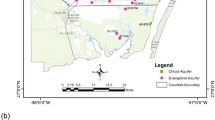
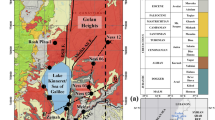
Abstract
Groundwater contamination by the adjacent seawater has been a global problem. To address the process and evolution of salinity in groundwater, different procedures such as major ion ratios, standard plots, geophysical techniques, isotopic techniques, and modelling methods were adopted. It is difficult to distinguish the groundwaters’ with salinity, similar or greater than the seawater by adopting major ions. Saline to hypersaline conditions are reported in coastal groundwater of the arid regions. In order to address the sources of salinity, evolution and geochemical nature, groundwater samples were collected near the shore along with adjacent seawater. The ion-ratio and the Piper diagram did not show a clear demarcation between groundwater and seawater, but the fact that seawater values were within a narrow range than the groundwater. Whereas the Cl/Br and Br/Si ratios, thermodynamic stability plots of K-Silica system, Plagioclase stability and carbonate system with respect to logpCO2 reflected geochemical variation between the seawater and groundwater samples. Since the silica values of seawater samples were lesser, they proved to be a significant tracer to characterize the non-contaminated groundwater samples. The seawater–groundwater interaction was inferred from the study and probable locations of SGD were identified. The evolution mechanism of the brine composition with the present scenario was studied considering the saturation states of halite, silicates, carbonate and sulfate minerals. It was identified that the evolutionary pathway of brine from groundwater composition is governed by the Ca ion, which is a common ion for most of the carbonate and sulfate minerals. The groundwater chemistry indicates the Cl-SO4 brine evolution pathway leading to the formation of Mg-SO4 brine. Thus, the study proves that ratios of Cl/Br, Br/Si, thermodynamic stability plots with respect to silicate minerals and logpCO2 along with saturation states of minerals can serve as significant tool to characterize the hypersaline groundwater.













Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Full data will be provided if requested.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Abusada SM (1988) The essentials of groundwater resources of Kuwait. Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research, Report No. KISR2665, Kuwait
Al-Abdulghani E, El-Sammak A, Sarawi M (2013) Environmental assessment of Kuwait Bay: an integrated approach. J Coast Conserv 17:445–462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11852-013-0242-7
Alcalá FJ, Custodio E (2008) Using the Cl/Br ratio as a tracer to identify the origin of salinity in aquifers in Spain and Portugal. J Hydrol 359:189–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.06.028
Al-Ghadban N, Al-Majed A-M (2002) The state of Marine Pollution in Kuwait: Northern Arabian Gulf. Technology 8:7–26
Al-Ghadban A, El-Sammak A (2005) Sources, distribution and composition of the suspended sediments, Kuwait Bay, Northern Arabian Gulf. J Arid Environ 60:647–661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2004.07.017
Ali A, Chidambaram S (2020) Assessment of trace inorganic contaminates in water and sediment to address its impact on common fish varieties along Kuwait Bay. Environ Geochem Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00559-6
Al-Ruwaih F (1995) Chemistry of groundwater in the Dammam Aquifer, Kuwait. Hydrogeol J 3:42–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s100400050064
Al-Ruwaih FM, Shehata M (2004) Hydrochemical processes and environmental isotopic study of groundwater in Kuwait. Water Int 29:158–166. https://doi.org/10.1080/02508060408691765
Al-Ruwiah FM (1987) Groundwater classification and quality trends of Al-Rawdhatain field, Kuwait. J Univ Kuwait (sci) 14:395–414
Al-Sarawi HA, Jha AN, Al-Sarawi MA, Lyons BP (2015) Historic and contemporary contamination in the marine environment of Kuwait: an overview. Mar Pollut Bull 100:621–628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.07.052
Al-Senafy M, Al-Fahad K (2000) Petrography of Calcretes and Their Effects on the Hydrology of Kuwait Group Aquifer. In: Proceedings, First International Conference on Geotechnical, Geoenvironmental Engineering and Management in Arid Lands, Al-Ain, United Arab Emirates, pp. 481–484
Al-Shamari (2013) Some empirical observations about bacteria proliferation and corrosion damage morphology in Kuwait oilfield waters. NACE International. Paper No. 2748
Al-Sulaimi J, Mukhopadhyay A (2000) An overview of the surface and near-surface geology, geomorphology and natural resources of Kuwait. Earth Sci Rev 50:227–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0012-8252(00)00005-2
Anschutz P, Smith T, Mouret A, Deborde J, Bujan S, Poirier D, Lecroart P (2009) Tidal sands as biogeochemical reactors. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 84:84–90. https://doi.org/10.1002/lom3.1008510.1016/j.ecss.2009.06.015
Appelo C, Willemsen A (1987) Geochemical calculations and observations on salt water intrusions, I. A combined geochemical/minxing cell model. J Hydrol 94:313–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(87)90058-8
Aziz R, Joekar-Niasar V, Martínez-Ferrer PJ et al (2019) Novel insights into pore-scale dynamics of wettability alteration during low salinity waterflooding. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-45434-2
Bąbel M, Schreiber B (2014) Geochemistry of evaporites and evolution of seawater. Treatise Geochem. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-08-095975-7.00718-x
Ball J, Nordstrom DK (1991) WATEQ4F - User’s manual with revised thermodynamic data base and test cases for calculating speciation of major, trace and redox elements in natural waters. Open-File Rep. https://doi.org/10.3133/ofr90129
Banner JL, Wasserburg G, Dobson PF et al (1989) Isotopic and trace element constraints on the origin and evolution of saline groundwaters from central Missouri. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 53:383–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(89)90390-6
Barbecot F, Marlin C, Gibert E, Dever L (2000) Hydrochemical and isotopic characterisation of the Bathonian and Bajocian coastal aquifer of the Caen area (northern France). Appl Geochem 15:791–805. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0883-2927(99)00088-8
Batayneh A (2013) Hydrochemical facies and ionic ratios of the coastal groundwater aquifer of Saudi Gulf of Aqaba: implication for seawater intrusion. J Coastal Res 30:75. https://doi.org/10.2112/jcoastres-d-13-00021.1
Bear J, Cheng AH, Sorek S, Ouazar D, Herrers I (1999) Seawater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifer Concepts, Methods, and Practices. Kluwer Academic Publishers, London
Behl E, Davis SN, Goldowitz J (1987) Cl/Br ratios as an environmental tracer of altered waters. Geol Soc Am Abstr Prog 19:686
Bhandary H, Chidambaram S (2020) Estimation of submarine groundwater discharge and nutrient loading using radium isotopes quartet in Kuwait. Arab J Geosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05754-4 (in press)
Bhandary H, Sabarathinam C, Al-Khalid A (2018) Occurrence of hypersaline groundwater along the coastal aquifers of Kuwait. Desalination 436:15–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2018.02.004
Bohn A (2014) Hydrogeochemische Analyse und Modellierung von Lösungs- und Reaktion sprozessen im Salinar- und Deckgebirge am Staßfurter Sattel. PhD thesis. Brandenburg University of Technology, Cottbus 185 pp
Borges A, Abril G (2011) Carbon dioxide and methane dynamics in estuaries. Treatise Estuarine Coastal Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-374711-2.00504-0
Brown CL, Starn JJ, Stollenwerk K, Mondazzi RA, Trombley TJ (2009) Aquifer Chemistry and Transport Processes in the Zone of Contribution to a Public-Supply Well in Woodbury, Connecticut, 2002–06. US Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2009–5051, 158pp
Bu-olayan A, Subrahmanyam M, Alsarawi M, Thomas B (1998) Effects of the Gulf War oil spill in relation to trace metals in water, particulate matter, and PAHs from the Kuwait coast. Environ Int 24:789–797. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0160-4120(98)00056-7
Bu-Olayan AH, Thomas BV (2012) Dispersion model on PM 2.5 fugitive dust and trace metals levels in Kuwait Governorates. Environ Monit Assess 184:1731–1737. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2074-y
Bu-Olayan AH, Thomas BV (2014) Assessment of the ultra-trace mercury levels in selected desert plants. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11:1413–1420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0324-y
Bu-Olayan A, Al-Hassan R, Thomas B, Subrahmanyam M (2001a) Impact of trace metals and nutrients levels on phytoplankton from the Kuwait Coast. Environ Int 26:199–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0160-4120(00)00106-9
Bu-Olayan AH, Al-Hassan R, Thomas BV (2001b) Trace metal toxicity to phytoplankton of Kuwait coastal waters. Ecotoxicology 10(3):185–189
Buttle JM, Labadia CF (1999) Deicing salt accumulation and loss in highway snowbanks. J Environ Qual 28:155–164. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1999.00472425002800010018x
Cai S, Ni Z, Li Y et al (2012) Metals in the tissues of two fish species from the rare and endemic fish nature reserve in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River, China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 88:922–927. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0564-4
Carol ES, Kruse EE, Laurencena PC et al (2012) Ionic exchange in groundwater hydrochemical evolution. Study case: the drainage basin of El Pescado creek (Buenos Aires province, Argentina). Environ Earth Sci 65:421–428. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1318-z
Cartwright I, Weaver TR, Fifield LK (2006) Cl/Br ratios and environmental isotopes as indicators of recharge variability and groundwater flow: an example from the southeast Murray Basin, Australia. Chem Geol 231:38–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2005.12.009
Chandrasekar T, Sabarathinam C, Nadesan D et al (2019) Geochemical (process based) characterization of groundwater along the KT boundary of South India. Geochemistry 79:62–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoch.2018.11.005
Chidambaram S, Ramanathan AL, Anandhan P, Srinivasamoorthy K, Prasanna MV (2005) A comparative study on the coastal surface and groundwater in and around Puduchattiram to Coleroon. Tamilnadu Int J Ecol Environ Sci 31(3):209–306 (Special issue)
Chidambaram S, Vijayakumar V, Srinivasamoorthy K, Anandhan P, Prasanna MV, Vasudevan S (2007) A study on variation in ionic composition of aqueous system in different lithounits around Perambalur region, Tamil Nadu. J Geol Soc India 06:1061–1069
Chidambaram S, Ramanathan A, Prasanna MV et al (2009) Study on the hydrogeochemical characteristics in groundwater, post- and pre-tsunami scenario, from Portnova to Pumpuhar, southeast coast of India. Environ Monit Assess 169:553–568. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-1196-y
Chidambaram S, Karmegam U, Prasanna MV et al (2011a) A study on hydrochemical elucidation of coastal groundwater in and around Kalpakkam region, Southern India. Environ Earth Sci 64:1419–1431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-0966-3
Chidambaram S, Prasanna MV, Karmegam U, Singaraja C, Pethaperumal S, Manivannan R, Anandhan P, Tirumalesh K (2011b) Significance of pCO2 values in determining carbonate chemistry in groundwater of Pondicherry region. India Front Earth Sci 5(2):197–206
Chidambaram S, Anandhan P, Prasanna MV, Ramanathan AL, Srinivasamoorthy K, Senthil KG (2012) Hydrogeochemical modelling for groundwater in Neyveli Aquifer, Tamil Nadu, India. Using PHREEQC: a case study. Nat Resour Res 21:311–324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-012-9180-6
Chidambaram S, Prasad MBK, Manivannan R (2013) Environmental hydrogeochemistry and genesis of fluoride in groundwaters of Dindigul district, Tamilnadu (India). Environ Earth Sci 68:333–342. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1741-9
Chidambaram S, Sarathidasan J, Srinivasamoorthy K et al (2018) Assessment of hydrogeochemical status of groundwater in a coastal region of Southeast coast of India. Appl Water Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0649-2
Chidambaram S (2000) Hydrogeochemical studies of groundwater in Periyar district, Tamilnadu, India. Unpublished Ph.D thesis, Department of Geology, Annamalai University, India
Coggon RM, Teagle DAH, Smith-Duque CE et al (2010) Reconstructing Past Seawater Mg/Ca and Sr/Ca from Mid-Ocean Ridge Flank Calcium Carbonate Veins. Science 327:1114–1117. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1182252
Custodio E (2002) Aquifer overexploitation: what does it mean? Hydrogeol J 10:254–277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-002-0188-6
Damault CJG, Godinez G (2008) Coastal aquifers and saltwater intrusion. Over Exploit Contam Shared Groundw Resour NATO Sci Peace Secur Ser. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-6985-7_9
Davis SN, Whittemore DO, Fabryka-Martin J (1998) Uses of chloride/bromide ratios in studies of potable water. Ground Water 36:338–350. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.1998.tb01099.x
Drever JI (1988) The geochemistry of natural waters, 2nd edn. Prentice- Hall, Englewood Cliffs, N.J., pp 437
Elderfield H (2010) Seawater chemistry and climate. Science 327:1092. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1186769
Eleonora C, Kruse E, Mas-Pla J (2009) Hydrochemical and isotopical evidence of groundwater salinization processes on the coastal plain of Samborombón Bay Argentina. J Hydrol 365(3–4):335–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.11.041
Eugster HP (1980) Geochemistry of evaporitic lacustrine deposits. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 8:35–63
Fallick AE, Hamilton PJ (1989) The isotopic geochemistry of ocean waters through time. Earth Environ Sci Trans R Soc Edinb 80:177–181. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0263593300028613
Fathiabdalla SM (2015) Quantification of River Nile/Quaternary aquifer exchanges via riverbank filtration by hydrochemical and biological indicators, Assiut. Egypt J Earth Syst Sci 125:1697–1711. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-016-0755-1
Flury M, Papritz A (1993) Bromide in the natural environment: occurrence and toxicity. J Environ Qual 22:747–758. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1993.00472425002200040017x
Gaofeng Z, Yonghong S, Chunlin H et al (2010) Hydrogeochemical processes in the groundwater environment of Heihe River Basin, northwest China. Environ Earth Sci 60:139–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0175-5
Garcia G, Hidalgo V, Blesa A (2001) Geochemistry of groundwater in alluvial plain of Tucuman province, Argentina. Hydrogeol J 9:597–610
Garcia-Solsona E, Garcia-Orellana J, Masqué P et al (2010) Groundwater and nutrient discharge through karstic coastal springs (Castelló, Spain). Biogeosciences 7:2625–2638. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-7-2625-2010
Garrels RM, Christ CL (1965) Solutions, Minerals, and Equilibria. Harper and Rowe, New York, p 450
Garrett DE (1970) The chemistry and origin of potash deposits. In: Rau JL, Dellwig LF (eds) 3rd Symposium on Salt, Cleveland, April 21–24, 1969, vol 1. Northern Ohio Geological Society, Cleveland, pp 211–222
Gassama N, Dia A, Violette S (2012) Origin of salinity in a multilayered aquifer with high salinization vulnerability. Hydrol Process 26:168–188. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.8125
Gerritse RG, George RJ (1988) The role of soil organic matter in the geochemical cycling of chloride and bromide. J Hydrol 101:83–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(88)90029-7
Ghabayen SM, Mckee M, Kemblowski M (2006) Ionic and isotopic ratios for identification of salinity sources and missing data in the Gaza aquifer. J Hydrol 318:360–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2005.06.041
Ghannoum MA, Al-Sarawi M, Alyan AA, Baca B (1991) Microbiological water quality along the Kuwait waterfront project, Kuwait. Int J Environ Stud 37:65–71. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207239108710617
Ghiglieri G, Barbieri G, Vernier A et al (2009) Potential risks of nitrate pollution in aquifers from agricultural practices in the Nurra region, northwestern Sardinia, Italy. J Hydrol 379:339–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.10.020
Giambastiani B, Colombani N, Mastrocicco M, Fidelibus M (2013) Characterization of the lowland coastal aquifer of Comacchio (Ferrara, Italy): Hydrology, hydrochemistry and evolution of the system. J Hydrol 501:35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.07.037
Goldberg ED (1954) Marine Geochemistry 1. Chemical Scavengers of the Sea. J Geol 62:249–265. https://doi.org/10.1086/626161
Gomes OV, Marques ED, Kütter VT et al (2019) Origin of salinity and hydrogeochemical features of porous aquifers from northeastern Guanabara Bay, Rio de Janeiro, SE - Brazil. J Hydrol Reg Stud 22:100601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2019.100601
Gunder K (1973) Some chemical and microbiological observations in the Pacific Ocean off the Hawaiian Islands1. Limnol Oceanogr 17:524–532. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1972.17.4.0524
Hadi KM, Al-Ruwaih FM (2005) Impact of the environmental deposition on water quality of the limestone aquifer. Kuwait Emir J Eng Res 10(2):37–49
Hardie LA (1987) Dolomitization: a critical view of some current views. J Sediment Res 57:166–183
Hardie LA, Lowenstein TK, Timofeeff MN, Demicco RV (2003) Secular variation in seawater chemistry and the origin of calcium chloride basinal brines. Geology 31:857. https://doi.org/10.1130/g19728r.1
Harris KE, Degrandpre MD, Hales B (2013) Aragonite saturation state dynamics in a coastal upwelling zone. Geophys Res Lett 40:2720–2725. https://doi.org/10.1002/grl.50460
Hauri C, Gruber N, Mcdonnell AMP, Vogt M (2013) The intensity, duration, and severity of low aragonite saturation state events on the California continental shelf. Geophys Res Lett 40:3424–3428. https://doi.org/10.1002/grl.50618
Hem JD (1985) Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water. USGS Water Supply Paper 2254:117–120
Herbert HJ (2000) Zur Geochemie und geochemischen Modellierung hochsalinarer Lösungen mineralischer Rohstoffe. Geologisches Jahrbuch, Reihe D (SD 1), Hannover, pp 392
Herczeg A, Edmunds M (1999) Inorganic ions as tracers in Environmental Tracers in Subsurface Hydrology, Cook P, Herczeg A, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston, 31–78
Hite CD, Cheng S (1996) Spatial characterization of hydrogeochemistry within a constructed fen, Greene County, Ohio. Ground Water 34:415–424. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.1996.tb02022.x
Holland HD, Malinin SD (1979) The solubility and occurrence of non-ore minerals. In: Barnes HL (ed) Geochemistry of hydrothermal ore deposits, Chap. 9. Wiley, pp 461–508
Hwang D-W, Lee I-S, Choi M, Kim T-H (2016) Estimating the input of submarine groundwater discharge (SGD) and SGD-derived nutrients in Geoje Bay, Korea using 222Rn-Si mass balance model. Mar Pollut Bull 110:119–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.06.073
IPCC (2013) Summary for policymakers. In: Stocker TF, Qin D, Plattner G-K, Tignor M, Allen SK, Boschung J, Nauels A et al. Climate Change 2013: the Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group 1 to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, New York
Iqbal MZ, Krothe NC (1996) Transport of bromide and other inorganic ions by infiltrating storm water beneath a farmland plot. Ground Water 34:972–978. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.1996.tb02162.x
Jeandel C, Oelkers EH (2015) The influence of terrigenous particulate material dissolution on ocean chemistry and global element cycles. Chem Geol 395:50–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.12.001
Jones BF, Naftz DL, Spencer RJ, Oviatt CG (2009) Geochemical evolution of Great Salt Lake, Utah, USA. Aquat Geochem 15:95–121
Jones BF, Vengosh A, Rosenthal E,Yechiele Y (1999) Geochemical investigation. In: Bear J, Cheng AH, Sorek S, Ouazar D, Herrers I (eds) Seawater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifer Concepts, Methods, and Practices. Kluwer Academic Publishers, London
Kass A, Gavrieli I, Yechieli Y et al (2005) The impact of freshwater and wastewater irrigation on the chemistry of shallow groundwater: a case study from the Israeli Coastal Aquifer. J Hydrol 300:314–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2004.06.013
Katz BG, Eberts SM, Kauffman LJ (2011) Using Cl/Br ratios and other indicators to assess potential impacts on groundwater quality from septic systems: a review and examples from principal aquifers in the United States. J Hydrol 397:151–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.11.017
Kelly WR, Wilson S (2002) Temporal changes in shallow groundwater quality in northeastern Illinois. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual Research Conference of the Illinois Groundwater Consortium. Research on Agrichemicals in Illinois, Groundwater Status and Future Directions XII. Carbondale, Illinois. www.siu.edu/worda/igc/
Kim JH, Kim RH, Lee J, Chang HW (2003) Hydrogeochemical characterization of major factors affecting the quality of shallow groundwater in the coastal area at Kimje in South Korea. Environ Geol 44:478–489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-003-0782-5
Kim K, Rajmohan N, Kim HJ et al (2004) Assessment of groundwater chemistry in a coastal region (Kunsan, Korea) having complex contaminant sources: a stoichiometric approach. Environ Geol 46:763–774. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-004-1109-x
Kim G, Ryu J-W, Yang H-S, Yun S-T (2005) Submarine groundwater discharge (SGD) into the Yellow Sea revealed by 228Ra and 226Ra isotopes: implications for global silicate fluxes. Earth Planet Sci Lett 237:156–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2005.06.011
Kim G, Ryu J-W, Hwang D-W (2008) Radium tracing of submarine groundwater discharge (SGD) and associated nutrient fluxes in a highly-permeable bed coastal zone, Korea. Mar Chem 109:307–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2007.07.002
Klassen J, Allen DM, Kirste D (2014) Chemical Indicators of Saltwater Intrusion for the Gulf Islands, British Columbia, BC Ministry of Forests, Lands and Natural Resource Operations and BC Ministry of Environment p 42
Landon MK, Belitz K (2008) Ground-Water Quality Data in the Central Eastside San Joaquin Basin 2006: Results from the California GAMA Program. Data Ser. https://doi.org/10.3133/ds325
Lee J-Y, Song S-H (2007) Evaluation of groundwater quality in coastal areas: implications for sustainable agriculture. Environ Geol 52:1231–1242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-006-0560-2
Lorenzen G, Sprenger C, Baudron P et al (2011) Origin and dynamics of groundwater salinity in the alluvial plains of western Delhi and adjacent territories of Haryana State, India. Hydrol Process 26:2333–2345. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.8311
Lowenstein TK, Risacher F (2009) Closed basin brine evolution and the influence of Ca–Cl inflow waters: Death Valley and Bristol Dry Lake California, Qaidam Basin, China, and Salar de Atacama, Chile. Aquat Geochem 15:71–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-008-9046-z
Lowenstein ECTK (1989) Diagenesis of Saline Pan Halite: Comparison of Petrographic Features of Modern, Quaternary and Permian Halites. SEPM J Sediment Ress. https://doi.org/10.1306/212f905c-2b24-11d7-8648000102c1865d
Lubarsky KA, Silbiger NJ, Donahue MJ (2018) Effects of submarine groundwater discharge on coral accretion and bioerosion on two shallow reef flats. Limnol Oceanogr 63:1660–1676. https://doi.org/10.1002/lno.10799
Lundström U, Olin Å (1986) Bromide concentration in Swedish precipitation, surface and ground waters. Water Res 20:751–756. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(86)90099-0
Mackenzie FT, Garrels RM (1966) Chemical mass balance between rivers and oceans. Am J Sci 264:507–525. https://doi.org/10.2475/ajs.264.7.507
Marion GM, Farren RE (1999) Mineral solubilities in the Na-K-Mg-Ca-Cl-SO4-H2O system: a re-evaluation of the sulfate chemistry in the Spencer-Møller-Weare model. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 63:1305–1318. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0016-7037(99)00102-7
Massoud (1998) The status of oil pollution in the Arabian Gulf by the end of 1993. Fuel Energy Abstr 39:224. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6701(98)80675-9
Metcafe E (2000) Integrated aquifer management plan: final report. Gaza Coastal Aquifer Management Program, USAID Contract No. 294-C-00-99-00038-00
Miller LD, Ortiz RF (2007) Ground-water quality and potential effects of individual sewage disposal system effluent on ground-water quality in Park County, Colorado, 2001–2004. Sci Investig Rep. https://doi.org/10.3133/sir20075220
Montety VD, Radakovitch O, Vallet-Coulomb C et al (2008) Origin of groundwater salinity and hydrogeochemical processes in a confined coastal aquifer: case of the Rhône delta (Southern France). Appl Geochem 23:2337–2349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2008.03.011
Moore WS (2010) A re-evaluation of submarine groundwater discharge along the southeastern coast of North America. Global Biogeochem Cycles. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009gb003747
Morin GP, Vigier N, Verney-Carron A (2015) Enhanced dissolution of basaltic glass in brackish waters: Impact on biogeochemical cycles. Earth Planet Sci Lett 417:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2015.02.005
Moujabber ME, Samra BB, Darwish T, Atallah T (2006) Comparison of different indicators for groundwater contamination by seawater intrusion on the Lebanese Coast. Water Resour Manag 20:161–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-006-7376-4
Mukhopadhyay A, Al-Sulaimi J, Barrat JM (1994) Numerical modeling of ground-water resource management options in Kuwait. Ground Water 32:917–928. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.1994.tb00931.x
Mukhopadhyay A, Alsulaimi J, Alawadi E, Alruwaih F (1996) An overview of the Tertiary geology and hydrogeology of the northern part of the Arabian Gulf region with special reference to Kuwait. Earth Sci Rev 40:259–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-8252(95)00068-2
Mukhopadhyay A, Al-Haddad A, Al-Otaibi M, Al-Senafy M (2006) Occurrence of hydrogen sulfide in the ground water of Kuwait. Environ Geol 52:1151–1161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-006-0552-2
Naseeb (2005) Identification of nitrogen sources in the groundwater of Kuwait using nitrogen isotopes. Eur J Sci Res. ISSN 1450–216X Vol 15, No 2, pp 220–234
Oelkers EH, Gislason SR (2001) Mechanism, rates, and consequences of basaltic glass dissolution: II. An experimental study of the dissolution rates of basaltic glass as a function of pH and temperature. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 67:3817–3832. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0016-7037(03)00176-5
Oldenburg CM, Rinaldi AP (2011) Buoyancy effects on upward brine displacement caused by CO2 injection. Transp Porous Media 87:525–540. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-010-9699-0
Omar SA, A1-Yaqubi A, Senay Y (1981) Geology and Groundwater Hydrology of the State of Kuwait. Ministry of Electricity and Water, Kuwait
Ortega L, Manzano M, Custodio E et al (2015) Using 222Rn to identify and quantify groundwater inflows to the Mundo River (SE Spain). Chem Geol 395:67–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.12.002
Panno S, Hackley K, Hwang H, Kelly W (2001) Determination of the sources of nitrate contamination in karst springs using isotopic and chemical indicators. Chem Geol 179:113–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0009-2541(01)00318-7
Panno S, Hackley K, Hwang H et al (2006) Characterization and identification of Na-Cl sources in ground water. Ground Water 44:176–187. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.2005.00127.x
Panno SV, Kelly W, Hackley K, Weibel C (2007) Chemical and bacterial quality of aeration-type waste water treatment system discharge. Groundw Monit Remediat 27:71–76. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6592.2007.00138.x
Panno SV, Hackley KC, Greenberg S (2002) Source identification of sodium and chloride in natural waters: Preliminary results. In: Proceedings of the 12th Annual Research Conference of the Illinois Groundwater Consortium. Research on Agrichemicals in Illinois, Groundwater Status and Future Directions XII, Carbondale, Illinois. www.siu.edu/worda/igc
Panno SV, Hackley KC, Hwang HH, Greenberg S, Krapac IG, Landsberger S, (2005) Data table for characterization and identification of the sources of Na- Cl in natural waters. Illinois State Geological Survey Open File Series 2005–1. Champaign, Illinois
Parkhurst DL, Appelo C (2013) Description of input and examples for PHREEQC version 3: a computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations. Tech Methods. https://doi.org/10.3133/tm6a43
Pethaperumal S, Chidambaram S, Prasanna MV, Verma VN, Balaji K, Ramesh R, Karmegam U, Paramaguru P (2008) A study on Groundwater quality in the Pondicherry region. Eco-Chronicle 3(2):85–90
Plummer LN, Parkhurst D, Kosiur DR (1975) MIX2 : A computer program for modeling chemical reaction in natural waters. U.S. Geol. Suru., B’RI Rep. 61–7.5 https://doi.org/10.3133/wri7561
Pokavanich T, Alosairi Y, Graaff RD et al (2014) Three-dimensional hydro-environment characterization and modeling of The Northern Arabian Gulf. Coast Eng Proc 1:41. https://doi.org/10.9753/icce.v34.management.41
Prasanna MV, Chidambaram S, Kumar GS (2011) Hydrogeochemical assessment of groundwater in Neyveli Basin, Cuddalore District, South India. Arab J Geosci 4:319–330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-010-0191-5
Prasanna M, Chidambaram S, Nagarajan R, Kumar AA (2016) Monsoon climate impact on drip water geochemistry at Niah Great Cave, NW Borneo, Malaysia: evaluating the spatial and temporal trends. J Clim Change 2:89–98. https://doi.org/10.3233/jcc-160020
Price NN, Martz TR, Brainard RE, Smith JE (2012) Dual variability in seawater pH relates to calcification and benthic community structure on coral reefs. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0043843
Pulido-Leboeuf P (2004) Seawater intrusion and associated processes in a small coastal complex aquifer (Castell de Ferro, Spain). Appl Geochem 19:1517–1527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2004.02.004
Rad S, Allegre C, Louvat P (2007) Hidden erosion on volcanic islands. Earth Planet Sci Lett 262:109–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2007.07.019
Rahman S, Tamborski JJ, Charette MA, Cochran JK (2019) Dissolved silica in the subterranean estuary and the impact of submarine groundwater discharge on the global marine silica budget. Mar Chem 208:29–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2018.11.006
Raymahasay BC (1986) Geochemistry of bicarbonate in river water. J Geol Soc India 27:114–118
Readman J, Bartocci J, Tolosa I et al (1996) Recovery of the coastal marine environment in the Gulf following the 1991 war-related oil spills. Mar Pollut Bull 32:493–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-326x(95)00227-e
Reum JCP, Alin SR, Feely RA et al (2014) Seasonal carbonate chemistry covariation with temperature, oxygen, and salinity in a fjord estuary: implications for the design of ocean acidification experiments. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0089619
Richter BC, Kreitler CW (1993) Geochemical Techniques for identifying sources of ground-water salinization. CRN Press Inc, Florida
Robertson WD (1998) Use of multiple isotope tracers to evaluate denitrification in ground water: study of nitrate from a large-flux septic system plume. Ground Water 36:975–982. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.1998.tb02104.x
Sabarathinam C, Bhandary H, Al-Khalid A (2019) A geochemical analogy between the metal sources in Kuwait Bay and territorial sea water of Kuwait. Environ Monit Assess. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7219-4
Saeed T, Afrin R, Muyeed AA, Sun G (2012) Treatment of tannery wastewater in a pilot-scale hybrid constructed wetland system in Bangladesh. Chemosphere 88:1065–1073. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.04.055
Saeed T, Al-Shimmari F, Al-Mutairi A, Abdullah H (2015) Spatial assessment of the sewage contamination of Kuwait’s marine areas. Mar Pollut Bull 94:307–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.01.030
Samayamanthula DR, Sabarathinam C, Alayyadhi NA (2020) Trace elements and their variation with pH in rain water in arid environment. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 80:331–349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-020-00787-y
Sánchez-Martos F, Pulido-Bosch A, Molina-Sánchez L, Vallejos-Izquierdo A (2002) Identification of the origin of salinization in groundwater using minor ions (Lower Andarax, Southeast Spain). Sci Total Environ 297:43–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0048-9697(01)01011-7
Seaman J, Bertsch P, Korom S, Miller W (1996) Physicochemical Controls on Nonconservative Anion Migration in Coarse-Textured Alluvial Sediments. Ground Water 34:778–783. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.1996.tb02070.x
Senay, Y., Hamdan, L., Yacoubi, A., 1987. Study of the subsurface Water Rise in the Residential Areas of Kuwait. Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research. Report No. KISR2227, Kuwait.
Shahalam A, Zahra BMA, Jaradat A (1998) Wastewater irrigation effect on soil, crop and environment: a pilot scale study at Irbid, Jordan. Water Air Soil Pollut 106:425–428
Shalabi EWA, Sepehrnoori K (2017) Geochemistry of low salinity/engineered water injection processes. Low Salin Eng Water Inject Sandstone Carbonate Reserv. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-813604-1.00006-7
Singaraja C, Chidambaram S, Anandhan P et al (2013) Hydrochemistry of groundwater in a coastal region and its repercussion on quality, a case study—Thoothukudi district, Tamil Nadu, India. Arab J Geosci 7:939–950. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0794-0
Singaraja C, Chidambaram S, Anandhan P et al (2014) Determination of the utility of groundwater with respect to the geochemical parameters: a case study from Tuticorin District of Tamil Nadu (India). Environ Dev Sustain 16:689–721. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-013-9502-9
Singaraja C, Chidambaram S, Anandhan P et al (2015) A study on the status of saltwater intrusion in the coastal hard rock aquifer of South India. Environ Dev Sustain 17:443–475. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-014-9554-5
Singaraja C, Chidambaram S, Jacob N et al (2016) Radon levels in groundwater in the Tuticorin district of Tamil Nadu, South India. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 307:1165–1173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-015-4312-1
Sivakarun N, Udayaganesan P, Chidambaram S et al (2020) Factors determining the hydrogeochemical processes occurring in shallow groundwater of coastal alluvial aquifer. India Geochem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemer.2020.125623
Small DP, Milazzo M, Bertolini C et al (2015) Temporal fluctuations in seawater pCO2 may be as important as mean differences when determining physiological sensitivity in natural systems. ICES J Mar Sci 73:604–612. https://doi.org/10.1093/icesjms/fsv232
Spencer H (1990) The roles of rifting and hydrothermal CaCl2 brines in the origin of potash evaporites; an hypothesis. Am J Sci 290:43–106. https://doi.org/10.2475/ajs.290.1.43
Spencer RJ (2000) Sulfate minerals in evaporite deposits. In: Alpers CN, Jambor JL, Nordstrom DK (eds) Sulfate Minerals: Crystallography, Geochemistry, and Environmental Significance. In: Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, vol. 40. Mineralogical Society of America, Washington, DC, 173–192
Sprinkle CL (1989) Geochemistry of the Floridan aquifer system in Florida and in parts of Georgia, South Carolina, and Alabama. Prof Pap. https://doi.org/10.3133/pp1403i
Srinivasamoorthy K, Chidambaram S, Prasanna MV et al (2008) Identification of major sources controlling groundwater chemistry from a hard rock terrain—a case study from Mettur taluk, Salem district, Tamil Nadu, India. J Earth Syst Sci 117:49–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-008-0012-3
Steding S, Zirkler A, Kühn M (2020) Geochemical reaction models quantify the composition of transition zones between brine occurrence and unaffected salt rock. Chem Geol 532:119349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.119349
Street JH, Knee KL, Grossman EE, Paytan A (2008) Submarine groundwater discharge and nutrient addition to the coastal zone and coral reefs of leeward Hawai’i. Mar Chem 109:355–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2007.08.009
Stumm W, Morgan JJ (1996) Aquatic Chemistry. 3rd Ed. John Wiley and Sons Inc, pp 533–550
Sutton TT, Clark MR, Dunn DC et al (2017) A global biogeographic classification of the mesopelagic zone. Deep Sea Res Part I 126:85–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr.2017.05.006
Tale F, Kalantariasl A, Shabani A et al (2020) Experimental and simulation study of low salinity brine interactions with carbonate rocks. J Petrol Sci Eng 184:106497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2019.106497
Tamborski J, Simon B, Jordi G-O, Marc S, Céline C et al (2018) A comparison between water circulation and terrestrially-driven dissolved silica fluxes to the Mediterranean Sea traced using radium isotopes. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, Elsevier 238:496–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2018.07.022
Tanveer, Chen (2019) A comprehensive thermodynamic model for high salinity produced waters. AIChE J. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.16818
Thilagavathi R, Chidambaram S, Prasanna MV et al (2012) A study on groundwater geochemistry and water quality in layered aquifers system of Pondicherry region, southeast India. Appl Water Sci 2:253–269. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-012-0045-2
Thilagavathi R, Chidambaram S, Prasanna MV, Pethaperumal S (2013) A study on the interpretation of spontaneous potential and resistivity logs in layered aquifer sequence of Pondicherry Region, South India. Arab J Geosci 7:3715–3729. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-1041-z
Thilagavathi R, Chidambaram S, Thivya C et al (2014a) Delineation of natural and anthropogenic process controlling hydrogeochemistry of layered aquifer sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci India Sect A 84:95–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40010-013-0114-4
Thilagavathi R, Chidambaram S, Ramanathan AL, Rao MS, Prasanna MV, Tirumalesh K, Pethaperumal S (2014b) An attempt to evaluate the influence of Geomorphology on the hydrogeology of coastal Aquifer. Indian J Geomorphol 18(2):103–114
Thivya C, Chidambaram S, Singaraja C et al (2013) A study on the significance of lithology in groundwater quality of Madurai district, Tamil Nadu (India). Environ Dev Sustain 15:1365–1387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-013-9439-z
Todd DK (1959) Ground water hydrology. United States. John Wiley and Sons. Inc, pp 277–294
Treguer P, Nelson DM, van Bennekom AJ, DeMaster DJ, Leynaert A, Queguiner B (1995) The balance of ´ silica in the world ocean: a re-estimate. Science 268:375–379
Turner RE, Rabalais NN (1994) Coastal eutrophication near the Mississippi river delta. Nature 368:619–621. https://doi.org/10.1038/368619a0
USEPA (2002) Calculating Upper Confidence Limits for Exposure Point Concentrations at Hazardous Waste Sites. OSWER 9285.6–10. Washington, D.C.: United States Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development. http://itrcweb.org/FileCabinet/GetFile?fileID=6873.
Vengosh A (2002) An enigmatic salinity source in the Mediterranean coastal aquifer and Gaza strip: utilization of isotopic (B, Sr, O) constraints for searching the sources of groundwater contamination. Geochim Et Cosmochim Acta 66(15A):804
Vengosh A, Keren R (1996) Chemical modifications of groundwater contaminated by recharge of treated sewage effluent. J Contam Hydrol 23:347–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/0169-7722(96)00019-8
Vengosh A, Pankratov I (1998) Chloride/bromide and chloride/fluoride ratios of domestic sewage effluents and associated contaminated ground water. Ground Water 36:815–824. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.1998.tb02200.x
Vengosh A, Heumann KG, Juraske S, Kasher R (1994) Boron isotope application for tracing sources of contamination in groundwater. Environ Sci Technol 28:1968–1974. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00060a030
Vengosh A, Spivack AJ, Artzi Y, Ayalon A (1999) Geochemical and boron, strontium, and oxygen isotopic constraints on the origin of the salinity in groundwater from the Mediterranean Coast of Israel. Water Resour Res 35:1877–1894. https://doi.org/10.1029/1999wr900024
Vengosh A, Kloppmann W, Marei A et al (2005) Sources of salinity and boron in the Gaza strip: natural contaminant flow in the southern Mediterranean coastal aquifer. Water Resour Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004wr003344
Walter LM, Stueber AM, Huston TJ (1990) Br-Cl-Na systematics in Illinois basin fluids: constraints on fluid origin and evolution. Geology 18:315. https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(1990)0182.3.co;2
Warren JK (2006) Evaporites: sediments, resources and hydrocarbons. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York. p 1019. ISBN-13 978-3-540-26011-0
Whittemore DO (1995) Geochemical differentiation of oil and gas brine from other saltwater sources contaminating water resources: case studies from Kansas and Oklahoma. Environ Geosci 2(1):15–31
Wigley TML (1975) The incongruent solution of dolomite. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 37:1397–1402
Wilkinson BH, Algeo TJ (1989) Sedimentary carbonate record of calcium-magnesium cycling. Am J Sci 289:1158–1194. https://doi.org/10.2475/ajs.289.10.1158
Worden R, Manning D, Bottrell S (2006) Multiple generations of high salinity formation water in the Triassic Sherwood Sandstone: Wytch Farm oilfield, onshore UK. Appl Geochem 21:455–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2005.12.007
Yamanaka M, Kumagai Y (2006) Sulfur isotope constraint on the provenance of salinity in a confined aquifer system of the southwestern Nobi Plain, central Japan. J Hydrol 325:35–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2005.09.026
Zilberbrand M, Rosenthal E, Shachnai E (2001) Impact of urbanization on hydrochemical evolution of groundwater and on unsaturated-zone gas composition in the coastal city of Tel Aviv, Israel. J Contam Hydrol 50:175–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0169-7722(01)00118-8
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the help and support received from Dr. Muhammad Al-Rashed, Executive Director, WRC, Dr. Khaled Hadi, Operations Director, WRC, and Dr. Yousef Al-Wazzan, Science and Technology Director, WRC, during the successful execution of the study.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CS: Conceptualization, Writing—review & editing. HB: Software: data Validation and Visualization. AA: Investigation, Formal analysis. Additional declarations for articles in life science journals that report the results of studies involving humans and/or animals.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of a Topical Collection in Environmental Earth Sciences on Groundwater quality and contamination and the application of GIS, guest edited by Narsimha Adimalla and Hui Qian.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sabarathinam, C., Bhandary, H. & Ali, A. Strategies to characterize the geochemical interrelationship between coastal saline groundwater and seawater. Environ Earth Sci 80, 642 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09924-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09924-9