic subjects. Physiol. Res 66, S113–S120 (2017). https://doi.org/10.33549/physiolres.933583.
G. Ferretti, T. Bacchetti, T.P. Johnston, M. Banach, M. Pirro, A. Sahebkar, Lipoprotein(a): a missing culprit in the management of athero-thrombosis? J. Cell Physiol. 233(4), 2966–81 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26050
J.P. Fisher, C.N. Young, P.J. Fadel, Central sympathetic overactivity: maladies and mechanisms. Auton. Neurosci. 148(1-2), 5–15 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autneu.2009.02.003
Lautt WW. Hepatic Circulation: Physiology and Pathophysiology. San Rafael (CA): Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences. 2009. Colloquium Series on Integrated Systems Physiology: From Molecule to Function to Disease. https://doi.org/10.4199/C00004ED1V01Y200910ISP001
R.A. Rizza, E. Cryer, Haymond, J.E. Gerich, Adrenergic mechanisms for effects of epinephrine on glucose production and clearance in man. J. Clin. Invest 65, 682–689 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI109714
T.K.T. Lam, H. Yoshii, C.A. Haber, E. Bogdanovic, L. Lam, I.G. Fantus, A. Giacca, Free fatty acid-induced hepatic insulin resistance: a potential role for protein kinase C-delta. Am. J. Physiol. 283, E682–E691 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00038.2002
L. Li, G.-Y. Yang, Effect of hepatic glucose production on acute insulin resistance induced by lipid-infusion in awake rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 10, 3208–3211 (2004). https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i21.3208
E.W. Kraegen, G.J. Cooney, J. Ye, A.L. Thompson, Triglycerides, fatty acids and insulin resistance—hyperinsulinemia. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 109, S516–26 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2001-15114
Author contributions
PMP and LDM designed the study. PMP, LDM, and AM conducted clinical determinations, BF, EG, and SS acquired data, PMP, LDM and CBC performed statistical analysis. PMP, LDM, and CBC wrote the manuscript. PMP, LDM, and EB contributed to the manuscript revision
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monti, L.D., Genzano, C.B., Fontana, B. et al. Association between new markers of cardiovascular risk and hepatic insulin resistance in those at high risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Endocrine 75, 409–417 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-021-02868-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-021-02868-x