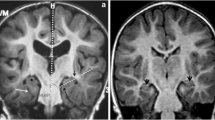
Abstract
Objective
The glymphatic system is a glial cell-dependent waste clearance pathway in the brain that is essential for the maintenance of brain homeostasis. In this study, we evaluated glymphatic system function in patients with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy (JME) compared with healthy controls.
Methods
Patients with JME and healthy controls were retrospectively enrolled in this study. All the participants underwent brain diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). The “DTI-analysis along the perivascular space (ALPS)”-index was calculated to evaluate the glymphatic system function of the participants. The ALPS-indices of the patients with JME were compared with those of the healthy controls. In addition, the correlations between ALPS-index and the clinical characteristics of the patients with JME were analyzed to validate changes in glymphatic system function.
Results
A total of 39 patients with JME and 38 healthy controls were enrolled in this study. The mean ALPS- index of the patients with JME was significantly lower than that of the healthy controls (1.541 vs. 1.653, p = 0.041). ALPS-index was negatively correlated with age in patients with JME (r = -0.375, p = 0.018). However, ALPS-index was not correlated with age at onset, duration of epilepsy, or anti-seizure medication load in patients with JME.
Conclusion
This study is the first in which the ALPS method was used to demonstrate that patients with JME have significant glymphatic system dysfunction. The results also show that glymphatic system index is negatively correlated with age in patients with JME, a finding which demonstrates that the glymphatic system function of patients with JME gradually declines with age. The ALPS-index might be a potential biomarker for monitoring glymphatic system function in patients with epilepsy.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Data that support the findings of this study are available upon reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Benveniste H, Liu X, Koundal S, Sanggaard S, Lee H, Wardlaw J (2019) The glymphatic system and waste clearance with brain aging: a review. Gerontology 65(2):106–119. https://doi.org/10.1159/000490349
Mestre H, Mori Y, Nedergaard M (2020) The Brain’s glymphatic system: current controversies. Trends Neurosci 43(7):458–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2020.04.003
Jessen NA, Munk AS, Lundgaard I, Nedergaard M (2015) The glymphatic system: a Beginner’s guide. Neurochem Res 40(12):2583–2599. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1581-6
Iliff JJ, Wang M, Liao Y, Plogg BA, Peng W, Gundersen GA, Benveniste H, Vates GE, Deane R, Goldman SA, Nagelhus EA, Nedergaard M (2012) A paravascular pathway facilitates CSF flow through the brain parenchyma and the clearance of interstitial solutes, including amyloid beta. Sci Transl Med 4(147):147ra111. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3003748
Takano K, Yamada M (2020) Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging evidence for the role of astrocytic aquaporin-4 water channels in glymphatic influx and interstitial solute transport. Magn Reson Imaging 71:11–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2020.05.001
Taoka T, Naganawa S (2020) Neurofluid dynamics and the glymphatic system: a neuroimaging perspective. Korean J Radiol 21(11):1199–1209. https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2020.0042
Taoka T, Naganawa S (2020) Glymphatic imaging using MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 51(1):11–24. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.26892
Xie L, Kang H, Xu Q, Chen MJ, Liao Y, Thiyagarajan M, O’Donnell J, Christensen DJ, Nicholson C, Iliff JJ, Takano T, Deane R, Nedergaard M (2013) Sleep drives metabolite clearance from the adult brain. Science 342(6156):373–377. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1241224
Rasmussen MK, Mestre H, Nedergaard M (2018) The glymphatic pathway in neurological disorders. Lancet Neurol 17(11):1016–1024. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30318-1
Jiang Q (2019) MRI and glymphatic system. Stroke Vasc Neurol 4(2):75–77. https://doi.org/10.1136/svn-2018-000197
Taoka T, Masutani Y, Kawai H, Nakane T, Matsuoka K, Yasuno F, Kishimoto T, Naganawa S (2017) Evaluation of glymphatic system activity with the diffusion MR technique: diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) in Alzheimer’s disease cases. Jpn J Radiol 35(4):172–178. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-017-0617-z
Nedergaard M, Goldman SA (2020) Glymphatic failure as a final common pathway to dementia. Science 370(6512):50–56. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abb8739
Bae YJ, Choi BS, Kim JM, Choi JH, Cho SJ, Kim JH (2021) Altered glymphatic system in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 82:56–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2020.11.009
Li L, Chopp M, Ding G, Davoodi-Bojd E, Zhang L, Li Q, Zhang Y, Xiong Y, Jiang Q (2020) MRI detection of impairment of glymphatic function in rat after mild traumatic brain injury. Brain Res 1747:147062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2020.147062
Gaberel T, Gakuba C, Goulay R, Martinez De Lizarrondo S, Hanouz JL, Emery E, Touze E, Vivien D, Gauberti M (2014) Impaired glymphatic perfusion after strokes revealed by contrast-enhanced MRI: a new target for fibrinolysis? Stroke 45(10):3092–3096. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.114.006617
Liu C, Habib T, Salimeen M, Pradhan A, Singh M, Wang M, Wu F, Zhang Y, Gao L, Yang G, Li X, Yang J (2020) Quantification of visible Virchow-Robin spaces for detecting the functional status of the glymphatic system in children with newly diagnosed idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Seizure 78:12–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seizure.2020.02.015
Salimeen MSA, Liu C, Li X, Wang M, Singh M, Si S, Li M, Cheng Y, Wang X, Zhao H, Wu F, Zhang Y, Tafawa H, Pradhan A, Yang G, Yang J (2021) Exploring variances of white matter integrity and the glymphatic system in simple febrile seizures and epilepsy. Front Neurol 12:595647. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2021.595647
Feldman RE, Rutland JW, Fields MC, Marcuse LV, Pawha PS, Delman BN, Balchandani P (2018) Quantification of perivascular spaces at 7T: a potential MRI biomarker for epilepsy. Seizure 54:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seizure.2017.11.004
Baykan B, Wolf P (2017) Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy as a spectrum disorder: a focused review. Seizure 49:36–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seizure.2017.05.011
Grunewald RA, Panayiotopoulos CP (1993) Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. A review. Arch Neurol 50(6):594–598. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.1993.00540060034013
Roshan S, Puri V, Chaudhry N, Gupta A, Rabi SK (2017) Sleep abnormalities in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy-A sleep questionnaire and polysomnography based study. Seizure 50:194–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seizure.2017.06.021
Reddy OC, van der Werf YD (2020) The sleeping brain: harnessing the power of the glymphatic system through lifestyle choices. Brain Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10110868
Jang H, Lee JY, Lee KI, Park KM (2017) Are there differences in brain morphology according to handedness? Brain Behav 7(7):e00730. https://doi.org/10.1002/brb3.730
Ringstad G, Vatnehol SAS, Eide PK (2017) Glymphatic MRI in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Brain 140(10):2691–2705. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awx191
Zhang W, Zhou Y, Wang J, Gong X, Chen Z, Zhang X, Cai J, Chen S, Fang L, Sun J, Lou M (2021) Glymphatic clearance function in patients with cerebral small vessel disease. Neuroimage 238:118257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2021.118257
Plog BA, Nedergaard M (2018) The glymphatic system in central nervous system health and disease: past, present, and future. Annu Rev Pathol 13:379–394. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathol-051217-111018
Gorter JA, van Vliet EA, Aronica E (2015) Status epilepticus, blood-brain barrier disruption, inflammation, and epileptogenesis. Epilepsy Behav 49:13–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2015.04.047
Hanael E, Veksler R, Friedman A, Bar-Klein G, Senatorov VV Jr, Kaufer D, Konstantin L, Elkin M, Chai O, Peery D, Shamir MH (2019) Blood-brain barrier dysfunction in canine epileptic seizures detected by dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Epilepsia 60(5):1005–1016. https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.14739
Dadas A, Washington J, Janigro D (2016) Cerebral waste accumulation and glymphatic clearance as mechanisms of human neurological diseases. J Neurol Neuromed 1(7):15–19. https://doi.org/10.29245/2572.942X/2016/7.1082
Girouard H, Iadecola C (2006) Neurovascular coupling in the normal brain and in hypertension, stroke, and Alzheimer disease. J Appl Physiol 100(1):328–335. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00966.2005
Rabinovitch A, Aviram I, Biton Y, Braunstein D (2020) Explaining recent postictal epilepsy EEG results by the G-lymphatic clearance hypothesis. Med Hypotheses 137:109600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109600
Rabinovitch A, Aviramd I, Biton Y, Braunstein D (2019) A combined astrocyte - G-lymphatic model of epilepsy initiation, maintenance and termination. Med Hypotheses 133:109384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2019.109384
Kress BT, Iliff JJ, Xia M, Wang M, Wei HS, Zeppenfeld D, Xie L, Kang H, Xu Q, Liew JA, Plog BA, Ding F, Deane R, Nedergaard M (2014) Impairment of paravascular clearance pathways in the aging brain. Ann Neurol 76(6):845–861. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24271
Ahn JH, Cho H, Kim JH, Kim SH, Ham JS, Park I, Suh SH, Hong SP, Song JH, Hong YK, Jeong Y, Park SH, Koh GY (2019) Meningeal lymphatic vessels at the skull base drain cerebrospinal fluid. Nature 572(7767):62–66. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1419-5
Landolt HP, Borbely AA (2001) Age-dependent changes in sleep EEG topography. Clin Neurophysiol 112(2):369–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1388-2457(00)00542-3
Hoyer S (1994) Age as risk factor for sporadic dementia of the Alzheimer type? Ann N Y Acad Sci 719:248–256. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1994.tb56833.x
Taoka T, Naganawa S (2021) Imaging for central nervous system (CNS) interstitial fluidopathy: disorders with impaired interstitial fluid dynamics. Jpn J Radiol 39(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-020-01017-0
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT of the Republic of Korea (NRF-2021R1F1A1049605).
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by H-JL, DAL, KJS and KMP. The first draft of the manuscript was written by KMP, and all the authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
Neither of the authors has any conflict of interest to disclose.
Ethical standards
This protocol was approved and carried out in accordance with the recommendation of the local Institutional Review Board (Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, HJ., Lee, D.A., Shin, K.J. et al. Glymphatic system dysfunction in patients with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. J Neurol 269, 2133–2139 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-021-10799-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-021-10799-w