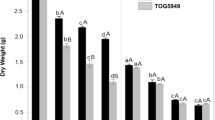
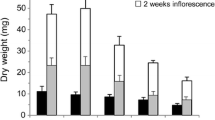
Abstract
A pharmacological study was conducted to analyze the impact of inhibitors of Na+-H+ antiporters (amiloride 100 µM) and cation-chloride-cotransporters (bumetanide 200 µM) on two cultivars of the African rice species (Oryza glaberrima Steud) differing in salt resistance (TOG5307: salt-resistant and TOG5949: salt-sensitive) exposed to 75 mM NaCl during 3 days. Amiloride increased Na+ accumulation in roots and leaves to a higher extent in salt-resistant TOG5307 than in salt-sensitive TOG5949. Bumetanide reduced Cl− accumulation in both cultivars as well as K+ accumulation in TOG5307 and Na+ accumulation in TOG5949, suggesting that the cation-chloride-cotransporter in O. glaberrima does not necessarily strictly behave as a Na+:K+:2Cl− transporter. Inhibitors mainly acted on the absorption step but had low impact on root-to-shoot translocation process. The salt-resistant cultivar TOG5307 was able to efficiently regulate Na+ uptake and to cope with high concentration of accumulated toxic ions, as demonstrated by a higher cell viability index and a higher concentration of protein and photosynthetic pigments in NaCl-exposed plants comparatively to salt-sensitive TOG5949.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bajji M, Kinet JM, Lutts S (2002) The use of electrolyte leakage method assessing cell membrane stability as a water stress tolerance test in durum wheat. Plant Growth Regul 36:61–70
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid sensitive method for quantification of microquantities of protein utilizing he principle of protein dye binding. Annal Biochem 16:559–566
Chen ZC, Yamaji N, Fujii-Kashino M, Ma JF (2016) A cation-chloride-cotransporter gene is required for cell elongation and osmoregulation in rice. Plant Physiol 171:494–507
Colmenero-Flores JM, Martínez G, Gamba G, Vázquez N, Igleisias DJ, Brumós J, Talón M (2007) Identification and functional characterization of cation-chloride-cotransporters in plants. Plant J 50:278–292
Deng YQ, Bao J, Yuan F, Liang X, Feng ZT, Wang BS (2016) Exogenous hydrogen sulfide alleviates salt stress in wheat seedlings by decreasing Na+ content. Plant Growth Regul 79:391–399
Fukuda A, Yazaki Y, Ishikawa T, Koike S, Tanaka Y (1998) Na+/H+ antiporter in tonoplast vesicles from rice roots. Plant Cell Physiol 39:196–201
Guo KM, Babourina O, Rengel Z (2009) Na+/H+ antiporter activity of the SOS1 gene: lifetime imaging analysis and electrophysiological studies on Arabidopsis seedlings. Physiol Plant 137:155–165
Han B, Jiang Y, Cui G, Mi J, Rob M et al (2020) Cation-chloride co-transporter 1 (CCC1) mediates plant resistance against Pseudomonas syringae. Plant Physiol 182:1052–1065
Henderson SW, Wege S, Qiu J, Blackmore DH, Walker AR, Tyrman SD, Walker RR, Gilligham M (2015) Grapevine and Arabidopsis cation-chloride-cotransporters localize to the Golgi and trans-Golgi network and indirectly influence long-distance ion transport and plant salt tolerance. Plant Physiol 169:2215–2229
Henderson SW, Wege S, Gilliham M (2018) Plant-cation-chloride-cotransporters (CCC): evolutionary origins and functional insights. Int J Mol Sci 19:492
Horie T, Hauser F, Schroeder JI (2009) HKT transporter-mediated salinity resistance mechanisms in Arabidopsis and monocot crop plants. Trends Plant Sci 14:660–668
Kong XQ, Gao XH, Sun W, An J, Zhao YX, Zhang H (2011) Cloning and functional characterization of a cation-chloride-cotransporter gene OsCCC1. Plant Mol Biol 75:567–578
Li P, Luo T, Pu X, Zhou Y, Yu J, Liu L (2021) Plant transporters: roles in stress responses and effects on growth and development. Plant Growth Regul 93:253–266
Lichtenthaler HK (1987) Chlorophylls and carotenoids: pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. Meth Enzymol 148:350–382
Lutts S, Kinet JM, Bouharmont J (1996) NaCl-induced senescence in leaves of rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars differing in salinity resistance. Ann Bot 78:389–398
Lutts S, Almansouri M, Kinet JM (2004) Salinity and water stress have contrasting effects on the relationship between growth and cell viability during and after stress exposure in durum wheat callus. Plant Sci 67:9–18
Prodjinoto H, Gandonou C, Lutts S (2018) Screening for salinity tolerance of Oryza glaberrima Steud. seedlings. Afr J Agric Res 133:561–583
Prodjinoto H, Irakoze W, Gandonou C, Lepoint G, Lutts S (2021) Discriminating the impact of Na+ and Cl− in the deleterious effects of salt stress on the African rice species (Oryza glaberrima Steud.). Plant Growth Regul 94:201–219
Qu Y, Guan R, Bose J, Henderson SW, Wege S, Qiu L, Gilliham M (2021) Soybean CHX-type ion transport protein GmSALT3 confers leaf Na+ exclusion via a root derived mechanism, and Cl− exclusion via a shoot derived process. Plant Cell Environ 44:856–869
Shi HZ, Quintero FJ, Pardo JM, Zhu JK (2002) The putative plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter SOS1 controls long-distance Na+ transport in plants. Plant Cell 14:465–477
Solis CA, Yong MT, Vinarao R, Jena K, Holford P, Shabala L, Zhou M, Shabala S, Chen ZH (2020) Back to the wild: on quest for donors towards salinity tolerant rice. Front Plant Sci 11:323
Taleisnik E, Grunberg K, Lino A (1991) Effects of amiloride on sodium accumulation in intact Lycopersicum esculentum plants. J Plant Physiol 138:634–639
Teakle NL, Tyerman SD (2010) Mechanisms of Cl− transport contributing to salt tolerance. Plant Cell Environ 33:566–589
Van Zelm E, Zhang Y, Testerink C (2020) Salt tolerance mechanisms of plants. Ann Rev Plant Biol 71:403–433
Veltlman MA, Flowers JM, van Andel TR, Schranz ME (2019) Origins and geographic diversification of African rice (Oryza glaberrima). PLoS One 14:e0203508
Wang B, Zhai H, He S, Zhang H, Ren Z, Zhang D, Liu Q (2016) A vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene, INHX2, enhances salt and drought tolerance in transgenic sweet potato. Scien Hort 201:153–166
Yoshida S, Forno DA, Cock JH, Gomez KA (1976) Laboratory manual for physiological studies of rice, 3rd edn. International Rice Research Institute, Manila, Philippines
Zhang JL, Flowers TJ, Wang SM (2010) Mechanisms of sodium uptake by root of higher plants. Plant Soil 326:45–60
Zhu M, Zhou M, Shabala L, Shabala S (2017) Physiological and molecular mechanisms mediating xylem Na+ loading in barley in the context of salinity stress tolerance. Plant Cell Environ 40:1009–1020
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Mrs. Brigitte Van Pee and to Mr. Baudouin Capelle for the efficient technical assistance
Funding
CAI (Comité d’Action Internationale) from the Université catholique de Louvain (UCLouvain) provided the research grant of H. Prodjinoto.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HP performed the whole experiment, SL and CG managed the project, SL conceived the experimental design, WI conducted the statistical treatment of the data, SL and HP wrote the first draft, and all the authors prepared the final version and approved submission.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prodjinoto, H., Irakoze, W., Gandonou, C. et al. Inhibitors of Na/H Antiporter and Cation-Chloride-Cotransporters Have Contrasting Effects on Two Cultivars of Oryza glaberrima Steud. Differing in Salinity Resistance. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 21, 3247–3253 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00603-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00603-z