Abstract
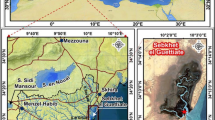
The characterization of organic matter (OM) composition, physico-chemical, geochemical, and mineralogical studies of sedimentary core can help to better understand the paleoclimates and the depositional environments. The purpose of this work is to identify the factors monitoring the mineralogical composition and the sedimentation of sebkha Mhabeul sediments (southeastern Tunisia), during the Holocene. A 100.5 cm core (Mh 1) collected from this sebkha was analyzed for the determination of chemical composition by X-ray fluorescence (XRF), carbonate content by Bernard calcimetry, grain-sized sediments by AFNOR sieves, OM content by Rock-Eval 6 Pyrolysis, and mineralogical composition by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electronic microscope (SEM), and infrared spectroscopy (IR). The sedimentary fillings of this sebkha, constituted by fine fractions, are characterized by the dominance of the detrital minerals (72–96 %) with high quartz percentages (42.2–91.5 %). The mineralogical composition of the studied sediments included detrital minerals (clay minerals, quartz, and feldspars), carbonate minerals (ankerite, dolomite, and calcite), and evaporitic minerals (halite, bassanite). The clay minerals (11–14%) are composed of a mixture of kaolinite, illite and palygorskite. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) absorption spectra of all sediment samples confirm the mineralogical composition obtained by XRD and the existence of OM, by defining the band assignments for OM and different minerals as quartz, feldspar, clay, and carbonate minerals. The Rock Eval pyrolysis shows that the OM is immature and has a mixed origin (terrestrial and aquatic). The statistical analyses prove the results of geochemical and mineralogical studies. Indeed, the principal component analysis (PCA) of geochemical and mineralogical data and the depth help to prove the relationships between minerals and chemical elements. Moreover, the negative correlation between the Rock Eval Pyrolysis parameters and the depth shows a homogenous statistical group.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abichou A (2002) Les changements de paysages du bassin-versant de l’oued-Tataouine Fessi (sud-est tunisien). Étude multiscalaire et micromorphologie des remplissages des sebkhas et des états de surface des sols. PhD thesis, Univ. Michel de Montaigne, Bordeaux-3, France
Adatte TH, Rumley G (1989) Sedimentology and mineralogy of the Valanginian and Hauterivian in the Stratotypic Region (Jura Mountains, Switzerland). In: Wiedmann J (ed) Cretaceous of the Western Tethys: proceedings 3 International Cretaceous Symposium. Schweizerbartsche Verlagsbuchandl-hung, Stuttgart
Alassane A, Trabelsi R, Dovon LF, Odeloui DJ, Boukari M, Zouari K, Mama D (2015) Chemical evolution of the continental terminal shallow aquifer in the south of coastal sedimentary basin of Benin (West-Africa) Using Multivariate Factor Analysis. J Water Resource Protect 7:496–515. https://doi.org/10.4236/jwarp.2015.76040
Alin SR, Cohen AS (2003) Lake level history of Lake Tanganyika, East Africa, for the past 2500 years based on ostracodeinferred water depth reconstruction. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 199(1-2):31–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-0182(03)00484-X
Alpert NL, Keiser WE, Szymanshi HA (1970) IR-Theory and practice of infrared spectroscopy, 2nd edn. Plenum Press, New York
Barahona E (1974) Arcillas de ladrillerga de la provincia de Granada: evaluacion de algunos ensayos de mate ias primas. PhD thesis, Univ. Granada, Spain
Bellamy LJ (1958) The Infrared spectra of complex molecules. Methuen, London and Wiley, New York
Ben Ameur M, Masmoudi S, Abichou A, Medhioub M, Yaich C (2019) Use of the magnetic, geochemical, and sedimentary records in establishing paleoclimate change in the environment of Sebkha: Case of the Sebkha Mhabeul in southeastern Tunisia. Comptes Rendus-Geosci 351:487–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crte.2019.10.003
Benito G, Macklin MG, Zielhofer C, Jones AF, Machado MJ (2015) Holocene flooding and climate change in the Mediterranean. Catena 130:13–33
Benton MJ, Bouaziz S, Buffetaut E, Martill D, Ouaja M, Soussi M, Trueman C (2000) Dinosaurs and other fossil vertebrates from fluvial deposits in the Lower Cretaceous of Southern Tunisia. Palaeolgeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 157:227–246
Bjorlykke K (1984) Formation of secondary porosity. How important is it? In D.A. McDonald and R.C. Surdam (eds.). Clastic diagenesis: AAPG Memoir 37:277–286
Bjorlykke K (1998) Clay mineral diagenesis in sedimentary basins- a key to the prediction of rock proprieties. Example from the North Sea Basin. Clay Miner 33:15–34
Blanc-Alétru MC (1995) Importance des discontinuités dans l’enregistrement sédimentaire de l’Urgonien Jurassien : micropaléontologie, sédimentologie, minéralogie et stratigraphie séquentielle. Géologie Alpine, Mémoire Hors-Série 24:299 pp. https://tel.archives-ouvertes.fr/tel-00723728
Bouaziz S (1986) La déformation dans la plateforme du sud Tunisien (Dahar et Jeffara): approche Multiscalaire et pluridisciplinaire. PhD thesis, Univ. Tunis II, Faculty of Sciences of Tunis.87), 197 pp
Bouaziz S (1995) Etude de la tectonique cassante dans la plate-forme et l’atlas saharien (Tunisie Méridionale): Evolution des paléochamps de contraintes et implications géodynamiques. PhD Thesis, Univ. Tunis II, Faculty of Science of Tunis, 485 pp
Bouaziz S, Jedoui Y, Barrier E, Angelier J (2003) Néotectonique affectant les dépôts marins tyrrhéniens du littoral sud-est tunisien: implication pour les variations du niveau marin. C.R. Geosci 335:247–254
Brindley GW, Grim RE (1969) Mica clay minerals. In: In X-ray identification and crystal structure of clay minerals, 2, Edi edn. Mineralogical Society, London, p 544
Brostoff W, Lichvar R, Sprecher S (2001) Delineating playas in the arid southwest: a literature review. In: ERDC Technical Report. U.S.Army Corps of Engineers, Engineer Research and Development Center, Vicksburg, MS, USA, pp 04–01
Brown JK (1955) The infrared spectra coals. J Chem Soc 1995:744–752
Busson G (1961) Sur la stratigraphie des séries triasiques et jurassiques du Sahara tunisien entre la latitude de Foum Tataouine et celle de Medenine. Acad Sci T 253
Castany G (1954) L’accident Sud tunisien, son âge et ses relations avec l’accident Sud atlasique d’Algérie. Note H. Devaux, Bull. Soc. Franç. Phys, séance du 8 Février, p 184
Chairi R (2004) Etude du remplissage sédimentaire récente et de la matière organique associée, dans la sebkha de Moknine. PhD. Univ, Tunis El Manar, Faculty of Sciences of Tunis
Chairi R (2005) Etude du remplissage sédimentaire d’un système hypersalin de la Tunisie orientale au cours du Quaternaire récent: la sebkha de Moknine. Quaternaire 16(2):107–117
Chamley H (1981) Long-time trends in clay deposition in the ocean. Oceanol Acta Special issue:105–110pp
Chamley H (1989) Clay sedimentology. Springer, Berlin
Chopin Ch (2016) Analyse géochimique de la composition des sédiments permiens-triasiques du bassin de Graissessac-Lodève: traçage des sources. Master’s thesis, Univ. Rennes 1, France
Christidis G, Marcopolous T (1992) Kaolinite generating processes in the Milos Bentonites and their influence on the physical properties of Bentonites. Bullet Geol Soc Greece
Cojan I, Renard M (1995) Sédimentologie (418pp). Masson, Paris
Condie CK, Noll PD, Conway CM (1992) Geochemical and detrital mode evidence for two sources of Early Proterozoic sedimentary rocks from the Tonto Basin Super group, central Arizona. Sediment Geol 77:51–76
Copard Y, Di-Giovanni C, Martaud T, Albéric P, Olivier JE (2006) Using rock-eval 6 pyrolysis for tracking fossil organic carbon in modern environments: Implications for the roles of erosion and weathering. Earth Surf Process Landf 31(2):135–153
Dabard MP (1990) Lower Brioverian formations (Upper Proterozoic) of the Armorican Massif (France): geodynamic evolution of source areas revealed by sandstone petrography and geochemistry. Sediment Geol 69:45–58
Desprat S, Sanchez Goni MF, Loutre MF (2003) Revealing climatic variability of the last three millennia in northwestern Iberia using pollen influx data. Earth Plan Sci Lett 213:63–78
Di-Giovanni C, Disnar JR, Campy M, Macaire JJ (1999) Variability of the ancient organic matter supply in modern humus. ANALUSIS 27(5):398–402
Disnar JR, Guillet B, Keravis D, Di-Giovanni C, Sebag D (2003) Soil organic matter (SOM) characterization by Rock-Eval pyrolysis: Scope and limitations. Org Geochem 34(3):327–343
Espitalié J, Laporte JL, Madec M, Marquis F, Leplat P, Paulet J, Boutefeu A (1977) Méthode rapide de caractérisation des roches mères de leur potentiel pétrolier et de leur degré d’évolution. Revue de l’Institut Français du Pétrole 32:23–42
Espitalié J, Deroo G, Marquis F (1985a) Rock val pyrolysis and its applications. Revue de l’Institut Français du Pétrole 40(5):563–579
Espitalié J, Deroo G, Marquis F (1985b) Rock Eval pyrolysis and its applications. Revue de l’Institut Français du Pétrole, 40, 653–578 (Part I) ; 40, 755–784 (Part II) ; 41, 73–89 (Part III)
Essefi E, Jmaa H, Touire J, Tagortig MA, Yaich C (2013) Variability to sedimentary dynamics and climatic conditions during the last two millennia at sebkha Souassi in eastern Tunisia. Papers on Global Change 20:29–45. https://doi.org/10.2478/igbp-2013-0001
Essefi E, Mefteh S, Medhioub M, Yaich C (2014) Magnetic study of the heated and unheated sedimentary fillings of Sebkha Mhabeul, Southeast Tunisia: a geophysical method for paleoclimatic investigation and tephrochronological dating. Int J Geophys 2014:7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/908395
Essefi E, Gharsalli N, Yaich C (2015a) Climatic significance aeolian sedimentary filling of sebkha Mhabeul, Southeastern Tunisia: Contribution of the genetic approach. J Basic Appl Res Int 15(2-4):140–152
Essefi E, Gharsalli N, Salhi S, Yaich C (2015b) Cyclicity of grain size parameters along a core from the Gleysol of Sebkha Ennoual, Southeastern Tunisia. J Basic Appl Res Int 15(5-3):124–134
Essefi E, Gharsalli N, Yaich C (2015c) Geophysical and geochemical study of the silico-evaporitic sedimentary filling of Boujmal wetland, Estern Tunisia: Inferring the climatic signal within groundwater Noice. J Basic Appl Res Int 15(2-2):14–25
Farmer VC (1974) The infrared spectra of minerals. Mineralogical Society, London 366, 369, 437pp
Faust D, Zielhofer C, Baena ER, Diaz del Olmo F (2004) High resolution fluvial record of late Holocene geomorphic change in northern Tunisia: climatic or human impact? Quat Sci Rev 23:1757–1775
Felhi M (2010) Les niveaux intercalaires de la série yprésienne du bassin Gafsa-Métlaoui : Apports de la minéralogie des argiles et de la géochimie de la matière organique résiduelle à la reconstitution paléoenvironnementale. PhD thesis, Univ. Sfax. Faculty of Sciences of Sfax, 82–84 pp
Fernández-Carrasco L, Torrens-Martín D, Morales LM, Martínez-Ramírez S (2012) Infrared spectroscopy in the analysis of building and construction materials, infrared spectroscopy–materials science, engineering and technology, Prof. Theophanides Theophile (Ed.), ISBN: 978-953-51-0537-4, InTech. Available from: http://www.intechopen.com/books/infrared-spectroscopymaterials-scienceengineeringand-technology/infrared-spectroscopy-ofcementitious-materials. https://doi.org/10.5772/36186
Folk RL (1980) Petrology of sedimentary rocks. Hemphills 182
Gabtini H, Jallouli C, Mickus KL, Zouari H, Turki M (2009) Deep structure and crustal configuration of the Jeffara basin (Southern Tunisia) based on regional gravity, seismic reflection and borehole data: How to explain a gravity maximum within a large sedimentary basin? J Geodyn 47:142–152
Gallela W (2010) Les sables quartzo-feldspathiques de la Tunisie centro-méridionale : sédimentologie, minéralogie et applications industrielles. PhD thesis, Univ. Sfax. Faculty of Sciences of Sfax. 79 –82pp
Gammar AM (2002) Végétation. Atlas National de la Tunisie. Carte au 1/1 000 000+ notice. CERES, Tunis
Gammar AM (2008) Carte de la végétation de la Tunisie. In: Henia L (ed) Atlas de l’eau en Tunisie. Faculté des sciences humaines et sociales de Tunis, Tunis, pp 130–133
Gammoudi A, Essefi E, Rigane H (2019) Variability of the grain-sized fractions during the last three millennia within the sedimentary fillings of the saline system of Mhabeul: the Holocene cyclostratigraphy. Arab J Geosci 12:296. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4472-3
Gargouri Z (2011) Etude sédimentologique et radiochronologique des dépôts du domaine paralique dans le Golfe de Gabes (Sebkha El Guettiate-Sebkha Dreiaa). PhD thesis. Univ. Sfax. Faculty of Sciences of Sfax. 111, 112, 115, 118pp
Glasmann JR, Clark RA, Larter S, Briedis NA, Lundegard PD (1989) Diagenesis and hydrocarbon accumulation, Brent sandstone (Jurassic), Bergen High Area, North Sea. AAPG Bulll 73:341–1360
Greenwood PJ, Shaw HF, Fallick AE (1994) Petrographic and isotopic evidence for diagenetic processes in Middle Jurassic sandstones and mudrocks from the Brea Area, North Sea. Clay Miner 29:637–650
Hambrey MJ, Ehrann WU, Larsen B (1991) Cenozoic glacial record of the Prydz Bay continental shelf, East Antarctica. In: Barron J, Larsen B et al (eds) Proc. ODP, Sci. Results, 119th edn. Ocean Drilling Program, College Station, pp 77–132
Hancock NJ, Taylor AM (1978) Clay minerals diagenesis and oil migration in the middle jurassique Brent sand formation. J Geol Soc Lond 135:69–72
Hetényi M, Nyilas T, Toth TM (2005) Stepwise Rock-Eval pyrolysis as a tool for typing heterogeneous organic matter in soils. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 74(1-2):45–54
Hfaiedh R (2014) Paléoenvironnement, evolution et géométrie du bassin crétacé (Aptien-Albien) de la région de chotts à travers l’étude de l’anticlinal du Bir Oum Ali : interaction événements climatiques globaux / eustatisme/tectonique. PhD thesis. Univ Sfax. National School of Engineers of Sfax, 33-36pp
IPCC (2014) In: Pachauri RK, Meyer LA (eds) Climate Change (2014) Synthesis report, contribution of working groups I, II and III to the Fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. IPCC, Geneva, 15pp
Jaouadi S, Lebreton V, Bout-Roumazeilles V, Siani G, Lakhdar R, Boussoffara R, Dezileau L, Kallel N, Mannai-Tayech B, Combourieu-Nebout N (2016) Environmental changes, climate and anthropogenic impact in south-east Tunisia during the last 8 kyr. Clim Past 12:1339–1359. https://doi.org/10.5194/cp-12-1339-2016
Jedoui Y, Kallel N, Fontugne M, Ben Ismail MH, M'rabet A, Montacer M (1998) A high relative sea level stand in the middle Holocene of southeastern Tunisia. Mar Geol Amst 147:123–130
Jedoui Y, Davaud E, Ben Ismail H, Reyss JL (2002) Analyse sédimentologique des dépôts marins pléistocènes du sud-est tunisien: mise en évidence de deux périodes de haut niveau marin pendant le sous-stade isotopique marin 5 (Eemien, Tyrrhénien). Bulletin de la Société Géologique de France 173:63–72
Lafargue E, Marquis F, Pillot D (1998) Rock-Eval 6 applications in hydrocarbon exploration, production, and soils contamination studies. Rev Instit Franç Pétrole 53:421–437
Lakhdar R (2009) Les sédiments holocènes et les tapis microbiens du littoral du Sud-Est de la Tunisie: sédimentologie et paléoenvironnements. PhD thesis. Univ. Sfax, Fac. Sciences of Sfax 42, 45, 47, 62, 63 pp
Lakhdar R, Soussi M, Ben Ismail MH, M'Rabet A (2006) A Mediterranean Holocene restricted coastal lagoon under arid climate:case of the sedimentary record of Sabkha Boujmel (SE Tunisia). Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 241:177–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2006.02.014
Lamourou A, Touir J, Fagel N (2017) Reconstructing the Holocene depositional environments along the northern coast of Sfax (Tunisia): Mineralogical and sedimentological approaches. J Afr Earth Sci 129:713–727
Le Houérou HN (1969) La végétation de la Tunisie steppique et des régions limitrophes. Ariana: Annales de l’Institut National de la Recherche Agronomique de Tunisie 42(5)
Lebreton V, Jaouadi S, Mulazzani S, Boujelben A, Belhouchet L, Gammar AM, Combourieu-Nebout N, Saliège JF, Karray MR, Fouache E (2016) Early oleiculture or native wild Olea in eastern Maghreb: new pollen data from the sebkha-lagoon Halk el Menjel (Hergla, Central Tunisia). Environ Archaeol 20:265–273
Lewis DG, Mc Conchie D (1994) Analytical sedimentology. Chapman & Hall, London, p 360
Lebreiro SM, Frances G, Abrantes FFG, Diz P, Bartels-Jonsdottir HB, Stroynowski ZN, Gil IM, Pena LD, Rodrigues T, Jones PD, Nombela MA, Alejo I, Briffa KR, Harris I, Grimalt JO (2006) Climate change and coastal hydrographic response along the Atlantic Iberian margin (Tagus Prodelta and Muros Ria) during the last two millennia. The Holocene 16(7):1003–1015
Li W, Shao LY, Shen R, Wang Z, Yang S, Tang U (2010) Size, composition, and mixing state of individual aerosol particles in a South China coastal city. J Environ Sci 22(4):561–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(09)60146-7
Maglione G, Carn M (1977) Spectres infrarouges des minéraux salins et des silicates néoformés dans le bassin tchadien. Cah. ORSTOM, sér. Géol. 7:3–9
Marchand C, Lallier-Vergès E, Baltzer F (2003) The composition of sedimentary organic matter in relation to the dynamic features of a mangrove-fringed coast in French Guiana
Marquer L, Pomel S, Abichou A, Schulz E, Kaniewski D, Van Campo E (2008) Late Holocene high resolution palaeoclimatic reconstruction inferred from Sabkha Mhabeul, southeast Tunisia. Quat Res 70:240–250
Mefteh S, Medhioub M, Essefi E, Jamoussi F (2014) Effect of diagenesis on clay mineralogy and organic matter in the Tunisian southern subsurface. J Geol Soc India 83:198–210
Meyers PA, Lallier-Vergès E (1999) Lacustrine sedimentary organic matter records of Late Quaternary paleoclimates. J Paleolimnol 21(3):345–372
Millot G (1964) Géologie des argiles. Masson, Paris, p 499
Moore DM, Reynolds RCJ (1989) X-ray diffraction and the identification and analysis of clay minerals. Oxford University Press, Oxford, p 332
Mouchet P (1995) Le Kimméridgien du Jura central. Microfaciès, minéralogie et interprétation séquentielle. PhD thesis, Univ. Neuchâtel, 350pp
Mukasa-Tebandeke IZ, Ssebuwufu PJM, Nyanzi SA, Schumann A, Nyakairu GWA, Ntale M, Lugolobi F (2015) The elemental, mineralogical, IR, DTA and XRD analyses characterized clays and clay Minerals of Central and Eastern Uganda. Adv Mater Physics Chem 5:67–86. https://doi.org/10.4236/ampc.2015.52010
Nguyen T, Janik LJ, Raupach M (1991) Diffuse reflectance infrared fourier transform (DRIFT) spectroscopy in soil studies. Aust J Soil Res 29:49–67
Noffke N, Gerdes G, Klenke T, Krumbein WE et al (1997) A microscopic sedimentary succession of graded sand and microbial mats in modern siliciclastic tidal flats. Sediment Geol 110:1–6
Obame RM, Copard Y, Sebag D, Boussafir M, Bichet V et al. (2010) Apport de la matière organique dans l’étude de la dynamique sédimentaire lacustre en zone sahélienne (exemples de deux complexes limniques, SW Niger). In Z. Garba, B. Ngounou Ngatcha, D. Sebag & A. Durand (eds), Géosciences & Développement : impacts de l’homme et du climat sur les mileux saheliens (pp. 47–52pp). Pangea
Osborne MJ, Swarbrick RE (1994) Diagenesis in North Sea HTHP clastic reservoirs-consequences for porosity and overpressure prediction. Mar Pet Geol 16:337–353
Ossorio M, Van Driessche AES, Pérez P, García-Ruiz JM (2014) The gypsum-anhydrite paradox revisited. Chem Geol 386:16–21
Otmane R (2014) Evénements extrêmes du passé et paleo-environnements: Reconstitution à partir des archives sédimentaires de la lagune de Nador, Maroc. PhD thesis. Univ. Mohammed V de Rabat. Faculty of Sciences of Rabat, p 118
Pachauri T, Singla V, Satsangi A, Lakhani A, Kumari KM (2013) SEM-EDX Characterization of Individual Coarse Particles in Agra, India. Aerosol Air Qual Res 13:523–536. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2012.04.0095
Paskoff R, Sanlaville P (1983) Les côtes de la Tunisie: variation du niveau marin depuis le Tyrrhénien. Ed. Maison de l'orient, Lyon, Fr., 78 fig., 21 photos, 192pp
Patience AJ, Lallier-Verges E, Alberic P, Desprairies A, Tribovillard N (1996) Relationships between organo-mineral supply and early diagenesis in the lacustrine environment: a study of surficial sediments from the lac du bouchet (Haute Loire, France). Quat Sci Rev 15(2-3):213–221
Pelletier JD, Cook JP (2005) Deposition of playa windblown dust over geologic times scales. Geology 33:909–912 Schulz E, Abichou H, Hachicha T, Pomel S, Salzmann U, Zouari K (2005) The Mid-Holocene vegetation and landscape history of Southeastern Tunisia. Archaeobotany and Vegetation History, Springer Verlag Berlin (in press)
Pomel S, Abichou A, Schulz E (2008) La signification paléoimpluviométrique des sédiments de la sebkha Mhabeul (Sud-Est de la Tunisie). Presses Université Blaise Pascal, pp 435–442, 2006, Collection Nature et Société. https://halshs.archivesouvertes.fr/halshs-00335804
Ramasamy V, Rajkumar P, Ponnusamy V (2006) FT-IR Spectroscopic analysis and mineralogical characterization of Velar river sediments. Bullet Pure Appl Sci 25:49–55
Robin PL, Rouxhet PG (1978) Caracterization of kerogens and study of their évolution by infrared spectroscopy: carbonyl and carboxyl groups. Geochim Cosmochin Acta 42:1341–1349
Sanei H, Stasiuk LD, Goodarzi F (2005) Petrological changes occurring in organic matter from recent lacustrine sediments during thermal alteration by rock-eval pyrolysis. Org Geochem 36(8):1190–1203
Schlumberger J (1987) Log interpretation principles/applications. Schlumberger Education Services, Houton, pp 69–94
Schulz E, Smykatz-Kloss W, Abichou H et al (1995) Zaderg environmental history of the semidesert region in southernTunisia. Zentralblatt fur Geologie und Palaontologie Teil I(3-4):423–440
Schulz E, Abichou A, Hachicha T, Pomel S, Salzmann U, Zouari K (2002) Sebkhas as ecological archives and the vegetation and landscape history of southeastern Tunisia during the last two millennia. J Afr Earth Sci 34(3-4):223–229
Schulz E, Abichou H, Hachicha T, Pomel S, Salzmann U, Zouari K (2005) The Mid-Holocene vegetation and landscape history of Southeastern Tunisia. Archaeobotany and Vegetation History, Springer Verlag Berlin (in press)
Sebag D, Disnar JR, Guillet B, Di Giovanni C, Verrecchia EP, Durand A (2006) Monitoring organic matter dynamics in soil profiles by 'Rock-Eval pyrolysis': bulk characterization and quantification of degradation. Eur J Soil Sci 57(3):344–355
Serna C, Van Scoyoc GE, Ahlrichs JL (1977) Hydroxyl groups and water in palygorskite. Am Mineral 62(7-8):784–792
Shi ZB, Shao LY, Jones TP, Whittaker AG, Lu SL, Berube KA, He T, Richards RJ (2003) Characterization of airborne individual particles collected in an urban area, a satellite city and a clean air area in Beijing, 2001. Atmos Environ 37:4097–4108
Sifeddine A, Laggoun-Défarge F, Lallier-Vergès E, Disnar JR, Williamson D, Gasse F, Gibert E (1995) Lacustrine organic sedimentation in the southern tropical zone in the last 36 kyears (Lake Tritrivakely, Madagascar). Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences. Série 2. Sci de la Terre et des Planètes 321(5):385–391
Silambarasan S, Jeelani SH, Sundararajan M, Pruthiviraj N (2017) Sea bed sediments along Bay of Bengal and Palk Strait, East coast of India: physico-chemical approach. In: Sundararajan M, Nallusamy B, Mohammed MA, Chidambaram AS (eds) Geochemistry and Mineralogy of Coastal Sediments in Tamil Nadu. Assessment of ecosystems trace element in short core sediment of Devipattinam Mangrove, PA. Aarhat Publication and Aarhat Journal’s. ISBN: 978-81-933440-8-8, pp 104–198
Sivakumar S, Ravisankar R, Raghu Y, Chandrasekaran A, Chandramohan J (2012) FTIR Spectroscopic studies on coastal sediment samples from Cuddalore District, Tamilnadu, India. Indian J Adv Chem Sci 1:40–46
Tissot B, Welte DH (1984) Petroleum Formation and Occurrence. Springer, Berlin, p 699
Trabelsi W (2017) Effet de l’activation acido-basique sur la minéralogie des argiles smectitiques crétacés éocènes de la Tunisie méridionale : Application à la purification de l’acide phosphorique. PhD thesis. Univ. Sfax. Faculty of Sciences of Sfax, p 80
Trabelsi R, Abid K, Zouari K, Yahyaoui H (2011) Groundwater salinization processes in shallow coastal aquifer of Djeffara plain of Medenine, Southeastern Tunisia. Environ Earth Sci 54(4):641–653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1273-8
Trabelsi R, Abid K, Zouari K (2012) Geochemistry processes of the Djeffara palaeogroundwater (Southeastern Tunisia). Quat Int 257:43–55
Van Driessche AES, Benning LG, Rodriguez-Blanco JD, Ossorio M, Bots P, Gárcia-Ruiz JM (2012) The role and implications of bassanite as a stable precursor phase to gypsum precipitation. Science 336:69–72
Viscarra Rossel RA, Jeon YS, Odeh IOA, McBratney AB (2008) Using a legacy soil sample to develop a mid-IR spectral library. Aust J Soil Res 46(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1071/SR07099
Volzone C, Zalba PE, Pereira E (1988) Activación ácida de esmectitas. II-Estudo mineralogico. Anales de la Asociación Química Argentina 76:57–68
Worden RH, Morad S (2000) Quartz cementation in oil field sandstones: a review of the key controuversies. Special Publ Int Assoc Sedimentol 29:1–20pp
Zaîbi C, Kamoun F, Carbonel P, Montacer M (2011) Distribution des ostracodes dans les sédiments de subsurface de la Sebkha El-Guettiate (Skhira, golfe de Gabès). In: Intérêt pour la reconstitution des paléo-environnements de l'Holocène. Carnets de Géologie / Notebooks on Geology, Brest, (CG2011-A03), pp 63–81
Acknowledgements
All authors thank the Sfax Preparatory Engineering Institute which provided logistical support and authorization for coring. Also, they would like to thank Mrs. S. Chtourou, technician of the research laboratory of ‘Environmental Sciences and Sustainable Environments’ and Mr. H. Gargouri, engineer from the National Engineering School of Sfax for their help during the laboratory measurements. Also, the authors thank Mr. M. S. Ben Reguiga, the laboratory member of ETAP (Tunisia), for his advice and for his help in the SEM analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Domenico M Doronzo
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gammoudi, A., Tlili, A., Essefi, E. et al. Contribution of the geochemical, physico-chemical, mineralogical, and statistical approaches to the reconstructing of the Holocene depositional environments along South-Eastern Tunisia. Arab J Geosci 14, 2029 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-08227-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-08227-4