Abstract
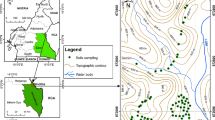
This study aims to assess the metallic contamination of soils and water resources in the environment of the Ouixane mining area (North East Morocco). Six metallic elements (Fe, Cu, Pb, Zn, Ni, and Cd) were analyzed by ICP-AES and ICP-MS. To evaluate the contamination of the soils, three contamination assessment methods were used as follows: enrichment factor (EF), pollution index (PI), and geo-accumulation index (Igeo). The results showed that the soils of the studied area are highly enriched in metallic elements Cd, Cu, Zn, and Pb. Thus, the enrichment factor (EF) revealed an anthropogenic contamination of the majority of studied soils with an extreme contamination by Cd (EFm = 59.29), Cu (EFm = 45.93), and Zn (EFm = 44.73). The results of PI revealed extreme contamination by Cu (PIm = 7.12) and considerable contamination by Zn (PIm = 5.61), Cd (PIm = 4.83), Fe (PIm = 3.09), and Pb (PIm = 3). The Igeo results showed strong contamination for most of the metallic elements and extreme accumulation for Cu and Zn in the Axara-Imnassen lake and the valley located downstream from the Ouixane deposit. Depressions and lakes are highly contaminated by heavy metals due to the leaching phenomenon of surrounding geological formations rich in sulfides. The significant leaching of metallic elements (Cu, Pb, Zn, Ni…) led to significant acid mine drainage (AMD). On the other hand, the geochemistry of the water samples revealed the transfer of metallic pollutants to the water resources which become very acidic locally. Using the contamination degree index (Cd), surface water was found to be highly contaminated by heavy metals (Cd > 3) compared to well water (1 < Cd < 3). Contamination assessment indices combined with the geographic information system (GIS) have been used successfully to identify the most polluted sites.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Backman, B., Bodiš, D., Lahermo, P., Rapant, S., & Tarvainen, T. (1998). Application of a groundwater contamination index in Finland and Slovakia. Environmental Geology, 36(1–2), 55–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002540050320
Barbieri, M. (2016). The importance of enrichment factor (EF) and geoaccumulation index (Igeo) to evaluate the soil contamination. Journal of Geology & Geophysics, 5(1), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.4172/2381-8719.1000237
Bilos, C., Colombo, J. C., Skorupka, C. N., & Rodriguez Presa, M. J. (2001). Sources, distribution and variability of airborne trace metals in La Plata City area. Argentina. Environmental Pollution, 111(1), 149–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(99)00328-0
Bloundi, M. K., Duplay, J., & Quaranta, G. (2009). Heavy metal contamination of coastal lagoon sediments by anthropogenic activities: The case of Nador (East Morocco). Environmental Geology, 56(5), 833–843. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-1184-x
Bouabdellah, M., Lebret, N., Marcoux, E., & Sadequi, M. (2012). Les mines des Beni Bou Ifrour-Ouixane (Rif Oriental): un district ferrugineux néogène de type skarns The Beni Bou Ifrour-Ouixane mines (Eastern Rif), Neogene Skarn Type Iron Deposits.
Boularbah, A., Schwartz, C., Bitton, G., Aboudrar, W., Ahmed, O., & Morel, J.-L. (2006). Heavy metal contamination from mining sites in South Morocco: 2. Assessment of metal accumulation and toxicity in plants. Chemosphere, 63, 811–817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.07.076
Camobreco, V. J., Richards, B. K., Steenhuis, T. S., Peverly, J. H., & McBride, M. B. (1996). Movement of heavy metals through undisturbed and homogenized soil columns. Soil Science, 161(11), 740–750.
CCME. (2007). Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment: Canadian soil quality guidelines for the protection of environmental and human health.
CCME. (2007). Chinese Environmental Protection Administration: Environmental quality standard for soils (GB 15618-1995). Available: http://kjs.mep.gov.cn/hjbhbz/bzwb/trhj/trhjzlbz/199603/W020070313485587994018.pdf.
Chang, A. C., Warneke, J. E., Page, A. L., & Lund, L. J. (1984). Accumulation of heavy metals in sewage sludge treated soils. J. Envir. Qual., 13, 87–91.
Evangelou, V. P., & Zhang, Y. L. (1995). A review: Pyrite oxidation mechanisms and acid mine drainage prevention. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 25(2), 141–199. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389509388477
El Bakkali, S., Gourgaud, A., Bourdier, J.-L., Bellon, H., & Gundogdu, N. (1998). Post-collision Neogene volcanism of the Eastern Rif (Morocco): Magmatic evolution through time. Lithos, 45, 523–543.
Fadil, F., Maarouf, A., & Zaid, A. (1997). Utilisation de Gammarus gauthieri Pinkster (Crustacé: Amphipode) pour tester la toxicité des sédiments des eaux douces. Annales de Limnologie-International Journal of Limnology, 33(2), 73–78.
Förstner, U. (1981). Accumulative phases for heavy metals in limnic sediments. Hydrobiologia, 91(1), 269–284.
Faure-Muret A. (1996). Carte géologique du Maroc au 1/50000, feuille de Zeghanghane. Notes Mém. Serv. Géol. Maroc, n° 370.
François, M., Dubourguier, H. C., Li, D., & Douay, F. (2004). Prediction of heavy metal solubility in agricultural topsoils around two smelters by the physico-chemical parameters of the soils. Aquatic Sciences, 66(1), 78-85
Galán, E., González, I., & Fernández-Caliani, J. C. (2002). Residual pollution load of soils impacted by the Aznalcóllar (Spain) mining spill after clean-up operations. Science of the Total Environment, 286(1–3), 167–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(01)00974-3
Hakanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control a sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14(8), 975–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
Hakkou, R., Benzaazoua, M., & Bussière, B. (2008). Acid mine drainage at the abandoned Kettara Mine (Morocco): 1. Environmental characterization. Mine Water and the Environment, 27(3), 145–159.
Hernandez, J., & Bellon, H. (1985). Chronologie K-Ar du volcanisme miocène du Rif oriental (Maroc): Implications tectoniques et magmatique. Revue De Géologie Et De Géographie Physique, 26, 85–94.
Jabrane, R. (1993). Etudes génétiques de la minéralisation en fer de Nador (Maroc nord oriental). PhD thesis, Univ. Libre Bruxelles, 566p.
Jaquet, J. M., Gavaud, E., & Vernet, J. P. (1982). Basic concepts and associated statistical methodology in the geochemical study of lake sediments. Hydrobiologia, 91(1), 139–146.
Kandpal, G., Srivastava, P. C., & Ram, B. (2005). Kinetics of desorption of heavy metals from polluted soils: Influence of soil type and metal source. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 161(1), 353–363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-005-5548-0
Kerchaoui, S. (1985). Etude géologique et structurale du massif des Beni Bou Ifrour (Rif oriental, Maroc) - Thèse 3ème Cycle (p. 193). Univ.
Kerchaoui, S. (1994). Pétrologie, géochimie et âges des roches magmatiques, leur place dans l’évolution structurale du Massif des Beni Bou Ifrour et du Rif oriental (p. 396p). Thèse Ph D., Univ. Laval, Quebec.
Kuo, S. A., Heilman, P. E., & Baker, A. S. (1983). Distribution and forms of copper, zinc, cadmium, iron, and manganese in soils near a copper smelter. Soil Science, 135(2), 101–109.
Lakrim, M., Mesrar, L., El Aroussi, O., Lahrach, A., Beaabidate, L., Garouani, A., Chaouni, A., Tabyaoui, H., & Jabrane, R. (2011). Impact study of mining waste of the Nador mine on the environment (north-eastern of Morocco). Revue LJEE N, 18, 78–94.
Lee, C. G., Chon, H. T., & Jung, M. C. (2001). Heavy metal contamination in the vicinity of the Daduk Au–Ag–Pb–Zn mine in Korea. Applied Geochemistry, 16(11–12), 1377–1386.
Lee, J. S., & Chon, H. T. (2003). Exposure assessment of heavy metals on abandoned metal mine areas by ingestion of soil, crop plant and groundwater. Journal De Physique IV (proceedings), 107, 757–760.
Legret, M., & Juste, L. D. C. (1988). Migration et spéciation des métaux lourds dans un sol soumis à des épandages de boues de station d’épuration à très forte charge en Cd et Ni. Water Ressources, 22(8), 953–959.
Lepel, E. A., Stefansson, K. M., & Zoller, W. H. (1978). The enrichment of volatile elements in the atmosphere by volcanic activity: Augustine volcano 1976. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 83(C12), 6213–6220.
Lghoul, M., Kchikach, A., Hakkou, R., Teixidó, T., Peña, J. A., & Guérin, R. (2011). Contribution au projet de réhabilitation du site minier abandonné de Kettara (région de Marrakech, Maroc): Apport de l’outil géophysique. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 57(February), 12–15.
Li, Z., Ma, Z., van der Kuijp, T. J., Yuan, Z., & Huang, L. (2014). A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: Pollution and health risk assessment. Science of the Total Environment, 468–469, 843–853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.08.090
Liang, Y., Yi, X., Dang, Z., Wang, Q., Luo, H., & Tang, J. (2017). Heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment in the vicinity of a tailing pond in Guangdong, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(12), 1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14121557
Lim, J., Lee, O. K., Hsu, Y. C., Singh, A., & Choi, K. W. (2007). Drosophila TRAP230/240 are essential coactivators for atonal in retinal neurogenesis. Developmental Biology, 308(2), 322–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.05.02
Lübben, S., & Sauerbeck, D. (1991). The uptake and distribution of heavy metals by spring wheat. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 57(1), 239–247. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00282887
Maanan, M., Saddik, M., Maanan, M., Chaibi, M., Assobhei, O., & Zourarah, B. (2015). Environmental and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Nador lagoon, Morocco. Ecological Indicators, 48, 616–626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.09.034
Manta, D. S., Angelone, M., Bellanca, A., Neri, R., & Sprovieri, M. (2002). Heavy metals in urban soils: A case study from the city of Palermo (Sicily). Italy. SCience of the Total Environment, 300(1–3), 229–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(02)00273-5
Müller, G. (1979). Schwermetalle in den Sedimenten, des Rheins-Veränderungen seit 1971. Umschau, 79(24), 778–783.
Nga, L. E., Sadjo, S. M., & Zame, P. Z. O. (2016). Evaluation de la contamination métallique des sols exposés à l’incinération des pneus d’automobiles dans la ville de Ngaoundéré (Cameroun). J. Mater. Environ. Sci, 7(12), 4633–4645.
Oujidi, B., Tahri, M., Layachi, M., Abid, A., Bouchnan, R., Selfati, M., Bounakhla, M., El Bouch, M., Maanan, M., Bazairi, H., & Snoussi, M. (2020). Effects of the watershed on the seasonal variation of the surface water quality of a post-restoration coastal wetland: The case of the Nador lagoon (Mediterranean Sea, Morocco). Regional Studies in Marine Science, 35, 101127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsma.2020.101127
SEFERIF (1985). Les gisements de fer du Rif Oriental (Nador): Synthèse géologique et évaluation des réserves. Document interne SEFERIF, 69 p.
Serpaud, B., Al-Shukry, R., Casteignau, M., & Matejka, G. (1994). Adsorption des métaux lourds (Cu, Zn, Cd et Pb) par les sédiments superficiels d’un cours d’eau: Rôle du pH, de la température et de la composition du sédiment. Journal of Water Science, 7(4), 343–365.
Sinex, S. A., & Helz, G. R. (1981). Regional geochemistry of trace elements in Chesapeake Bay sediments. Environnemental Geology, 3(6), 315–323. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02473521
Smouni, A., Ater, M., Auguy, F., Laplaze, L., Mzibri, M. E., Berhada, F., Filali-Maltouf, A., Laplaze, L., & Doumas, P. (2012). Evaluation de la contamination par les éléments-traces métalliques dans une zone minière du Maroc oriental. Cahiers Agricultures, 19(4), 273–279.
Sun, G. Q., Liu, Q. X., Jin, Z., Chakraborty, A., & Li, B. L. (2010). Influence of infection rate and migration on extinction of disease in spatial epidemics. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 264(1), 95–103.
Sutherland, R. A. (2000). Bed sediment associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu. Hawaii. Environmental Geology, 39(6), 611–627. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002540050473
Thornton, I. (1996). Risk assessment related to metals: the role of the geochemist. In Report of the international workshop on risk assessment of metals and their inorganic compounds. Angers, France: International Council on Metals and the Environment
Wang, J. (2019). Short-term geochemical investigation and assessment of dissolved elements from simulated ash reclaimed soil into groundwater. Environmental Pollution, 247, 302–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.01.060
Wedepohl, K. H. (1995). The composition of the continental crust. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 59(7), 1217–1232. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(95)00038-2
WHO. (2006). World Health Organization. Guidelines for drinking water quality.
Wiechula, D., & Kwapuliiqski, J. (1997). Use of enrichment, and contamination factors together with geoaccumulation indexes to evaluate the content of Cd, Cu, and Ni in the Rybnik water reservoir in Poland. Water, 93, 347–365.
Wu, J., Teng, Y., Lu, S., Wang, Y., & Jiao, X. (2014). Evaluation of soil contamination indices in a mining area of Jiangxi. China. Plos ONE, 9(11), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0112917
Xie, Y., Chen, T. B., Lei, M., Yang, J., Guo, Q. J., Song, B., & Zhou, X. Y. (2011). Spatial distribution of soil heavy metal pollution estimated by different interpolation methods: Accuracy and uncertainty analysis. Chemosphere, 82(3), 468–476.
Yaroshevsky, A. A. (2006). Abundances of chemical elements in the Earth’s crust. Geochemistry International, 44(1), 48–55.
Zhang, L., & Liu, J. (2012). Comprehensive assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediment of the Pearl River Estuary and adjacent shelf. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 64(9), 1947–1955.
Acknowledgements
This study has been supported by the French Embassy in Morocco within the framework of the APUR Call (Appel à Projet Universitaire et Recherche).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khafouri, A., Talbi, E.H. & Abdelouas, A. Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination of the Environment in the Mining Site of Ouixane (North East Morocco). Water Air Soil Pollut 232, 398 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05318-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05318-6