Abstract
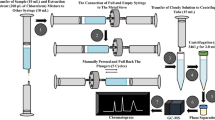
An automated online column extraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and equipped with a double-trap column system was developed to determine valproic acid in human plasma without derivatization for routine therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM). 300 μL of plasma sample pretreated by precipitating the protein was injected into a Diamonsil C18 extraction column in the first focusing step. After the elution of the pretreated sample, the targets were transferred from the extraction column to a strong cation exchange trap column through “central cutting” mode in the second focusing step. Finally, the targets were transferred from the strong cation exchange trap column to reverse-phase C18 analytical column and were detected under an UV wavelength of 215 nm. In this method, the extraction system performs the sample injection, extraction, and transfer of targets from the extraction column to one trap column. Meanwhile, the analytical system performs the transfer of targets from other trap column to the analytical column, separation, and detection of targets. This method showed good linearity of calibration curve (R = 0.9999), precision (relative standard deviation (RSD) < 5.4%), and accuracy (within 5.6% in terms of relative error). Therefore, a promising approach was developed for routine monitoring of valproic acid concentration in human plasma.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liampas I, Siokas V, Brotis A, Zintzaras E, Stefanidis I, Dardiotis E (2020) Intravenous sodium valproate in status epilepticus: review and Meta-analysis. Int J Neurosci 2:1–15
Wallenburg E, Klok B, Jong KD, Maat MD, Erp NV, Konijnenburg SS, Essink G, Luin MV (2017) Monitoring protein-unbound valproic acid serum concentrations in clinical practice. Ther Drug Monit 39:269–272
Mahmoud LB, Hakim A, Ghozzi H, Atheymen R, Sahnoun Z, Zeghal K (2017) Influence of age and co-medication on the steady-state pharmacokinetics of valproic acid in Tunisian patients with epilepsy. Rev Neurol 173:159–163
Methaneethorn J (2018) A systematic review of population pharmacokinetics of valproic acid. Br J Clin Pharmacol 84:816–834
Zhao MM, Li GF, Qiu F, Sun YX, Xu YH, ZhaoLM, (2016) Development and validation of a simple and rapid UPLC-MS assay for valproic acid and its comparison with immunoassay and HPLC methods. Ther Drug Monit 38:246–252
Yoon HY, Ahn MH, Yee J, Lee N, Han JM, Gwak HS (2020) Influence of CYP2C9 and CYP2A6 on plasma concentrations of valproic acid: a meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 76:1053–1058
Wang P, Lin XQ, Cai WK, Xu GL, Zhou MD, Yang M, He GH (2018) Effect of UGT2B7 genotypes on plasma concentration of valproic acid: a meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 74:433–442
Guo HL, Jing X, Sun JY, Hu YH, Xu ZJ, Ni MM, Chen F, Lu XP, Qiu JC, Wang TF (2019) Valproic acid and the liver injury in patients with epilepsy: an update. Curr Pharm Des 25:343–351
Liu W, Shang X, Yao SY, Wang F (2020) A novel and nonderivatization method for the determination of valproic acid in human serum by two-dimensional liquid chromatography. Biomed Chromatogr 34:e4695
Tseng YJ, Huang SY, Kuo CH, Wang CY, Wang KC, Wu CC (2020) Safety range of free valproic acid serum concentration in adult patients. PLoS ONE 15:e0238201
Wen DS, Chen ZY, Yang C, Liu HB, Li HL, Chen J, Dai QL, Zhong GP, Qin JM, Ni GZ, Huang MH, Zhou LM, Wang XD (2018) A rapid and simple HPLC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous quantification of valproic acid and its five metabolites in human plasma and application to study pharmacokinetic interaction in Chinese epilepsy patients. J Pharm Biomed Anal 149:448–456
Zhang H, Zhang WF, Li YC, Yan J, Zhang JF, Wang BJ (2018) Correlations between UGT2B7 * 2 gene polymorphisms and plasma concentrations of carbamazepine and valproic acid in epilepsy patients. Brain Dev 40:100–106
Zhao M, Zhang T, Li GF, Qiu F, Sun YX, Zhao LM (2020) Simultaneous determination of valproic acid and its major metabolites by UHPLC-MS/MS in Chinese patients: application to therapeutic drug monitoring. J Chromatogr Sci 55:436–444
Yin L, Wang TT, Shi MY, Zhang Y, Zhao XJ, Yang Y, Gu JK (2016) Simultaneous determination of ten antiepileptic drugs in human plasma by liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry with positive/negative ion-switching electrospray ionization and its application in therapeutic drug monitoring. J Sep Sci 39:964–972
Velghe S, Stove CP (2018) Volumetric absorptive microsampling as an alternative tool for therapeutic drug monitoring of first-generation anti-epileptic drugs. Anal Bioanal Chem 410:2331–2341
Xu SS, Chen YN, Zhao MM, Zhao LM (2017) Development of a simple and rapid method to measure free fraction of valproic acid in plasma using ultrafiltration and ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectroscopy: application to therapeutic drug monitoring. Ther Drug Monit 39:575–579
Kong ST, Lim SH, Lee WB, Kumar PK, Wang HYS, Ng YLS, Wong PS, Ho PC (2014) Clinical validation and implications of dried blood spot sampling of carbamazepine, valproic acid and phenytoin in patients with epilepsy. PLoS ONE 9:e108190
Kotani A, Kotani T, Ishii N, Hakamata H, Kusu F (2014) The effect of hyperglycemia on the pharmacokinetics of valproic acid studied by high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. J Pharm Biomed Anal 97:47–53
Zhong Y, Jiao Z, Yu YQ (2006) Simultaneous determination of mycophenolic acid and valproic acid based on derivatization by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. Biomed Chromatogr 20:319–326
Zhang JF, Zhang ZQ, Dong WC, Jiang Y (2014) A new derivatization method to enhance sensitivity for the determination of low levels of valproic acid in human plasma. J Chromatogr Sci Nov-Dec 52:1173–1180
Gu XR, Yu SR, Peng QL, Ma MB, Hu YN, Zhou BT (2020) Determination of unbound valproic acid in plasma using centrifugal ultrafiltration and gas chromatography: application in TDM. Anal Biochem 588:113475
Thi TTP, Hong HS, Réjane M, Stephan K, Peter CH (2012) Determination of free and total valproic acid in human plasma by capillary electrophoresis with contactless conductivity detection. J Chromatogr B 907:74–78
Mao GF, Zhao K, Sun SS, Lu YX, Li XG (2019) A new derivatization method for the determination of valproic acid in serum using tetramethylammonium hydroxide as a catalyst. Biomed Chromatogr 33:e4440
Odusote KA, Sherwin AL (1981) A simple, direct extraction for gas-liquid chromatographic determination of valproic acid in plasma. Ther Drug Monit 3:103–106
Zhou Y, Wang SH (2019) A robust LC-MS/MS assay with online cleanup for measurement of serum testosterone. J Sep Sci 42:2561–2568
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support received from Hunan Provincial People’s Hospital and the Central Hospital of Shaoyang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval of this research was obtained from the local research ethics committee (Hunan Cancer Hospital Ethics Committee).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Peng, M., Pan, Y. et al. Online Column Extraction Coupled with Double-Trap Column System for HPLC Determination of Valproic Acid in Human Plasma Without Derivatization. Chromatographia 84, 1049–1056 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-021-04089-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-021-04089-w