Abstract
Background
Plasma ghrelin levels can be elevated in patients with acute heart failure (AHF). This study aimed to analyze the temporal changes and prognostic value of ghrelin levels in patients with AHF.
Methods
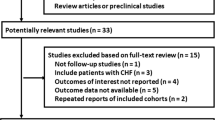
This prospective study included patients with AHF at the Cardiology Department, Weifang People’s Hospital (May 2018–October 2019), and age- and sex-matched healthy controls. Plasma ghrelin levels were measured. Multivariable logistic regression and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analyses were used to evaluate whether ghrelin levels could predict major cardiac adverse events (MACEs) during a 1-year follow-up.
Results
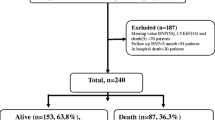
Finally, 92 patients with AHF and 50 healthy controls were enrolled. Ghrelin levels were higher in patients with AHF at 1, 3, 12, and 24 h compared with controls (all P < 0.01). Ghrelin levels in the AHF group were higher at 3 and 12 h than at 1 and 24 h (P < 0.001). Ghrelin level at 3 h in patients with AHF was negatively correlated with the left ventricular end-diastolic diameter and left ventricular ejection fraction (both P < 0.05). MACEs occurred in 48 patients with AHF. Ghrelin levels were higher in the MACE group than in the non-MACE group at 1 (P = 0.011) and 3 h (P = 0.034). Multivariable regression showed that ghrelin level at 3 h was independently associated with MACEs [OR = 0.629, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.515–0.742, P = 0.010], but the area under the ROC curve was only 0.629 (95% CI 0.515–0.742).
Conclusions
Plasma ghrelin levels are elevated in AHF and patients with MACEs during follow-up.



Similar content being viewed by others
References.
Kurmani S, Squire I (2017) Acute heart failure: definition, classification and epidemiology. Curr Heart Fail Rep 14(5):385–392
Ural D, Çavuşoğlu Y, Eren M, Karaüzüm K, Temizhan A, Yılmaz MB, Zoghi M, Ramassubu K, Bozkurt B (2015) Diagnosis and management of acute heart failure. Anatol J Cardiol 15(11):860–889
Tanaka TD, Sawano M, Ramani R, Friedman M, Kohsaka S (2018) Acute heart failure management in the USA and Japan: overview of practice patterns and review of evidence. ESC Heart Fail 5(5):931–947
Abraham WT, Fonarow GC, Albert NM, Stough WG, Gheorghiade M, Greenberg BH, O’Connor CM, Sun JL, Yancy CW, Young JB (2008) Predictors of in-hospital mortality in patients hospitalized for heart failure: insights from the organized program to initiate lifesaving treatment in hospitalized patients with heart failure (OPTIMIZE-HF). J Am Coll Cardiol 52(5):347–356
Nieminen MS, Brutsaert D, Dickstein K, Drexler H, Follath F, Harjola VP, Hochadel M, Komajda M, Lassus J, Lopez-Sendon JL, Ponikowski P, Tavazzi L (2006) EuroHeart failure survey II (EHFS II): a survey on hospitalized acute heart failure patients: description of population. Eur Heart J 27(22):2725–2736
Ahmed A, Allman RM, Fonarow GC, Love TE, Zannad F, Dell’italia LJ, White M, Gheorghiade M (2008) Incident heart failure hospitalization and subsequent mortality in chronic heart failure: a propensity-matched study. J Card Fail 14(3):211–218
Antonini L, Mollica C, Aspromonte N, Pasceri V, Auriti A, Gonzini L, Maggioni P, Colivicchi F (2019) A simple prognostic index in acute heart failure. Minerva Cardioangiol 67(1):73–78
Bayes-Genis A, de Antonio M, Vila J, Peñafiel J, Galán A, Barallat J, Zamora E, Urrutia A, Lupón J (2014) Head-to-head comparison of 2 myocardial fibrosis biomarkers for long-term heart failure risk stratification: ST2 versus galectin-3. J Am Coll Cardiol 63(2):158–166
Bettencourt P, Ferreira-Coimbra J, Rodrigues P, Marques P, Moreira H, Pinto MJ, Guimarães JT, Lourenço P (2018) Towards a multi-marker prognostic strategy in acute heart failure: a role for GDF-15. ESC Heart Fail 5(6):1017–1022
Mueller T, Gegenhuber A, Leitner I, Poelz W, Haltmayer M, Dieplinger B (2016) Diagnostic and prognostic accuracy of galectin-3 and soluble ST2 for acute heart failure. Clin Chim Acta 463:158–164
Sani MU, Damasceno A, Davison BA, Cotter G, Mayosi BM, Edwards C, Azibani F, Adam T, Arif G, Jessen N, Sliwa K (2020) N-terminal pro BNP and galectin-3 are prognostic biomarkers of acute heart failure in sub-Saharan Africa: lessons from the BAHEF trial. ESC Heart Fail. https://doi.org/10.1002/ehf2.13032
Salah K, Stienen S, Pinto YM, Eurlings LW, Metra M, Bayes-Genis A, Verdiani V, Tijssen JGP, Kok WE (2019) Prognosis and NT-proBNP in heart failure patients with preserved versus reduced ejection fraction. Heart 105(15):1182–1189
Aimo A, Januzzi JL Jr, Mueller C, Mirò O, Pascual Figal DA, Jacob J, Herrero-Puente P, Llorens P, Wussler D, Kozhuharov N, Sabti Z, Breidthardt T, Vergaro G, Ripoli A, Prontera C, Saccaro L, Passino C, Emdin M (2019) Admission high-sensitivity troponin T and NT-proBNP for outcome prediction in acute heart failure. Int J Cardiol 293:137–142
Tokudome T, Otani K, Miyazato M, Kangawa K (2019) Ghrelin and the heart. Peptides 111:42–46
Baldanzi G, Filigheddu N, Cutrupi S, Catapano F, Bonissoni S, Fubini A, Malan D, Baj G, Granata R, Broglio F, Papotti M, Surico N, Bussolino F, Isgaard J, Deghenghi R, Sinigaglia F, Prat M, Muccioli G, Ghigo E, Graziani A (2002) Ghrelin and des-acyl ghrelin inhibit cell death in cardiomyocytes and endothelial cells through ERK1/2 and PI 3-kinase/AKT. J Cell Biol 159(6):1029–1037
Chang L, Zhao J, Li GZ, Geng B, Pan CS, Qi YF, Tang CS (2004) Ghrelin protects myocardium from isoproterenol-induced injury in rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin 25(9):1131–1137
Kola B, Hubina E, Tucci SA, Kirkham TC, Garcia EA, Mitchell SE, Williams LM, Hawley SA, Hardie DG, Grossman AB, Korbonits M (2005) Cannabinoids and ghrelin have both central and peripheral metabolic and cardiac effects via AMP-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem 280(26):25196–25201
Nagaya N, Kangawa K (2006) Therapeutic potential of ghrelin in the treatment of heart failure. Drugs 66(4):439–448
Nagaya N, Miyatake K, Uematsu M, Oya H, Shimizu W, Hosoda H, Kojima M, Nakanishi N, Mori H, Kangawa K (2001) Hemodynamic, renal, and hormonal effects of ghrelin infusion in patients with chronic heart failure. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86(12):5854–5859
Yang C, Liu Z, Liu K, Yang P (2014) Mechanisms of Ghrelin anti-heart failure: inhibition of Ang II-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis by down-regulating AT1R expression. PLoS ONE 9(1):e85785
Nagaya N, Uematsu M, Kojima M, Date Y, Nakazato M, Okumura H, Hosoda H, Shimizu W, Yamagishi M, Oya H, Koh H, Yutani C, Kangawa K (2001) Elevated circulating level of ghrelin in cachexia associated with chronic heart failure: relationships between ghrelin and anabolic/catabolic factors. Circulation 104(17):2034–2038
Xin X, Ren AJ, Zheng X, Qin YW, Zhao XX, Yuan WJ, Guo ZF (2009) Disturbance of circulating ghrelin and obestatin in chronic heart failure patients especially in those with cachexia. Peptides 30(12):2281–2285
Chen Y, Ji XW, Zhang AY, Lv JC, Zhang JG, Zhao CH (2014) Prognostic value of plasma ghrelin in predicting the outcome of patients with chronic heart failure. Arch Med Res 45(3):263–269
Yuan Y, Huang F, Deng C, Zhu P (2020) The additional prognostic value of ghrelin for mortality and readmission in elderly patients with acute heart failure. Clin Interv Aging 15:1353–1363
Chinese Society of Cardiology of Chinese Medical Association; Editorial Board of Chinese Journal of Cardiology (2014) Chinese guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of heart failure 2014. Chin J Cardiol 42(2):98–122
Wang Z, Hua Q, Tan J, Zhou Y, Fu Y, Qin J, Tan S, Chen X, Guo J (2017) Comparison of therapeutic effects between urapidil and nitroglycerin for treatment of acute heart failure with hypertension and atrial fibrillation in elderly patients: a randomized multi-center parallel-control study in China. Int J Clin Exp Med 10(4):7020–7029
Jensen J, Ma LP, Bjurman C, Hammarsten O, Fu ML (2012) Prognostic values of NTpro BNP/BNP ratio in comparison with NTpro BNP or BNP alone in elderly patients with chronic heart failure in a 2 year follow up. Int J Cardiol 155(1):1–5
Hedayati N, Annambhotla S, Jiang J, Wang X, Chai H, Lin PH, Yao Q, Chen C (2009) Growth hormone-releasing peptide ghrelin inhibits homocysteine-induced endothelial dysfunction in porcine coronary arteries and human endothelial cells. J Vasc Surg 49(1):199–207
Wang D, Wang H, Luo P, Hwang A, Sun D, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Liu N, Wang S, Li C, Cao F (2012) Effects of ghrelin on homocysteine-induced dysfunction and inflammatory response in rat cardiac microvascular endothelial cells. Cell Biol Int 36(6):511–517
Mentz RJ, Stevens SR, DeVore AD, Lala A, Vader JM, AbouEzzeddine OF, Khazanie P, Redfield MM, Stevenson LW, O’Connor CM, Goldsmith SR, Bart BA, Anstrom KJ, Hernandez AF, Braunwald E, Felker GM (2015) Decongestion strategies and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system activation in acute heart failure. JACC Heart Fail 3(2):97–107
Boshra V, Abbas AM (2017) Effects of peripherally and centrally applied ghrelin on the oxidative stress induced by renin angiotensin system in a rat model of renovascular hypertension. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 28(4):347–354
Kojima M, Kangawa K (2008) Structure and function of ghrelin. Results Probl Cell Differ 46:89–115
Xu Z, Lin S, Wu W, Tan H, Wang Z, Cheng C, Lu L, Zhang X (2008) Ghrelin prevents doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity through TNF-alpha/NF-kappaB pathways and mitochondrial protective mechanisms. Toxicology 247(2–3):133–138
Yang C, Wang Y, Liu H, Li N, Sun Y, Liu Z, Yang P (2012) Ghrelin protects H9c2 cardiomyocytes from angiotensin II-induced apoptosis through the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 59(5):465–471
Beiras-Fernandez A, Kreth S, Weis F, Ledderose C, Pöttinger T, Dieguez C, Beiras A, Reichart B (2010) Altered myocardial expression of ghrelin and its receptor (GHSR-1a) in patients with severe heart failure. Peptides 31(12):2222–2228
Kim SH, Kim HJ, Han S, Yoo BS, Choi DJ, Kim JJ, Jeon ES, Cho MC, Chae SC, Ryu KH (2017) The limited prognostic role of echocardiograms in short-term follow-up after acute decompensated heart failure: An analysis of the Korean Heart Failure (KorHF) Registry. PLoS One 12(12):e0188938
Sherazi S, McNitt S, Choudhary N, Shah AH, Aktas MK, Asgher A, Schwarz KQ, Zareba W (2015) Predictors of mortality in patients hospitalized for congestive heart failure with left ventricular ejection fraction ≥ 40. Cardiol J 22(4):382–390
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of Weifang People’s Hospital.
Consent to participate
All study participants signed an informed consent form before enrollment in this study.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Zhou, S., Zhang, A. et al. Temporal changes and prognostic value of plasma ghrelin level in patients with acute heart failure: a prospective study. Heart Vessels 37, 419–425 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-021-01935-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-021-01935-7