Abstract
Purpose
Brain involvement in X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMTX) has been previously reported. We studied the brain structural and functional integrity using a multimodal neuroimaging approach in patients with no current central nervous system (CNS) symptoms, in order to further delineate the disease’s phenotype.
Methods
Seventeen CMTX patients with no current CNS symptoms and 24 matched healthy controls underwent brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Structural integrity was evaluated performing Gray matter analysis with voxel-based morphometry (VBM) and tract-based spatial statistics (TBSS) of diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). Functional integrity was evaluated with resting-state functional MRI (rs-fMRI).
Results
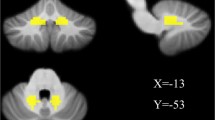
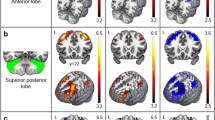
Decreased gray matter density was detected in CMTX patients compared to healthy controls in bilateral hippocampus, left thalamus, left postcentral gyrus, left superior parietal lobule, left cerebellum crus I and II, and vermis VI. DTI analysis showed increased fractional anisotropy and radial diffusivity in the right anterior insula and increased axial diffusivity in right cerebellum crus I in CMTX patients. rs-fMRI revealed decreased spontaneous neural activity on left precentral gyrus in patients compared to healthy controls.
Conclusion
Advanced magnetic resonance (MR) neuroimaging techniques in CMTX patients revealed structural and functional involvement of multiple motor and extra-motor brain areas. MR neuroimaging techniques have the potential to delineate the CNS phenotype of a peripheral neuropathy like CMTX.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the imaging and clinical data are available upon request.
Code availability
MATLAB toolboxes and FMRIB Software Library (FSL) software are publicly available.
References
Harding AE, Thomas PK (1980) The clinical features of hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy types I and II. Brain 103(2):259–280. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/103.2.259
Dermietzel R, Hwang TK, Spray DS (1990) The gap junction family: structure, function and chemistry. Anat Embryol (Berl) 182(6):517–528. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00186458
Bergoffen J, Scherer SS, Wang S, Scott MO, Bone LJ, Paul DL, Chen K, Lensch MW, Chance PF, Fischbeck KH (1993) Connexin mutations in X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Science 262(5142):2039–2042. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.8266101
Scherer SS, Deschenes SM, Xu YT, Grinspan JB, Fischbeck KH, Paul DL (1995) Connexin32 is a myelin-related protein in the PNS and CNS. J Neurosci 15(12):8281–8294
Nicholson G, Corbett A (1996) Slowing of central conduction in X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy shown by brain stem auditory evoked responses. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 61(1):43–46. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.61.1.43
Bahr M, Andres F, Timmerman V, Nelis ME, Van Broeckhoven C, Dichgans J (1999) Central visual, acoustic, and motor pathway involvement in a Charcot-Marie-Tooth family with an Asn205Ser mutation in the connexin 32 gene. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 66(2):202–206. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.66.2.202
Lee M, Park CH, Chung HK, Kim HJ, Choi Y, Yoo JH, Yoon YC, Hong YB, Chung KW, Choi BO, Lee HW (2017) Cerebral white matter abnormalities in patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Ann Neurol 81(1):147–151. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24824
Cortese R, Zoccolella S, Muglia M, Patitucci A, Scarafino A, Paolicelli D, Simone IL (2016) A rare association between multiple sclerosis and Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 1B. Brain Behav 6(12):e00580. https://doi.org/10.1002/brb3.580
Paulson HL, Garbern JY, Hoban TF, Krajewski KM, Lewis RA, Fischbeck KH, Grossman RI, Lenkinski R, Kamholz JA, Shy ME (2002) Transient central nervous system white matter abnormality in X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Ann Neurol 52(4):429–434. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.10305
Koutsis G, Breza M, Velonakis G, Tzartos J, Kasselimis D, Kartanou C, Karavasilis E, Tzanetakos D, Anagnostouli M, Andreadou E, Evangelopoulos ME, Kilidireas C, Potagas C, Panas M, Karadima G (2019) X linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and multiple sclerosis: emerging evidence for an association. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 90(2):187–194. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2018-319014
Alexander AL, Lee JE, Lazar M, Field AS (2007) Diffusion tensor imaging of the brain. Neurotherapeutics 4(3):316–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nurt.2007.05.011
Sundgren PC, Dong Q, Gomez-Hassan D, Mukherji SK, Maly P, Welsh R (2004) Diffusion tensor imaging of the brain: review of clinical applications. Neuroradiology 46(5):339–350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-003-1114-x
Greicius M (2008) Resting-state functional connectivity in neuropsychiatric disorders. Curr Opin Neurol 21(4):424–430. https://doi.org/10.1097/WCO.0b013e328306f2c5
Liu F, Hu M, Wang S, Guo W, Zhao J, Li J, Xun G, Long Z, Zhang J, Wang Y, Zeng L, Gao Q, Wooderson SC, Chen J, Chen H (2012) Abnormal regional spontaneous neural activity in first-episode, treatment-naive patients with late-life depression: a resting-state fMRI study. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 39(2):326–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2012.07.004
Liu F, Guo W, Fouche JP, Wang Y, Wang W, Ding J, Zeng L, Qiu C, Gong Q, Zhang W, Chen H (2015) Multivariate classification of social anxiety disorder using whole brain functional connectivity. Brain Struct Funct 220(1):101–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-013-0641-4
Guo WB, Liu F, Xue ZM, Xu XJ, Wu RR, Ma CQ, Wooderson SC, Tan CL, Sun XL, Chen JD, Liu ZN, Xiao CQ, Chen HF, Zhao JP (2012) Alterations of the amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations in treatment-resistant and treatment-response depression: a resting-state fMRI study. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 37(1):153–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2012.01.011
Yu H, Qiu X, Zhang YQ, Deng Y, He MY, Zhao YT, Zhai ZH (2019) Abnormal amplitude of low frequency fluctuation and functional connectivity in non-neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus: a resting-state fMRI study. Neuroradiology 61(3):331–340. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-018-2138-6
Zang YF, He Y, Zhu CZ, Cao QJ, Sui MQ, Liang M, Tian LX, Jiang TZ, Wang YF (2007) Altered baseline brain activity in children with ADHD revealed by resting-state functional MRI. Brain Dev 29(2):83–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.braindev.2006.07.002
Zou QH, Zhu CZ, Yang Y, Zuo XN, Long XY, Cao QJ, Wang YF, Zang YF (2008) An improved approach to detection of amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (ALFF) for resting-state fMRI: fractional ALFF. J Neurosci Methods 172(1):137–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2008.04.012
De Salvo S, Bonanno L, Giorgianni R, Muscara N, Freni F, Caminiti F, Milardi D, Bramanti P, Marino S (2018) Functional MRI and laser-evoked potentials evaluation in Charcot-Marie-Tooth syndrome. Neurol Sci 39(7):1185–1189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-018-3401-7
Pontillo G, Tozza S, Perillo T, Cocozza S, Dubbioso R, Severi D, Iodice R, Tedeschi E, Elefante A, Brunetti A, Manganelli F, Quarantelli M (2021) Diffuse brain connectivity changes in Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 1a patients: a resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Eur J Neurol 28(1):305–313. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.14540
Barnes J, Ridgway GR, Bartlett J, Henley SM, Lehmann M, Hobbs N, Clarkson MJ, MacManus DG, Ourselin S, Fox NC (2010) Head size, age and gender adjustment in MRI studies: a necessary nuisance? Neuroimage 53(4):1244–1255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.06.025
Kostic VS, Agosta F, Petrovic I, Galantucci S, Spica V, Jecmenica-Lukic M, Filippi M (2010) Regional patterns of brain tissue loss associated with depression in Parkinson disease. Neurology 75(10):857–863. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181f11c1d
Stonnington CM, Tan G, Kloppel S, Chu C, Draganski B, Jack CR Jr, Chen K, Ashburner J, Frackowiak RS (2008) Interpreting scan data acquired from multiple scanners: a study with Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage 39(3):1180–1185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.09.066
Rzezak P, Squarzoni P, Duran FL, de Toledo Ferraz Alves T, Tamashiro-Duran J, Bottino CM, Ribeiz S, Lotufo PA, Menezes PR, Scazufca M, Busatto GF (2015) Relationship between brain age-related reduction in gray matter and educational attainment. PLoS One 10(10):e0140945. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0140945
Maldjian JA, Laurienti PJ, Kraft RA, Burdette JH (2003) An automated method for neuroanatomic and cytoarchitectonic atlas-based interrogation of fMRI data sets. Neuroimage 19(3):1233–1239. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1053-8119(03)00169-1
Maldjian JA, Laurienti PJ, Burdette JH (2004) Precentral gyrus discrepancy in electronic versions of the Talairach atlas. Neuroimage 21(1):450–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2003.09.032
Tzourio-Mazoyer N, Landeau B, Papathanassiou D, Crivello F, Etard O, Delcroix N, Mazoyer B, Joliot M (2002) Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. Neuroimage 15(1):273–289. https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.2001.0978
Smith SM (2002) Fast robust automated brain extraction. Hum Brain Mapp 17(3):143–155. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.10062
Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Johansen-Berg H, Rueckert D, Nichols TE, Mackay CE, Watkins KE, Ciccarelli O, Cader MZ, Matthews PM, Behrens TE (2006) Tract-based spatial statistics: voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. Neuroimage 31(4):1487–1505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.02.024
Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Woolrich MW, Beckmann CF, Behrens TE, Johansen-Berg H, Bannister PR, De Luca M, Drobnjak I, Flitney DE, Niazy RK, Saunders J, Vickers J, Zhang Y, De Stefano N, Brady JM, Matthews PM (2004) Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. Neuroimage 23(Suppl 1):S208-219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.07.051
Whitfield-Gabrieli S, Nieto-Castanon A (2012) Conn: a functional connectivity toolbox for correlated and anticorrelated brain networks. Brain Connect 2(3):125–141. https://doi.org/10.1089/brain.2012.0073
Biswal B, Yetkin FZ, Haughton VM, Hyde JS (1995) Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar MRI. Magn Reson Med 34(4):537–541. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.1910340409
Sato K, Kubo S, Fujii H, Okamoto M, Takahashi K, Takamatsu K, Tanaka A, Kuriyama M (2012) Diffusion tensor imaging and magnetic resonance spectroscopy of transient cerebral white matter lesions in X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. J Neurol Sci 316(1–2):178–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2012.01.017
Srinivasan J, Leventer RJ, Kornberg AJ, Dahl HH, Ryan MM (2008) Central nervous system signs in X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease after hyperventilation. Pediatr Neurol 38(4):293–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2007.12.003
Rosser T, Muir J, Panigrahy A, Baldwin EE, Boles RG (2010) Transient leukoencephalopathy associated with X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. J Child Neurol 25(8):1013–1016. https://doi.org/10.1177/0883073809352378
Al-Mateen M, Craig AK, Chance PF (2014) The central nervous system phenotype of X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: a transient disorder of children and young adults. J Child Neurol 29(3):342–348. https://doi.org/10.1177/0883073812474343
Aktan Z, Akcakaya NH, Tekturk P, Deniz E, Koyuncu B, Yapici Z (2018) A case with CMTX1 disease showing transient ischemic-attack-like episodes. Neurol Neurochir Pol 52(2):285–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pjnns.2017.10.016
Anand G, Maheshwari N, Roberts D, Padeniya A, Hamilton-Ayers M, van der Knaap M, Fratter C, Jayawant S (2010) X-linked hereditary motor sensory neuropathy (type 1) presenting with a stroke-like episode. Dev Med Child Neurol 52(7):677–679. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2010.03674.x
Basu A, Horvath R, Esisi B, Birchall D, Chinnery PF (2011) Recurrent stroke-like episodes in X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Neurology 77(12):1205–1206. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e31822f046e
Halbrich M, Barnes J, Bunge M, Joshi C (2008) A V139M mutation also causes the reversible CNS phenotype in CMTX. Can J Neurol Sci 35(3):372–374. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0317167100008994
Isoardo G, Di Vito N, Nobile M, Benetton G, Fassio F (2005) X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and progressive-relapsing central demyelinating disease. Neurology 65(10):1672–1673. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000186032.06791.94
Taylor RA, Simon EM, Marks HG, Scherer SS (2003) The CNS phenotype of X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: more than a peripheral problem. Neurology 61(11):1475–1478. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000095960.48964.25
Uk-I JM, Yiu E, Donner EJ, Shroff M (2011) MRI findings in X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease associated with a novel connexin 32 mutation. Clin Radiol 66(5):471–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crad.2010.11.009
Zhong L, Yan K, Liu C, Xue J, Wu L, Yin F (2012) Clinical reasoning: a young man with reversible paralysis, cerebral white matter lesions, and peripheral neuropathy. Neurology 79(8):e70-72. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182661eca
Herrero MT, Barcia C, Navarro JM (2002) Functional anatomy of thalamus and basal ganglia. Childs Nerv Syst 18(8):386–404. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-002-0604-1
Kasselimis D, Karadima G, Angelopoulou G, Breza M, Tsolakopoulos D, Potagas C, Panas M, Koutsis G (2020) Evidence for cognitive deficits in X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 26(3):294–302. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1355617719001188
Kim C, Johnson NF, Cilles SE, Gold BT (2011) Common and distinct mechanisms of cognitive flexibility in prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci 31(13):4771–4779. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5923-10.2011
Rusch N, Spoletini I, Wilke M, Bria P, Di Paola M, Di Iulio F, Martinotti G, Caltagirone C, Spalletta G (2007) Prefrontal-thalamic-cerebellar gray matter networks and executive functioning in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 93(1–3):79–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2007.01.029
Giraldo-Chica M, Rogers BP, Damon SM, Landman BA, Woodward ND (2018) Prefrontal-thalamic anatomical connectivity and executive cognitive function in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 83(6):509–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2017.09.022
Law N, Smith ML, Widjaja E (2018) Thalamocortical connections and executive function in pediatric temporal and frontal lobe epilepsy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 39(8):1523–1529. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A5691
Tschentscher N, Ruisinger A, Blank H, Diaz B, von Kriegstein K (2019) Reduced structural connectivity between left auditory thalamus and the motion-sensitive planum temporale in developmental dyslexia. J Neurosci 39(9):1720–1732. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1435-18.2018
Diaz B, Hintz F, Kiebel SJ, von Kriegstein K (2012) Dysfunction of the auditory thalamus in developmental dyslexia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(34):13841–13846. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1119828109
Burgess N, Maguire EA, O’Keefe J (2002) The human hippocampus and spatial and episodic memory. Neuron 35(4):625–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0896-6273(02)00830-9
Karavasilis E, Christidi F, Velonakis G, Tzanetakos D, Zalonis I, Potagas C, Andreadou E, Efstathopoulos E, Kilidireas C, Kelekis N, Evdokimidis I (2019) Hippocampal structural and functional integrity in multiple sclerosis patients with or without memory impairment: a multimodal neuroimaging study. Brain Imaging Behav 13(4):1049–1059. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-018-9924-y
Koenigs M, Barbey AK, Postle BR, Grafman J (2009) Superior parietal cortex is critical for the manipulation of information in working memory. J Neurosci 29(47):14980–14986. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3706-09.2009
Tadayonnejad R, Anderson D, Molineux ML, Mehaffey WH, Jayasuriya K, Turner RW (2010) Rebound discharge in deep cerebellar nuclear neurons in vitro. Cerebellum 9(3):352–374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12311-010-0168-7
Wolpert DM, Goodbody SJ, Husain M (1998) Maintaining internal representations: the role of the human superior parietal lobe. Nat Neurosci 1(6):529–533. https://doi.org/10.1038/2245
Koziol LF, Budding D, Andreasen N, D’Arrigo S, Bulgheroni S, Imamizu H, Ito M, Manto M, Marvel C, Parker K, Pezzulo G, Ramnani N, Riva D, Schmahmann J, Vandervert L, Yamazaki T (2014) Consensus paper: the cerebellum’s role in movement and cognition. Cerebellum 13(1):151–177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12311-013-0511-x
Stoodley CJ, Schmahmann JD (2009) Functional topography in the human cerebellum: a meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies. Neuroimage 44(2):489–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.08.039
Buckner RL, Krienen FM, Castellanos A, Diaz JC, Yeo BT (2011) The organization of the human cerebellum estimated by intrinsic functional connectivity. J Neurophysiol 106(5):2322–2345. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00339.2011
Guell X, Schmahmann JD, Gabrieli J, Ghosh SS (2018) Functional gradients of the cerebellum. Elife 7:e36652. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.36652
Buckner RL (2013) The cerebellum and cognitive function: 25 years of insight from anatomy and neuroimaging. Neuron 80(3):807–815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2013.10.044
Lu C, Yang T, Zhao H, Zhang M, Meng F, Fu H, Xie Y, Xu H (2016) Insular cortex is critical for the perception, modulation, and chronification of pain. Neurosci Bull 32(2):191–201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-016-0016-y
Bjelica B, Peric S, Basta I, Bozovic I, Kacar A, Marjanovic A, Ivanovic V, Brankovic M, Jankovic M, Novakovic I, Rakocevic Stojanovic V (2020) Neuropathic pain in patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 1A. Neurol Sci 41(3):625–630. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-019-04142-5
Evarts EV, Thach WT (1969) Motor mechanisms of the CNS: cerebrocerebellar interrelations. Annu Rev Physiol 31:451–498. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ph.31.030169.002315
Palesi F, Tournier JD, Calamante F, Muhlert N, Castellazzi G, Chard D, D’Angelo E, Wheeler-Kingshott CG (2016) Reconstructing contralateral fiber tracts: methodological aspects of cerebello-thalamocortical pathway reconstruction. Funct Neurol. 31(4):229–238. https://doi.org/10.11138/fneur/2016.31.4.229
Karavasilis E, Christidi F, Velonakis G, Giavri Z, Kelekis NL, Efstathopoulos EP, Evdokimidis I, Dellatolas G (2019) Ipsilateral and contralateral cerebro-cerebellar white matter connections: a diffusion tensor imaging study in healthy adults. J Neuroradiol 46(1):52–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurad.2018.07.004
Azevedo H, Pupe C, Pereira R, Nascimento OJM (2018) Pain in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: an update. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 76(4):273–276. https://doi.org/10.1590/0004-282x20180021
Carter GT, Jensen MP, Galer BS, Kraft GH, Crabtree LD, Beardsley RM, Abresch RT, Bird TD (1998) Neuropathic pain in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 79(12):1560–1564. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0003-9993(98)90421-x
Tanasescu R, Cottam WJ, Condon L, Tench CR, Auer DP (2016) Functional reorganisation in chronic pain and neural correlates of pain sensitisation: a coordinate based meta-analysis of 266 cutaneous pain fMRI studies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 68:120–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.04.001
Zhang Y, Qu M, Yi X, Zhuo P, Tang J, Chen X, Zhou G, Hu P, Qiu T, Xing W, Mao Y, Chen BT, Wu J, Zhang Y, Liao W (2020) Sensorimotor and pain-related alterations of the gray matter and white matter in Type 2 diabetic patients with peripheral neuropathy. Hum Brain Mapp 41(3):710–725. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.24834
Pontillo G, Dubbioso R, Cocozza S, Tozza S, Severi D, Iodice R, Tedeschi E, Elefante A, Brunetti A, Manganelli F, Quarantelli M (2020) Brain plasticity in Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 1A patients? A combined structural and diffusion MRI study. Front Neurol 11:795. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2020.00795
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all patients and healthy controls for their generosity to participate in the present study.
Funding
FC is supported by the EU-IKY Scholarship Program (European Social Fund-ESF), the Greek “Reinforcement of Postdoctoral Researchers” grant (5033021) of the “Human Resources Development Program, Education and Lifelong Learning” of the National Strategic Reference Framework (NSRF 2014–2020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Georgios Velonakis and Georgios Koutsis contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation was performed by Efstratios Karavasilis, Georgios Velonakis, Georgios Koutsis, Marianthi Breza and Constantin Potagas, method preparation was performed by Georgios Velonakis, Efstratios Karavasilis, Dimitrios Filippiadis, clinical data collection was performed by Georgia Angelopoulou, Dimitrios Kasselimis, Zoi Kontogeorgiou, Georgia Karadima, Georgios Koutsis imaging data collection and evaluation were performed by Efstratios Karavasilis, Irene Pantou, Dimitrios Fillipiadis, Georgios Velonakis, the image post-processing and statistical analysis were performed by Efstratios Karavasilis and Foteini Christidi. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Efstratios Karavasilis, Georgios Velonakis, Foteini Christidi and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
This cross-sectional study was approved by the local ethical committee and conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments.
Consent to participate
All participants provided informed consent for their participation.
Consent for publication
All participants provided informed consent for the publication of results.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
GK and GV have equal contributions
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karavasilis, E., Christidi, F., Pantou, E. et al. Structural and functional brain changes in X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: insights from a multimodal neuroimaging study. Neuroradiology 64, 543–552 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-021-02730-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-021-02730-x