Abstract
Background
The potential role of HIST1H2BN in prostate cancer remains unclear.
Objective
To evaluate the carcinogenic role of HIST1H2BN in prostate cancer.
Methods
The expression of HIST1H2BN in prostate cancer was analyzed using TCGA database and clinical samples. The roles and mechanisms of HIST1H2BN were investigated in DU145 and PC3 cells.
Results
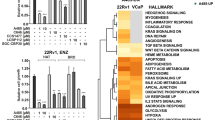
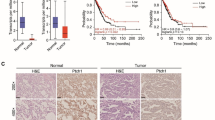
HIST1H2BN was significantly upregulated in prostate cancer. HIST1H2BN knockdown inhibited cell proliferation, migration and EMT phenotype in prostate cancer cells. Downregulating HIST1H2BN diminished the expression and binding activity of NF-κB p65, then influenced the expression of MMP2 and MMP9.
Conclusion
This is the first study to elaborate a HIST1H2BN-NF-κB-EMT regulatory axis in oncogenesis, indicating that HIST1H2BN might be potential therapeutic target for prostate cancer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alaseem A, Alhazzani K, Dondapati P, Alobid S, Bishayee A, Rathinavelu A (2019) Matrix metalloproteinases: a challenging paradigm of cancer management. Semin Cancer Biol 56:100–115
Allemani C, Matsuda T, Di Carlo V, Harewood R, Matz M, Nikšić M, Bonaventure A, Valkov M, Johnson C, Estève J et al (2018) Global surveillance of trends in cancer survival 2000-14 (CONCORD-3): analysis of individual records for 37 513 025 patients diagnosed with one of 18 cancers from 322 population-based registries in 71 countries. Lancet 391:1023–1075
Brabletz T (2012) To differentiate or not–routes towards metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer 12:425–436
Cang S, Xu X, Ma Y, Liu D, Chiao J (2016) Hypoacetylation, hypomethylation, and dephosphorylation of H2B histones and excessive histone deacetylase activity in DU-145 prostate cancer cells. J Hematol Oncol 9:3
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade P, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu X, He J (2016) Cancer statistics in China, 2015. Cancer J Clin 66:115–132
Chen W, Cen S, Zhou X, Yang T, Wu K, Zou L, Luo J, Li C, Lv D, Mao X (2020) Circular RNA CircNOLC1, upregulated by NF-KappaB, promotes the progression of prostate cancer via miR-647/PAQR4 axis. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:624764
Dai R, Yu F, Goh S, Chng H, Tan Y, Fu J, Zheng L, Luo Y (2008) Histone 2B (H2B) expression is confined to a proper NAD+/NADH redox status. J Biol Chem 283:26894–26901
Dongre A, Weinberg RA (2019) New insights into the mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and implications for cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 20:69–84
Gupta P, Pastushenko I, Skibinski A, Blanpain C, Kuperwasser C (2019) Phenotypic plasticity: driver of cancer initiation, progression, and therapy resistance. Cell stem cell 24:65–78
Horejs CM, Serio A, Purvis A, Gormley AJ, Bertazzo S, Poliniewicz A, Wang AJ, DiMaggio P, Hohenester E, Stevens MM (2014) Biologically-active laminin-111 fragment that modulates the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:5908–5913
Jääskeläinen T, Makkonen H, Visakorpi T, Kim J, Roeder R, Palvimo J (2012) Histone H2B ubiquitin ligases RNF20 and RNF40 in androgen signaling and prostate cancer cell growth. Mol Cell Endocrinol 350:87–98
Kornberg R (1974) Chromatin structure: a repeating unit of histones and DNA. Science 184:868–871
Lee J, You J, Kim M, Roh J (2020) Epigenetic reprogramming of epithelial-mesenchymal transition promotes ferroptosis of head and neck cancer. Redox Biol 37:101697
Liao Y, Chen L, Huang R, Su P, Chan M, Chang C, Yu M, Wang P, Yen M, Nephew K et al (2014) Hypomethylation signature of tumor-initiating cells predicts poor prognosis of ovarian cancer patients. Hum Mol Genet 23:1894–1906
Liu T, Zhang L, Joo D, Sun S (2017) NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2:17023
Luger K, Mäder A, Richmond R, Sargent D, Richmond T (1997) Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle at 2.8 A resolution. Nature 389:251–260
Luo Z, Wang Q, Lau WB, Lau B, Xu L, Zhao L, Yang H, Feng M, Xuan Y, Yang Y (2016) Tumor microenvironment: the culprit for ovarian cancer metastasis? Cancer Lett 377:174–182
Marzluff W, Gongidi P, Woods K, Jin J, Maltais L (2002) The human and mouse replication-dependent histone genes. Genomics 80:487–498
Massie C, Mills I, Lynch A (2017) The importance of DNA methylation in prostate cancer development. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 166:1–15
Napetschnig J, Wu H (2013) Molecular basis of NF-κB signaling. Annu Rev Biophys 42:443–468
Nguyen T, Alchalabi S, Oluwatoyosi A, Ropri A, Herschkowitz J, Rosen J (2020) New twists on long noncoding RNAs: from mobile elements to motile cancer cells. RNA Biol 17:1535–1549
Nieto M, Huang R, Jackson R, Thiery J (2016) EMT: 2016. Cell 166:21–45
Pan X, Wang G, Wang B (2021) Ectopic expression of microRNA-874 represses epithelial mesenchymal transition through the NF-κB pathway via CCNE1 in cholangiocarcinoma. Cell Signal 82:109927
Pastushenko I, Blanpain C (2019) EMT transition states during tumor progression and metastasis. Trends Cell Biol 29:212–226
Puisieux A, Brabletz T, Caramel J (2014) Oncogenic roles of EMT-inducing transcription factors. Nat Cell Biol 16:488–494
Ren D, Yang Q, Dai Y, Guo W, Du H, Song L, Peng X (2017) Oncogenic miR-210-3p promotes prostate cancer cell EMT and bone metastasis via NF-κB signaling pathway. Mol Cancer 16:117
Shang Z, Yu J, Sun L, Tian J, Zhu S, Zhang B, Dong Q, Jiang N, Flores-Morales A, Chang C et al (2019) LncRNA PCAT1 activates AKT and NF-κB signaling in castration-resistant prostate cancer by regulating the PHLPP/FKBP51/IKKα complex. Nucleic Acids Res 47:4211–4225
Strepkos D, Markouli M, Klonou A, Papavassiliou A, Piperi C (2021) Histone methyltransferase SETDB1: a common denominator of tumorigenesis with therapeutic potential. Cancer Res 81:525–534
Sweeney J, Debeljak M, Riel S, Millena A, Eshleman J, Paller C, Odero-Marah V (2021) Val16A SOD2 polymorphism promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition antagonized by muscadine grape skin extract in prostate cancer cells. Antioxidants (Basel Switzerland) 10(2):213
Udager A, Tomlins S (2018) Molecular biomarkers in the clinical management of prostate cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 8(11):a030601
Wu G, Chen T, Shahsafaei A, Hu W, Bronson RT, Shi GP, Halperin JA, Aktas H, Qin X (2010) Complement regulator CD59 protects against angiotensin II-induced abdominal aortic aneurysms in mice. Circulation 121:1338–1346
Wu Y, Gu Y, Guo S, Dai Q, Zhang W (2016) Expressing status and correlation of ARID1A and histone H2B on breast cancer. Biomed Res Int 2016:7593787
Wu Y, Cao H, Baranova A, Huang H, Li S, Cai L, Rao S, Dai M, Xie M, Dou Y et al (2020) Multi-trait analysis for genome-wide association study of five psychiatric disorders. Transl Psychiatry 10:209
Zhang B, Zhang Z, Li L, Qin YR, Liu H, Jiang C, Zeng TT, Li MQ, Xie D, Li Y et al (2018) TSPAN15 interacts with BTRC to promote oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via activating NF-κB signaling. Nat Commun 9:1423
Zhang J, Zhao R, Xing D, Cao J, Guo Y, Li L, Sun Y, Tian L, Liu M (2020) Magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate induces an inhibitory effect on progression and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of laryngeal cancer via the NF-κB/Twist signaling. Drug Des Devel Ther 14:5633–5644
Zhang B, Li Y, Wu Q, Xie L, Barwick B, Fu C, Li X, Wu D, Xia S, Chen J et al (2021a) Acetylation of KLF5 maintains EMT and tumorigenicity to cause chemoresistant bone metastasis in prostate cancer. Nat Commun 12:1714
Zhang Y, Ren H, Li J, Xue R, Liu H, Zhu Z, Pan C, Lin Y, Hu A, Gou P et al (2021b) Elevated HMGB1 expression induced by hepatitis B virus X protein promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis through STAT3/miR-34a/NF-κB in primary liver cancer. Am J Cancer Res 11:479–494
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81773240), The Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Grant No. BK20181118), Nanjing Medical Science and technique Development Foundation (Grant No. QRX17062) and Csco-Haosen Cancer Research Foundation (Grant No. Y-HS2019/2–028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Xiaowei Wei, Luwei Xu, Haiyan Xia, Juan Zhang and Yuhan Chang declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study had been approved by the Ethics Committee of Nanjing First Hospital (approval number 2017 − 155). Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
13258_2021_1164_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary material 1 Lentivirus-mediated shRNA infection efficiency of DU145 and PC3 cells. A, B, Relative mRNA expression level of HIST1H2BN in DU145 and PC3 cells infected with shCtrl lentivirus and shHIST1H2BN lentivirus( **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). C, HIST1H2BN protein in DU145 and PC3 cells infected with shCtrl lentivirus and shHIST1H2BN lentivirus were tested by western blot. D, The relationship between HIST1H2BN and RelA-MMP2/9 signal pathway was evaluated in DU145 cells (TIF 1454.5 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Chang, Y., Xia, H. et al. HIST1H2BN induced cell proliferation and EMT phenotype in prostate cancer via NF-κB signal pathway. Genes Genom 43, 1361–1369 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-021-01164-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-021-01164-2