Abstract
Using MIL-101(Fe) as the source of carbon and Fe, a magnetic porous carbon (MPC) material with Fe3C nanoparticles encapsulated in porous carbon was prepared through one-pot pyrolysis under N2 atmosphere. With MPC as adsorption material, a stir bar sorptive-dispersive microextraction (SBSDME) method was proposed to extract and preconcentrate sulfonamides (SAs) prior to HPLC-DAD determination. To investigate their extraction ability, different MPC materials were prepared under different carbonization temperatures (600, 700, 800, 900, and 1000 °C). The material prepared under 900 °C (MPC-900) exhibited the highest extraction ability for SAs. The as-prepared MPC materials were also characterized by Raman spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, zeta potential, and other techniques. The main parameters that affect extraction were systematically studied. Under optimal conditions, favorable linearity (R2 ≥ 0.9938) and detection limits (0.02–0.04 ng mL−1) of sulfonamides were obtained. The average recoveries for spiked milk and lake water samples ranged from 76.9 to 109% and from 75.4 to 118% with RSDs of 3.10–9.63% and 1.71–11.3%, respectively. Sulfameter and sulfisoxazole were detected in milk sample. Sulfisoxazole was detected in the lake water sample. The MPC-900 material demonstrated excellent reusability. It can be reused 24 times with peak areas having no obvious decline. The method can be applied to extract ultra-trace compounds in complex sample matrices.
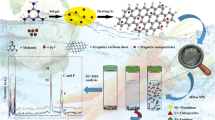
Graphical abstract

Schematic presentation of a stir bar sorptive-dispersive microextraction (SBSDME) by using magnetic porous carbon (MPC) composites as sorbent combined with high-performance liquid chromatography for sensitive analysis of sulfonamides in milk and lake water samples.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tang S, Zhang H, Lee HK (2016) Advances in sample extraction. Anal Chem 88:228–249. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b04040
Yu Q, Liu S, Zheng F, Xiao H, Guan H, Feng Y (2020) Identification and quantification of benzimidazole metabolites of thiophonate-methyl sprayed on celery cabbage using SiO2@NiO solid-phase extraction in combination with HPLC-MS/MS. Chin Chem Lett 31:482–486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2019.07.065
Jiang L-P, Li N, Liu L-Q, Zheng X, Du F-Y, Ruan G-H (2020) Preparation and application of polymerized high internal phase emulsion monoliths for the preconcentration and determination of malachite green and leucomalachite green in water samples. J Anal Test 4:264–272. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41664-020-00145-w
Wang X, Ji H, Wang F, Cui X, Liu Y, Du X, Lu X (2021) NiFe2O4-based magnetic covalent organic framework nanocomposites for the efficient adsorption of brominated flame retardants from water. Microchim Acta 188:161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04809-x
Si R, Han Y, Wu D, Qiao F, Bai L, Wang Z, Yan H (2020) Ionic liquid-organic-functionalized ordered mesoporous silica-integrated dispersive solid-phase extraction for determination of plant growth regulators in fresh Panax ginseng. Talanta 207:120247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120247
David F, Ochiai N, Sandra P (2019) Two decades of stir bar sorptive extraction: a retrospective and future outlook. Trends Anal Chem 112:102–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.12.006
He M, Wang Y, Zhang Q, Zang L, Chen B, Hu B (1637) Stir bar sorptive extraction and its application. J Chromatogr A 2021:461810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2020.461810
Zhang J, Li W, Zhu W, Qin P, Lu M, Zhang X, Miao Y, Cai Z (2019) Mesoporous graphitic carbon nitride@NiCo2O4 nanocomposite as a solid phase microextraction coating for sensitive determination of environmental pollutants in human serum samples. Chem Comm 55:10019. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9cc04348a
Xiao R, Zhang X, Zhang X, Niu J, Lu M, Liu X, Cai Z (2017) Analysis of flavors and fragrances by HPLC with Fe3O4@GO magnetic nanocomposite as the adsorbent. Talanta 166:262–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.01.065
Benedé JL, Chisvert A, Giokas DL, Salvador A (2014) Development of stir bar sorptive-dispersive microextraction mediated by magnetic nanoparticles and its analytical application to the determination of hydrophobic organic compounds in aqueous media. J Chromatogr A 1362:25–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2014.08.024
Vállez-Gomis V, Grau J, Benedé JL, Giokas DL, Chisvert A, Salvador A (2021) Fundamentals and applications of stir bar sorptive dispersive microextraction: a tutorial review. Anal Chim Acta 1153:338271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2021.338271
Vállez-Gomis V, Grau J, Benedé JL, Chisvert A, Salvador A (1624) Reduced graphene oxide-based magnetic composite for trace determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in cosmetics by stir bar sorptive dispersive microextraction. J Chromatogr A 2020:461229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2020.461229
Miralles P, Gemert IV, Chisvert A, Salvador A (2019) Stir bar sorptive-dispersive microextraction mediated by magnetic nanoparticles-metal organic framework composite: determination of N-nitrosamines in cosmetic products. J Chromatogra A 1604:460465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2019.460465
Guo W, Wang W, Yang Y, Zhang S, Yang B, Ma W, He Y, Lin Z, Cai Z (2021) Facile fabrication of magnetic covalent organic frameworks and their application in selective enrichment of polychlorinated naphthalenes from fine particulate matter. Microchim Acta 188:91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04750-z
Han X, Chen J, Li Z, Qiu H (2019) Combustion fabrication of magnetic porous carbon as a novel magnetic solid-phase extraction adsorbent for the determination of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Anal Chim Acta 1078:78–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.06.022
Aladaghlo Z, Javanbakht S, Fakhari AR, Shaabani A (2021) Gelatin microsphere coated Fe3O4@graphene quantum dots nanoparticles as a novel magnetic sorbent for ultrasound-assisted dispersive magnetic solid-phase extraction of tricyclic antidepressants in biological samples. Microchim Acta 188:73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04727-y
Han X, Chen J, Li Z, Quan K, Qiu H (2020) Magnetic solid-phase extraction of triazole fungicides based on magnetic porous carbon prepared by combustion combined with solvothermal method. Anal Chim Acta 1129:85–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.06.077
Wang M, Wang J, Wang K, Chen T, Wang J (2020) Magnetic porous carbon derived from Zn/Co metal-organic framework as an adsorbent for extraction and determination of carbamates. Microchim Acta 187:507. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04426-0
Hao L, Wang C, Wu Q, Li Z, Zang X, Wang Z (2014) Metal-organic framework derived magnetic nanoporous carbon: novel adsorbent for magnetic solid-phase extraction. Anal Chem 86:12199–12205. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac5031896
Jiao C, Li M, Ma R, Wang C, Wu Q, Wang Z (2016) Preparation of a co-doped hierarchically porous carbon from Co/Zn-ZIF: an efficient adsorbent for the extraction of trizine herbicides from environment water and white gourd samples. Talanta 152:321–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.02.005
Guo Y, He X, Huang C, Chen H, Lu Q, Zhang L (2020) Metal-organic framework-derived nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube cages as efficient adsorbents for solid-phase microextraction of polychlorinated biphenyls. Anal Chim Acta 1095:99–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.10.023
Wang D, Jia F, Wang H, Chen F, Fang Y, Dong W, Zeng G, Li X, Yang Q, Yuan X (2018) Simultaneously efficient adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline by Fe-based MOFs. J Colloid Interf Sci 519:273–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.02.067
Chen Z, Yu C, Xi J, Tang S, Bao T, Zhang J (2019) A hybrid material prepared by controlled growth of a covalent organic framework on amino-modified MIL-68 for pipette tip solid-phase extraction of sulfonamides prior to their determination by HPLC. Microchim Acta 186:393. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3513-7
Tomai P, Martinelli A, Morosetti S, Curini R, Fanali S, Gentili A (2018) Oxidized buckypaper for stir-disc solid phase extraction: evaluation of several classes of environmental pollutants recovered from surface water samples. Anal Chem 90:6827–6834. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b00927
Zhang J, Li W, Zhu W, Yang Y, Qin P, Zhou Q, Lu M, Cai Z (2019) Mesoporous graphitic carbon nitride as an efficient sorbent for extraction of sulfonamides prior to HPLC analysis. Microchim Acta 186:279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3394-9
Qin P, Zhu W, Han L, Zhang X, Zhao B, Zhang X, Lu M (2020) Monodispersed mesoporous SiO2@metal-organic framework (MSN@MIL-101(Fe)) composites as sorbent for extraction and preconcentration of phytohormones prior to HPLC-DAD analysis. Microchim Acta 187:367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04326-3
Naga EIAOA, Shaban SA, Kady EIFYA (2018) Metal organic framework-derived nitrogen-doped nanoporous carbon as an efficient adsorbent for methyl orange removal from aqueous solution. J Taiwan Inst Chem E 000:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2018.07.044
Zhao J, Yang X, Liang G, Wang Z, Li S, Wang Z, Xie X (2019) Effective removal of two fluoroquinolone antibiotics by PEG-4000 stabilized nanoscale zero-valent iron supported onto zeolite (PZ-NZVI). Sci Total Environ 710:136289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136289
Chatzimitakos T, Samanidou V, Stalikas CD (2017) Graphene-functionalized melamine sponges for microextraction of sulfonamides from food and environmental samples. J Chromatogr A 1522:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2017.09.043
Chatzimitakos TG, Stalikas CD (2018) Melamine sponge decorated with copper sheets as a material with outstanding properties for microextraction of sulfonamides prior to their determination by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1554:28–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.04.015
Li Y, Wu X, Li Z, Zhong S, Wang W, Wang A, Chen J (2015) Fabrication of CoFe2O4-graphene nanocomposite and its application in the magnetic solid phase extraction of sulfonamides from milk samples. Talanta 144:1279–1286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.08.006
Jia X, Zhao P, Ye X, Zhang L, Wang T, Chen Q, Hou X (2016) A novel metal-organic framework composite MIL-101(Cr)@GO as an efficient sorbent in dispersive micro-solid phase extraction coupling with UHPLC-MS/MS for the determination of sulfonamides in milk samples. Talanta 169:227–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.08.086
Sigmund G, Gharasoo M, Hüffer T, Hofmann T (2020) Deep learning neural network approach for predicting the sorption of ionizable and polar organic pollutants to a wide range of carbonaceous materials. Environ Sci Technol 54:4583–4591. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b06287
Liu C, Wang P, Liu X, Yi X, Zhou Z, Liu D (2019) Multifunctional β-cyclodextrin MOF-derived porous carbon as efficient herbicides adsorbent and potassium fertilizer. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:14479–14489. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b01911
Fan S, Qu Y, Yao L, Ren J, Luque R, He Z, Bai C (2020) MOF-derived cluster-shaped magnetic nanocomposite with hierarchical pores as an efficient and regenerative adsorbent for chlortetracycline removal. J Colloid Interf Sci 586:433–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.10.107
Acknowledgements
This work was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22076038) and the Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province (202300410044).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOC 1.01 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, ., Han, L., Zhang, X. et al. MIL-101(Fe)-derived magnetic porous carbon as sorbent for stir bar sorptive-dispersive microextraction of sulfonamides. Microchim Acta 188, 340 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04993-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04993-w