Abstract
This study elucidates the biosynthesis of two various metal nanoparticles using brown seaweed algae from the southeast coast region of Tamil Nadu. The synthesized SiO2–ZnO nanocomposite was analyzed using UV–Vis, SEM, FT-IR and XRD analysis. The biomedical studies of synthesized SiO2–ZnO nanocomposite on antioxidant, antibacterial and anticancer activity were evaluated. Antioxidant screening assays were performed by using nitric oxide, hydrogen peroxide and ABTS assay. MTT assay and well-cut drug diffusion assay were performed for anticancer and antibacterial studies. The bio-synthesized SiO2–ZnO nanocomposites have acted as a promising potential drug against HT29 cancer cell line of colon cancer and explore the best range of zone inhibition upon gram-negative and gram-positive bacterial strains. The results provide the facts that the seaweed mediated synthesis of SiO2–ZnO nanocomposite might be the potential source to treat adenorectal colon cancer cell and exhibits significant effect on Escherichia coli, Vibrio cholera, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus. This study confirms that seaweed extract mediated synthesis of SiO2–ZnO nanocomposites significantly inhibits bacterial colonies especially urinary tract infection pathogens and shows excellent antioxidant activity.
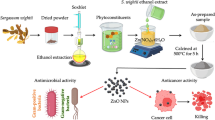
Graphic Abstract
Schematic representation of synthesized SiO2–ZnO nanocomposites and their therapeutic evaluation.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. E. D. Hassan, A. Fouda, A. A. Radwan, S. S. Salem, M. G. Barghoth, M. A. Awad, and M. S. El-Gamal (2019). Endophytic actinomycetes Streptomyces spp. mediated biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles as a promising tool for biotechnological applications. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 24 (3), 377–393.
A. A. Mohamed, A. Fouda, M. A. Abdel-Rahman, S. E. D. Hassan, M. S. El-Gamal, S. S. Salem, and T. I. Shaheen (2019). Fungal strain impacts the shape, bioactivity and multifunctional properties of green synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 19, 101103.
A. Fouda, G. Abdel-Maksoud, M. A. Abdel-Rahman, S. S. Salem, S. E. D. Hassan, and M. A. H. El-Sadany (2019). Eco-friendly approach utilizing green synthesized nanoparticles for paper conservation against microbes involved in biodeterioration of archaeological manuscript. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 142, 160–169.
T. I. Shaheen and A. Fouda (2018). Green approach for one-pot synthesis of silver nanorod using cellulose nanocrystal and their cytotoxicity and antibacterial assessment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 106, 784–792.
A. Fouda, E. L. Saad, S. S. Salem, and T. I. Shaheen (2018). In-vitro cytotoxicity, antibacterial, and UV protection properties of the biosynthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles for medical textile applications. Microb. Pathog. 125, 252–261.
R. S. Tomar, P. S. Chauhan, and V. Shrivastava (2014). A critical review on nanoparticle synthesis: physicochemical v/s biological approach. World J. Pharm. Res. 4 (1), 595–620.
X. Zheng, H. Lin, J. Zheng, X. Duan, and Y. Yuan (2013). Lanthanum oxide-modified Cu/SiO2 as a high-performance catalyst for chemoselective hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to ethylene glycol. ACS Catal. 3 (12), 2738–2749.
F. G. Nador, E. Guisasola Cal, A. Baeza, M. Á. Moreno Villaécija, M. Vallet Regí, and D. Ruiz Molina (2017). Synthesis of polydopamine-like nanocapsules via removal of a sacrificial mesoporous silica template with water. Chem. Eur. J. 23 (12), 2753–2758.
V. J. Mayani, S. V. Mayani, and S. W. Kim (2015). Simple preparation of tungsten supported carbon nanoreactors for specific applications: adsorption, catalysis and electrochemical activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 345, 433–439.
J. Shen, G. Ma, J. Zhang, W. Quan, and L. Li (2015). Facile fabrication of magnetic reduced graphene oxide-ZnFe2O4 composites with enhanced adsorption and photocatalytic activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 359, 455–468.
Z. L. Wang (2009). ZnO nanowire and nanobelt platform for nanotechnology. Mater. Sci. Eng.: R 64 (3–4), 33–71.
J. Santhosh kumar, S. V. Kumar, and S. Rajeshkumar (2017). Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using plant leaf extract against urinary tract infection pathogen. Resour.-Effic. Technol. 3 (4), 459–465.
B. Kumar, K. Smita, L. Cumbal, and A. Debut (2014). Green approach for fabrication and applications of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Bioinorg Chem Appl. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/523869.
T. K. Sau and C. J. Murphy (2004). Room temperature, high-yield synthesis of multiple shapes of gold nanoparticles in aqueous solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126 (28), 8648–8649.
L. Castro, M. L. Blázquez, J. A. Muñoz, F. González, and A. Ballester (2013). Biological synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using algae. IET Nanobiotechnol. 7 (3), 109–116.
M. Singh, R. Kalaivani, S. Manikandan, N. Sangeetha, and A. K. Kumaraguru (2013). Facile green synthesis of variable metallic gold nanoparticle using Padina gymnospora, a brown marine macroalga. Appl. Nanosci. 3 (2), 145–151.
M. Fresta, G. Puglisi, G. Giammona, G. Cavallaro, N. Micali, and P. M. Furneri (1995). Pefloxacinemesilate-and ofloxacin-loaded polyethylcyanoacrylate nanoparticles: characterization of the colloidal drug carrier formulation. J. Pharm. Sci. 84 (7), 895–902.
S. Nagarajan and K. A. Kuppusamy (2013). Extracellular synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticle using seaweeds of gulf of Mannar, India. J. Nanobiotechnol. 11 (1), 1–11.
Y. H. Kim, D. K. Lee, H. G. Cha, C. W. Kim, Y. C. Kang, and Y. S. Kang (2006). Preparation and characterization of the antibacterial Cu nanoparticle formed on the surface of SiO2 nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 110 (49), 24923–24928.
M. P. Vinardell, H. Llanas, L. Marics, and M. Mitjan (2017). In vitro comparative skin irritation induced by nano and non-nano zinc oxide. Nanomaterials 7 (3), 56.
J. W. Rasmussen, E. Martinez, P. Louka, and D. G. Wingett (2010). Zinc oxide nanoparticles for selective destruction of tumor cells and potential for drug delivery applications. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 7 (9), 1063–1077.
J.M. Antonisamy, K. Eahamban, (2012). UV—VIS spectroscopic and HPLC studies on Dictyota bartayresiana Lamour. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2 (2), S514–S518.
D. Huang, Y. Zhang, J. Zhang, H. Wang, M. Wang, C. Wu, and Z. Zhao (2019). The synergetic effect of a structure-engineered mesoporous SiO2–ZnO composite for doxycycline adsorption. RSC Adv. 9 (66), 38772–38782.
A. E. Bayat and R. Shams (2019). Appraising the impacts of SiO2, ZnO and TiO2 nanoparticles on rheological properties and shale inhibition of water-based drilling muds. Colloids Surf. A 581, 123792.
Z. Jin, H. Yang, J. Lv, L. Tong, G. Chen, and Q. Zhang (2018). Effect of ZnO on viscosity and structure of CaO–SiO2–ZnO–FeO–Al2O3 slags. JOM 70 (8), 1430–1436.
P. Maijan, P. Amornpitoksuk, and S. Chantarak (2020). Synthesis and characterization of poly (vinyl alcohol-g-acrylamide)/SiO2@ ZnO photocatalytic hydrogel composite for removal and degradation of methylene blue. Polymer 203, 122771.
Y. Wang, D. Sun, G. Liu, and W. Jiang (2015). Synthesis of Fe3O4@ SiO2@ ZnO core–shell structured microspheres and microwave absorption properties. Adv. Powder Technol. 26 (6), 1537–1543.
S. Badami, S. Moorkoth, S. R. Rai, E. Kannan, and S. Bhojraj (2003). Antioxidant activity of Caesalpinia sappan heartwood. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 26 (11), 1534–1537.
X. Y. Zhang, Principles of chemical analysis. (China Science Press, Beijing, 2000), pp. 275–276.
R. Re, N. Pellegrini, A. Proteggente, A. Pannala, M. Yang, and C. Rice-Evans (1999). Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 26 (9–10), 1231–1237.
D. Veer, R. M. Singhand, and H. Kumar (2017). Structural and optical characterization of ZnO-TiO2-SiO2 nanocomposites synthesized by sol-gel technique. Asian J. Chem. 29 (11), 2391–2395.
N. Suganthi and K. Pushpanathan (2018) Spherical and dumbbell shape biphasic paramagnetic ZnS: Fe nanoparticles on ferromagnetic ZnS host background. J. Electron. Mater. 47 (12), 7343–7357
B. D. Cullity, Elements of X-ray diffraction. (Addison-Wesley Publishing, Boston, 1956), pp. 1–13.
G. Gao, N. Da, S. Reibstein, and L. Wondraczek (2010). Enhanced photoluminescence from mixed-valence Eu-doped nanocrystalline silicate glass ceramics. Opt. Express 18 (104), A575–A583.
S. A. Wissinga, O. Kayserb, and R. H. Muller (2004). Solid lipid nanoparticles for parenteral drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 56, 1257–1272.
C. Jacobs, O. Kayser, and R. H. Muller (2000). Nanosuspensions asa new approach for the formulation for the poorlysoluble drug tarazepide. Int. J. Pharm. 196, 161–164.
N. Nasseh, A. H. Panahi, M. Esmati, N. Daglioglu, A. Asadi, H. Rajati, and F. Khodadoost (2020). Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline from aqueous solution by a novel magnetically separable FeNi3/SiO2/ZnO nano-composite under simulated sunlight: efficiency, stability, and kinetic studies. J. Mol. Liq. 301, 112434.
M. Qasim, J. Ananthaiah, S. Dhara, P. Paik, and D. Das (2014). Synthesis and characterization of ultra-fine colloidal silica NPs. Adv. Sci. Eng. Med. 6 (9), 965–973.
D. Y. Kong, M. Yu, C. K. Lin, X. M. Liu, J. Lin, and J. Fang (2005). Sol-gel synthesis and characterization of Zn2SiO4: Mn@ SiO2 spherical core-shell particles. J. Electrochem. Soc. 152 (9), H146. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1990612.
N. Suganthi, S. Thangavel, and K. Kannan (2020). Hibiscus subdariffa leaf extract mediated 2-D fern-like ZnO/TiO2 hierarchical nanoleaf for photocatalytic degradation. FlatChem 24, 100197.
P. Pacher, J. S. Beckman, and L. Liaudet (2007). Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 87 (1), 315–424.
A. Sirelkhatim, S. Mahmud, A. Seeni, N. H. Kaus, L. C. Ann, S. K. Bakhori, H. Hasan, and D. Mohamad (2015). Review on zinc oxide nanoparticles: antibacterial activity and toxicity mechanism. Nano-micro Lett. 7 (3), 219–242.
N. Suganthi and K. Pushpanathan (2019). Photocatalytic degradation and antimicrobial activity of transition metal doped mesoporous ZnS nanoparticles. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 3375–3388.
V. V. Shinde, D. S. Dalavi, S. S. Mali, C. K. Hong, J. H. Kim, and P. S. Patil (2014). Surfactant free microwave assisted synthesis of ZnO microspheres: study of their antibacterial activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 307, 495–502.
N. Padmavathy and R. Vijayaraghavan (2008). Enhanced bioactivity of ZnO nanoparticles—an antimicrobial study. Sci Technol. Adv. Mater. 9 (3), 035004.
S. Suresh, P. Saravanan, K. Jayamoorthy, S. A. Kumar, and S. Karthikeyan (2016). Development of silane grafted ZnO core shell nanoparticles loaded diglycidyl epoxy nanocomposites film for antimicrobial applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 64, 286–292.
B. L. Guo, P. Han, L. C. Guo, Y. Q. Cao, A. D. Li, J. Z. Kong, H. F. Zhai, and D. Wu (2015). The antibacterial activity of Ta-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 10 (1), 1.
J. Sawai, S. Shoji, H. Igarashi, A. Hashimoto, T. Kokugan, M. Shimizu, and H. Kojima (1998). Hydrogen peroxide as an antibacterial factor in zinc oxide powder slurry. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 86 (5), 521–522.
G. Applerot, J. Lellouche, N. Perkas, Y. Nitzan, A. Gedanken, and E. Banin (2012). ZnO nanoparticle-coated surfaces inhibit bacterial biofilm formation and increase antibiotic susceptibility. Rsc Adv. 2 (6), 2314–2321.
J. Pasquet, Y. Chevalier, E. Couval, D. Bouvier, and M. A. Bolzinger (2015). Zinc oxide as a new antimicrobial preservative of topical products: interactions with common formulation ingredients. Int. J. Pharm. 479 (1), 88–95.
T. J. Brunner, P. Wick, P. Manser, P. Spohn, R. N. Grass, L. K. Limbach, A. Bruinink, and W. J. Stark (2006). In vitro cytotoxicity of oxide nanoparticles: comparison to asbestos, silica, and the effect of particle solubility. Environ. Sci. Technol. 40 (14), 4374–4381.
M. Li, L. Zhu, and D. Lin (2011). Toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles to Escherichia coli: mechanism and the influence of medium components. Environ. Sci. Technol. 45 (5), 1977–1983.
N. Talebian, S. M. Amininezhad, and M. Doudi (2013). Controllable synthesis of ZnONPs and their morphology-dependent antibacterial and optical properties. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 120, 66–73.
S. Ostrovsky, G. Kazimirsky, A. Gedanken, and C. Brodie (2009). Selective cytotoxic effect of ZnO NPs on glioma cells. Nano Res. 2 (11), 882–890.
M. J. Akhtar, M. Ahamed, S. Kumar, M. M. Khan, J. Ahmad, and S. A. Alrokayan (2012). Zinc oxide NPs selectively induce apoptosis in human cancer cells through reactive oxygen species. Int. J. Nanomed. 7, 845–857.
A. V. A. Mariadoss, V. Ramachandran, V. Shalini, B. Agilan, J. H. Franklin, K. Sanjay, Y. G. Alaa, M. A. Tawfiq, and D. Ernest (2019). Green synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles by Malus domestica and its cytotoxic effect on (MCF-7) cell line. Microb. Pathog. 135, 103609.
A. Stankovic, S. Dimitrijevic, and D. Uskokovic (2013). Influence of size scale and morphology on antibacterial properties of ZnO powders hydrothemally synthesized using different surface stabilizing agents. Colloids Surf. B 102, 21–28.
D. C. Hooper (2001). Mechanisms of action of antimicrobials: focus on fluoroquinolones. Clin. Infect. Dis. 32 (Supplement_1), S9–S15.
P. Arya (2018). Antioxidant, phytochemical and antibacterial action of Himalayan medicinal herbs Peristrophebicalyculata leaves extract against respiratory tract pathogens. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 10, 16–21.
S. Shaaban, A. Negm, M. A. Sobhand, and L. A. Wessjohann (2015). Organoselenocyanates and symmetrical diselenides redox modulators: design, synthesis and biological evaluation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 97, 190–201.
S. BarathManiKanth, K. Kalishwaralal, M. Sriram, S. R. K. Pandian, H. S. Youn, S. Eomand, and S. Gurunathan (2010). Anti-oxidant effect of gold NPs restrains hyperglycemic conditions in diabetic mice. J. Nanobiotechnol. 8 (1), 1–16.
L. Brannon-Peppas and J. O. Blanchette (2004). NPs and targeted systems for cancer therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 56 (11), 1649–1659.
F. T. Thema, E. Manikandan, M. S. Dhlamini, and M. Maaza (2015). Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles via Agathosma betulina natural extract. Mater. Lett. 161, 124–127.
M. Ramesh, M. Anbuvannan, and G. J. Viruthagiri (2015). Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Solanum nigrum leaf extract and their antibacterial activity. Spectrochim. Acta A 136, 864–870.
T. Bhuyan, K. Mishra, M. Khanuja, R. Prasad, and A. Varma (2015). Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles from Azadirachta indica for antibacterial and photocatalytic applications. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 32, 55–61.
H. Q. Alijani, S. Pourseyedi, M. T. Mahani, and M. Khatami (2019). Green synthesis of zinc sulfide (ZnS) nanoparticles using Stevia rebaudianaBertoni and evaluation of its cytotoxic properties. J. Mol. Struct. 1175, 214–218.
P. Jamdagni, P. Khatri, and J. S. Rana (2018). Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using flower extract of Nyctanthes arbor-tristis and their antifungal activity. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 30 (2), 168–175.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of other authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bharathi, D.S., Boopathyraja, A., Nachimuthu, S. et al. Green Synthesis, Characterization and Antibacterial Activity of SiO2–ZnO Nanocomposite by Dictyota bartayresiana Extract and Its Cytotoxic Effect on HT29 Cell Line. J Clust Sci 33, 2499–2515 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-021-02170-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-021-02170-w