Abstract
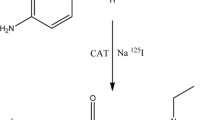
Azilsartan (AZ) was labeled with 131I using Chloramine-T as oxidizing agent. Factors affecting the labeling efficiency were systematically studied, and optimum conditions were found: oxidizing agent amount 100 μg, substrate amount 100 μg, pH 6, reaction time 30 min, and ambient temperature. Biodistribution studies showed that [131I]iodoAZ is concentrated in heart at 5 min post-injection to give high uptake of 29.0 ± 0.6% injected dose/g organ. Thus, iodoAZ shows promise as a radiotracer for heart imaging.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Austria-Codex, Haberfeld, H., Ed., Vienna: Österreichischer Apothekerverlag, 2015.
Arzneistoff-Profile, Dinnendahl, V. and Fricke, U., Eds., Eschborn, Germany: Govi Pharmazeutischer, 2012.
Cerqueira, M.D., Glob. J. Child Res., 2003, pp. 1448–1453.
Budoff, M.J. et al., J. Am. Coll. Cardiol., 2005, vol. 46, p. 383.
Bateman, T., Dilsizian, V., Beanlands, R., DePuey, E.G., Heller, G., and Wolinsky, D., J. Nucl. Med., 2016, vol. 57, no. 10, p. 1654.
Baggish, A.L. and Boucher, C.A., Circulation, 2008, vol. 118, no. 16, p. 1668.
Sanad, M.H., Sallam, Kh.M., Marzook, F.A., and Abd-Elhaliem, S.M., J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm., 2016, vol. 59, p. 48.
Sanad, M.H., Ebtisam, A.M., and Safaa, B.C., Radiochim. Acta, 2018, vol. 106, no. 4, pp. 329–336.
Sanad, M.H. and Alhussein, A., Radiochim. Acta, 2018, vol. 106, no. 10, pp. 843–850.
Sanad, M.H., Marzook, F.A., and Abd-Elhaliem, S.M., Radiochim. Acta, 2021, vol. 109, no. 1, pp. 41–46.
El-Tawoosy, M., Farouk, N., and El-Bayoumy, A.S., J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., 2011, vol. 290, pp. 595–600.
Amin, A., Abd El-Bary, A., Abd El-Mohty, A., Shokry, S., and El-Sharawy, M., J. Nat. Sci., 2013, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 526–531.
Bissessor, N. and White, H., Vasc. Health Risk Manag., 2007, vol. 3, no. 4, pp. 425–430.
El-Sharawy, D.M.M., Radioiodination and Bioevaluation of Some Cardiovascular Drugs for Nuclear Medicine Application: Thesis, Egypt: Cairo Univ., Faculty of Pharmacy, Department of Pharmaceutics and Industrial Pharmacy, 2013.
Ibrahim, I.T. and Sanad, M.H., Radiochemistry, 2013, vol. 55, no. 3, pp. 336–339.
. Sanad, M.H., Saleh, G.M., and Marzook, F.A., J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm., 2017, vol. 60, pp. 600–607.
Sanad, M.H., Salama, D.H., and Marzook, F.A., Radiochim. Acta, 2017, vol. 105, pp. 389–398.
Sanad, M.H. and Challan, S.B., Radiochemistry, 2017, vol. 59, pp. 307–312.
Abolfazl, H., Mohammad, A.K., Masoumeh, H., and Mahmoud, T.A., Monatsh. Chem., 2012, vol. 143, pp. 619–623.
Mohammad, A.K., Abolfazl, H., Iran J Org Chem., 2009,vol. 4, pp. 268–270.
Sanad, M.H., Farag, A.B., Salama, D.H., Journal of Labelled Compounds and Radiopharmaceuticals, 2018, vol. 61, pp. 501–508.
Borai, E., Sanad, M.H., and Fouzy, A.S.M., Radiochemistry, 2016, vol. 58, no. 1, pp. 84–91.
Sanad, M.H. and Emad, H.B., Radiochim. Acta, 2015, vol. 103(12), pp. 879–891.
Sanad, M.H. and El-Tawoosy, M., Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 2013, vol. 298(2), pp. 1105–1109.
Amin, A.M., Sanad, M.H., Abd-Elhaliem, S.M., Radiochemistry, 2013, vol. 55, pp. 624–628. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1066362213060118
Ebtisam, A.M., Ahmed, S.E., and Fawzy, A.M., Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences, 2019, vol. 12(1), pp. 304–310. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1066362213060118
Sanad, M.H. and Ibrahim, I.T., Radiochemistry, 2015, vol. 57, pp. 425–430. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1066362215040165
Sanad, M.H., El-Bayoumy, A.S.A., and Alhussein, I.A., J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., 2017, vol. 311(1), pp. 1–14.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by STDF – National Research Centre under project number 41535 – PI Ahmed Sayed Morsy Fouzy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sanad, M.H., Marzook, F.A., Rizvi, S.F.A. et al. Radioiodinated Azilsartan as a New Highly Selective Radiotracer for Myocardial Perfusion Imaging. Radiochemistry 63, 520–525 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1066362221040160
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1066362221040160