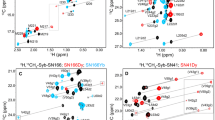
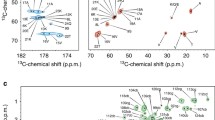
Abstract
The development of methyl transverse relaxation optimized spectroscopy has greatly facilitated the study of macromolecular assemblies by solution NMR spectroscopy. However, limited sample solubility and stability has hindered application of this technique to ongoing studies of complexes formed on membranes by the neuronal SNAREs that mediate neurotransmitter release and synaptotagmin-1, the Ca2+ sensor that triggers release. Since the 1H NMR signal of a tBu group attached to a large protein or complex can be observed with high sensitivity if the group retains high mobility, we have explored the use of this strategy to analyze presynaptic complexes involved in neurotransmitter release. For this purpose, we attached tBu groups at single cysteines of fragments of synaptotagmin-1, complexin-1 and the neuronal SNAREs by reaction with 5-(tert-butyldisulfaneyl)-2-nitrobenzoic acid (BDSNB), tBu iodoacetamide or tBu acrylate. The tBu resonances of the tagged proteins were generally sharp and intense, although tBu groups attached with BDSNB had a tendency to exhibit somewhat broader resonances that likely result because of the shorter linkage between the tBu and the tagged cysteine. Incorporation of the tagged proteins into complexes on nanodiscs led to severe broadening of the tBu resonances in some cases. However, sharp tBu resonances could readily be observed for some complexes of more than 200 kDa at low micromolar concentrations. Our results show that tagging of proteins with tBu groups provides a powerful approach to study large biomolecular assemblies of limited stability and/or solubility that may be applicable even at nanomolar concentrations.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data associated with this manuscript are available upon reasonable request.
References
Abdelkader EH, Qianzhu H, Tan YJ, Adams LA, Huber T, Otting G (2021) Genetic encoding of N(6)-(((trimethylsilyl)methoxy)carbonyl)-l-lysine for NMR studies of protein-protein and protein-ligand interactions. J Am Chem Soc 143:1133–1143
Arac D, Chen X, Khant HA, Ubach J, Ludtke SJ, Kikkawa M, Johnson AE, Chiu W, Sudhof TC, Rizo J (2006) Close membrane-membrane proximity induced by Ca(2+)-dependent multivalent binding of synaptotagmin-1 to phospholipids. Nat Struct Mol Biol 13:209–217
Arac D, Murphy T, Rizo J (2003) Facile detection of protein-protein interactions by one-dimensional NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry 42:2774–2780
Bai J, Tucker WC, Chapman ER (2004) PIP2 increases the speed of response of synaptotagmin and steers its membrane-penetration activity toward the plasma membrane. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11:36–44
Becker W, Adams LA, Graham B, Wagner GE, Zangger K, Otting G, Nitsche C (2018) Trimethylsilyl tag for probing protein-ligand interactions by NMR. J Biomol NMR 70:211–218
Brewer KD, Bacaj T, Cavalli A, Camilloni C, Swarbrick JD, Liu J, Zhou A, Zhou P, Barlow N, Xu J, Seven AB, Prinslow EA, Voleti R, Haussinger D, Bonvin AM, Tomchick DR, Vendruscolo M, Graham B, Sudhof TC, Rizo J (2015) Dynamic binding mode of a Synaptotagmin-1-SNARE complex in solution. Nat Struct Mol Biol 22:555–564
Chen WN, Kuppan KV, Lee MD, Jaudzems K, Huber T, Otting G (2015) O-tert-Butyltyrosine, an NMR tag for high-molecular-weight systems and measurements of submicromolar ligand binding affinities. J Am Chem Soc 137:4581–4586
Chen WN, Nitsche C, Pilla KB, Graham B, Huber T, Klein CD, Otting G (2016) Sensitive NMR approach for determining the binding mode of tightly binding ligand molecules to protein targets. J Am Chem Soc 138:4539–4546
Chen X, Arac D, Wang TM, Gilpin CJ, Zimmerberg J, Rizo J (2006) SNARE-mediated lipid mixing depends on the physical state of the vesicles. Biophys J 90:2062–2074
Chen X, Lu J, Dulubova I, Rizo J (2008) NMR analysis of the closed conformation of syntaxin-1. J Biomol NMR 41:43–54
Chen X, Tomchick DR, Kovrigin E, Arac D, Machius M, Sudhof TC, Rizo J (2002) Three-dimensional structure of the complexin/SNARE complex. Neuron 33:397–409
Delaglio F, Grzesiek S, Vuister GW, Zhu G, Pfeifer J, Bax A (1995) Nmrpipe—a multidimensional spectral processing system based on unix pipes. J Biomol NMR 6:277–293
Denisov IG, Baas BJ, Grinkova YV, Sligar SG (2007) Cooperativity in cytochrome P450 3A4: linkages in substrate binding, spin state, uncoupling, and product formation. J Biol Chem 282:7066–7076
Dulubova I, Sugita S, Hill S, Hosaka M, Fernandez I, Sudhof TC, Rizo J (1999) A conformational switch in syntaxin during exocytosis: role of munc18. EMBO J 18:4372–4382
Fernandez-Chacon R, Konigstorfer A, Gerber SH, Garcia J, Matos MF, Stevens CF, Brose N, Rizo J, Rosenmund C, Sudhof TC (2001) Synaptotagmin I functions as a calcium regulator of release probability. Nature 410:41–49
Fernandez I, Arac D, Ubach J, Gerber SH, Shin O, Gao Y, Anderson RG, Sudhof TC, Rizo J (2001) Three-dimensional structure of the synaptotagmin 1 c(2)b-domain. Synaptotagmin 1 as a phospholipid binding machine. Neuron 32:1057–1069
Garcia-Rubio I (2020) EPR of site-directed spin-labeled proteins: a powerful tool to study structural flexibility. Arch Biochem Biophys 684:108323
Giralt E, Rizo J, Pedroso E (1984) Application of gel-phase 13C-NMR to monitor solid phase peptide synthesis. Tetrahedron 40:4141–4152
Graham B, Loh CT, Swarbrick JD, Ung P, Shin J, Yagi H, Jia X, Chhabra S, Barlow N, Pintacuda G, Huber T, Otting G (2011) DOTA-amide lanthanide tag for reliable generation of pseudocontact shifts in protein NMR spectra. Bioconjug Chem 22:2118–2125
Hanson PI, Roth R, Morisaki H, Jahn R, Heuser JE (1997) Structure and conformational changes in NSF and its membrane receptor complexes visualized by quick-freeze/deep-etch electron microscopy. Cell 90:523–535
Hu W, Wang H, Hou Y, Hao Y, Liu D (2019) Trimethylsilyl reporter groups for NMR studies of conformational changes in G protein-coupled receptors. FEBS Lett 593:1113–1121
Huang C, Kalodimos CG (2017) Structures of large protein complexes determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Annu Rev Biophys 46:317–336
Jabar S, Adams LA, Wang Y, Aurelio L, Graham B, Otting G (2017) Chemical tagging with tert-butyl and trimethylsilyl groups for measuring intermolecular nuclear overhauser effects in a large protein-ligand complex. Chemistry 23:13033–13036
Johnson BA, Blevins RA (1994) Nmr view—a computer-program for the visualization and analysis of Nmr data. J Biomol NMR 4:603–614
Liu Q, He QT, Lyu X, Yang F, Zhu ZL, Xiao P, Yang Z, Zhang F, Yang ZY, Wang XY, Sun P, Wang QW, Qu CX, Gong Z, Lin JY, Xu Z, Song SL, Huang SM, Guo SC, Han MJ, Zhu KK, Chen X, Kahsai AW, Xiao KH, Kong W, Li FH, Ruan K, Li ZJ, Yu X, Niu XG, Jin CW, Wang J, Sun JP (2020) DeSiphering receptor core-induced and ligand-dependent conformational changes in arrestin via genetic encoded trimethylsilyl (1)H-NMR probe. Nat Commun 11:4857
Loh CT, Adams LA, Graham B, Otting G (2018) Genetically encoded amino acids with tert-butyl and trimethylsilyl groups for site-selective studies of proteins by NMR spectroscopy. J Biomol NMR 71:287–293
Ma C, Li W, Xu Y, Rizo J (2011) Munc13 mediates the transition from the closed syntaxin-Munc18 complex to the SNARE complex. Nat Struct Mol Biol 18:542–549
Ma C, Su L, Seven AB, Xu Y, Rizo J (2013) Reconstitution of the vital functions of Munc18 and Munc13 in neurotransmitter release. Science 339:421–425
McMahon HT, Missler M, Li C, Sudhof TC (1995) Complexins: cytosolic proteins that regulate SNAP receptor function. Cell 83:111–119
Pabst S, Hazzard JW, Antonin W, Sudhof TC, Jahn R, Rizo J, Fasshauer D (2000) Selective interaction of complexin with the neuronal SNARE complex. Determination of the binding regions. J Biol Chem 275:19808–19818
Pan YZ, Quade B, Brewer KD, Szabo M, Swarbrick JD, Graham B, Rizo J (2016) Sequence-specific assignment of methyl groups from the neuronal SNARE complex using lanthanide-induced pseudocontact shifts. J Biomol NMR 66:281–293
Poirier MA, Xiao W, Macosko JC, Chan C, Shin YK, Bennett MK (1998) The synaptic SNARE complex is a parallel four-stranded helical bundle. Nat Struct Biol 5:765–769
Rizo J (2018) Mechanism of neurotransmitter release coming into focus. Protein Sci 27:1364–1391
Rizo J, Chen X, Arac D (2006) Unraveling the mechanisms of synaptotagmin and SNARE function in neurotransmitter release. Trends Cell Biol 16:339–350
Rizo J, Rosen MK, Gardner KH (2012) Enlightening molecular mechanisms through study of protein interactions. J Mol Cell Biol 4:270–283
Rose-Sperling D, Tran MA, Lauth LM, Goretzki B, Hellmich UA (2019) 19F NMR as a versatile tool to study membrane protein structure and dynamics. Biol Chem 400:1277–1288
Rosenzweig R, Kay LE (2014) Bringing dynamic molecular machines into focus by methyl-TROSY NMR. Annu Rev Biochem 83:291–315
Rufener E, Frazier AA, Wieser CM, Hinderliter A, Cafiso DS (2005) Membrane-bound orientation and position of the synaptotagmin C2B domain determined by site-directed spin labeling. Biochemistry 44:18–28
Shao X, Fernandez I, Sudhof TC, Rizo J (1998) Solution structures of the Ca2+-free and Ca2+-bound C2A domain of synaptotagmin I: does Ca2+ induce a conformational change? Biochemistry 37:16106–16115
Sollner T, Bennett MK, Whiteheart SW, Scheller RH, Rothman JE (1993) A protein assembly-disassembly pathway in vitro that may correspond to sequential steps of synaptic vesicle docking, activation, and fusion. Cell 75:409–418
Sutton RB, Davletov BA, Berghuis AM, Sudhof TC, Sprang SR (1995) Structure of the first C2 domain of synaptotagmin I: a novel Ca2+/phospholipid-binding fold. Cell 80:929–938
Sutton RB, Fasshauer D, Jahn R, Brunger AT (1998) Crystal structure of a SNARE complex involved in synaptic exocytosis at 2.4 A resolution. Nature 395:347–353
Tang J, Maximov A, Shin OH, Dai H, Rizo J, Sudhof TC (2006) A complexin/synaptotagmin 1 switch controls fast synaptic vesicle exocytosis. Cell 126:1175–1187
Trimbuch T, Xu J, Flaherty D, Tomchick DR, Rizo J, Rosenmund C (2014) Re-examining how complexin inhibits neurotransmitter release. Elife 3:e02391
Tugarinov V, Sprangers R, Kay LE (2004) Line narrowing in methyl-TROSY using zero-quantum 1H–13C NMR spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 126:4921–4925
Ubach J, Zhang X, Shao X, Sudhof TC, Rizo J (1998) Ca2+ binding to synaptotagmin: how many Ca2+ ions bind to the tip of a C2-domain? EMBO J 17:3921–3930
Voleti R, Jaczynska K, Rizo J (2020) Ca(2+)-dependent release of Synaptotagmin-1 from the SNARE complex on phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate-containing membranes. Elife 9, e57154. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.57154
Xu J, Brewer KD, Perez-Castillejos R, Rizo J (2013) Subtle Interplay between Synaptotagmin and Complexin Binding to the SNARE Complex. J Mol Biol 425:3461–3475
Zhou A, Brewer KD, Rizo J (2013) Analysis of SNARE complex/synaptotagmin-1 interactions by one-dimensional NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry 52:3446–3456
Zhou Q, Lai Y, Bacaj T, Zhao M, Lyubimov AY, Uervirojnangkoorn M, Zeldin OB, Brewster AS, Sauter NK, Cohen AE, Soltis SM, Alonso-Mori R, Chollet M, Lemke HT, Pfuetzner RA, Choi UB, Weis WI, Diao J, Sudhof TC, Brunger AT (2015) Architecture of the synaptotagmin-SNARE machinery for neuronal exocytosis. Nature 525:62–67
Zhou Q, Zhou P, Wang AL, Wu D, Zhao M, Sudhof TC, Brunger AT (2017) The primed SNARE-complexin-synaptotagmin complex for neuronal exocytosis. Nature 548:420–425
Acknowledgements
We thank Ad Bax for the suggestion of exploring the use tBu groups as probes for structural studies of the neurotransmitter release machinery, and Ad Bax, Lewis Kay and Charampalos Kalodimos for fruitful discussions on this subject. The Agilent DD2 console of the 800 MHz spectromenter used for the research presented here was purchased with a shared instrumentation grant from the NIH (S10OD018027 to JR). Rashmi Voleti was supported by a fellowship from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. The preparation of BDSNB was performed at the NANBIOSIS –CIBER BBN Peptide Synthesis Unit (U3). This work was supported by grant I-1304 from the Welch Foundation (to JR) and by NIH Research Project Award R35 NS097333 (to JR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Voleti, R., Bali, S., Guerrero, J. et al. Evaluation of the tert-butyl group as a probe for NMR studies of macromolecular complexes. J Biomol NMR 75, 347–363 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-021-00380-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-021-00380-y