Abstract
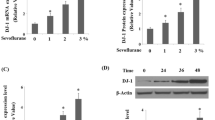
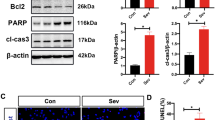
The effects of general anesthetics on the developing brain have aroused much attention in recent years. Sevoflurane, a commonly used inhalation anesthetic especially in pediatric anesthesia, can induce developmental neurotoxicity. In this study, the differentially expressed mRNAs in the hippocampus of newborn rats exposed to 3% sevoflurane for 6 h were detected by RNA-Sequencing. Those data indicated that the mRNA of Klotho was increased after exposure to sevoflurane. Moreover, the protein expression of Klotho was assayed by Western Blot. Besides over-expression and under-expression of Klotho protein, we also detected changes of cell proliferation, ROS, JC-1, and Bcl-2/Bax ratio in PC12 cells exposed to sevoflurane. After exposure to 3% sevoflurane, the expression of Klotho protein increased in the hippocampus of neonatal rats. In PC12 cells, exposure to sevoflurane could increase cellular ROS level, reduce mitochondrial membrane potential and Bcl-2/Bax ratio. While overexpression of Klotho alleviated the above changes, knockdown of Klotho aggravated the injury of sevoflurane. Klotho protein could reduce oxidative stress and mitochondrial injury induced by sevoflurane in the neuron.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Hartman R, Izumi Y, Benshoff N, Dikranian K, Zorumski C, Olney J, Wozniak D (2003) Early exposure to common anesthetic agents causes widespread neurodegeneration in the developing rat brain and persistent learning deficits. J Neurosci 23(3):876–882. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.23-03-00876.2003
Muramatsu R, Ikegaya Y, Matsuki N, Koyama R (2007) Neonatally born granule cells numerically dominate adult mice dentate gyrus. Neuroscience 148(3):593–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.06.040
Creeley C, Dikranian K, Dissen G, Back S, Olney J, Brambrink A (2014) Isoflurane-induced apoptosis of neurons and oligodendrocytes in the fetal rhesus macaque brain. Anesthesiology 120(3):626–638. https://doi.org/10.1097/aln.0000000000000037
Lu G, Zhao W, Rao D, Zhang S, Zhou M, Xu S (2019) Knockdown of long noncoding RNA WNT5A-AS restores the fate of neural stem cells exposed to sevoflurane via inhibiting WNT5A/Ryk-ROS signaling. Biomed Pharmacother 118:109334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109334
Nie Y, Li S, Yan T, Ma Y, Ni C, Wang H, Zheng H (2020) Propofol attenuates isoflurane-induced neurotoxicity and cognitive impairment in fetal and offspring mice. Anesth Analg 131(5):1616–1625. https://doi.org/10.1213/ane.0000000000004955
Ming G, Song H (2005) Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian central nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci 28:223–250. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.28.051804.101459
Deng W, Aimone J, Gage F (2010) New neurons and new memories: how does adult hippocampal neurogenesis affect learning and memory? Nat Rev Neurosci 11(5):339–350. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2822
Rice D, Barone S (2000) Critical periods of vulnerability for the developing nervous system: evidence from humans and animal models. Environ Health Perspect. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.00108s3511
Zhou X, Song F, He W, Yang X, Zhou Z, Feng X, Zhou L (2012) Neonatal exposure to sevoflurane causes apoptosis and reduces nNOS protein expression in rat hippocampus. Mol Med Rep 6(3):543–546. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2012.976
Satomoto M, Satoh Y, Terui K, Miyao H, Takishima K, Ito M, Imaki J (2009) Neonatal exposure to sevoflurane induces abnormal social behaviors and deficits in fear conditioning in mice. Anesthesiology 110(3):628–637. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181974fa2
Wang L, Tang Z, Han Y (2016) Neuroprotective effects of caffeic acid phenethyl ester against sevoflurane-induced neuronal degeneration in the hippocampus of neonatal rats involve MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Mol Med Rep 14(4):3403–3412. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2016.5586
Liu B, Xia J, Chen Y, Zhang J (2017) Sevoflurane-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress contributes to neuroapoptosis and BACE-1 expression in the developing brain: the role of eIF2α. Neurotoxicol Res 31(2):218–229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-016-9671-z
Zheng S, An L, Cheng X, Wang Y (2013) Sevoflurane causes neuronal apoptosis and adaptability changes of neonatal rats. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 57(9):1167–1174. https://doi.org/10.1111/aas.12163
Gao J, Kang XY, Sun S, Li L, Gao DS (2020) MES23.5 DA immortalized neuroblastoma cells self-protect against early injury by overexpressing glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor via Akt1/Eya1/Six2 signaling. J Mol Neurosci 70(3):328–339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-019-01416-7
Liu Y, Zhou G, Wang Z, Guo X, Xu Q, Huang Q, Su L (2015) NF-kappaB signaling is essential for resistance to heat stress-induced early stage apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Sci Rep 5:13547. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep13547
Shi Q, Zhang W, Guo S, Jian Z, Li S, Li K, Ge R, Dai W, Wang G, Gao T, Li C (2016) Oxidative stress-induced overexpression of miR-25: the mechanism underlying the degeneration of melanocytes in vitiligo. Cell Death Differ 23(3):496–508. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2015.117
Marchesini V, Disma N (2019) Anaesthetic neuroprotection in children: does it exist or is it all just bad? Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 32(3):363–369. https://doi.org/10.1097/ACO.0000000000000723
Wang Z, Gerstein M, Snyder M (2009) RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat Rev Genet 10(1):57–63. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2484
Dubal DB, Yokoyama JS, Zhu L, Broestl L, Worden K, Wang D, Sturm VE, Kim D, Klein E, Yu GQ, Ho K, Eilertson KE, Yu L, Kuro-o M, De Jager PL, Coppola G, Small GW, Bennett DA, Kramer JH, Abraham CR, Miller BL, Mucke L (2014) Life extension factor klotho enhances cognition. Cell Rep 7(4):1065–1076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2014.03.076
Laszczyk AM, Fox-Quick S, Vo HT, Nettles D, Pugh PC, Overstreet-Wadiche L, King GD (2017) Klotho regulates postnatal neurogenesis and protects against age-related spatial memory loss. Neurobiol Aging 59:41–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2017.07.008
Zeldich E, Chen CD, Colvin TA, Bove-Fenderson EA, Liang J, Tucker Zhou TB, Harris DA, Abraham CR (2014) The neuroprotective effect of Klotho is mediated via regulation of members of the redox system. J Biol Chem 289(35):24700–24715. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.567321
Mytych J, Solek P, Tabecka-Lonczynska A, Koziorowski M (2019) Klotho-mediated changes in shelterin complex promote cytotoxic autophagy and apoptosis in amitriptyline-treated hippocampal neuronal cells. Mol Neurobiol 56(10):6952–6963. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-019-1575-5
Zhang Y, Lu P, Liang F, Liufu N, Dong Y, Zheng JC, Xie Z (2019) Cyclophilin D contributes to anesthesia neurotoxicity in the developing brain. Front Cell Dev Biol 7:396. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2019.00396
Yonamine R, Satoh Y, Kodama M, Araki Y, Kazama T (2013) Coadministration of hydrogen gas as part of the carrier gas mixture suppresses neuronal apoptosis and subsequent behavioral deficits caused by neonatal exposure to sevoflurane in mice. Anesthesiology 118(1):105–113. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0b013e318275146d
Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (2011) 8th edn. National Academies Press (US), Washington, DC
Perez-Zoghbi JF, Zhu W, Grafe MR, Brambrink AM (2017) Dexmedetomidine-mediated neuroprotection against sevoflurane-induced neurotoxicity extends to several brain regions in neonatal rats. Br J Anaesth 119(3):506–516. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/aex222
Kobuszewska A, Jastrzebska E, Zukowski K, Brzozka Z (2020) Simulation of hypoxia of myocardial cells in microfluidic systems. Sci Rep 10(1):15524. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-72660-w
Kuro-o M, Matsumura Y, Aizawa H, Kawaguchi H, Suga T, Utsugi T, Ohyama Y, Kurabayashi M, Kaname T, Kume E, Iwasaki H, Iida A, Shiraki-Iida T, Nishikawa S, Nagai R, Nabeshima YI (1997) Mutation of the mouse klotho gene leads to a syndrome resembling ageing. Nature 390(6655):45–51. https://doi.org/10.1038/36285
Kurosu H, Yamamoto M, Clark JD, Pastor JV, Nandi A, Gurnani P, McGuinness OP, Chikuda H, Yamaguchi M, Kawaguchi H, Shimomura I, Takayama Y, Herz J, Kahn CR, Rosenblatt KP, Kuro-o M (2005) Suppression of aging in mice by the hormone Klotho. Science 309(5742):1829–1833. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1112766
Clinton SM, Glover ME, Maltare A, Laszczyk AM, Mehi SJ, Simmons RK, King GD (2013) Expression of klotho mRNA and protein in rat brain parenchyma from early postnatal development into adulthood. Brain Res 1527:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2013.06.044
Shiozaki M, Yoshimura K, Shibata M, Koike M, Matsuura N, Uchiyama Y, Gotow T (2008) Morphological and biochemical signs of age-related neurodegenerative changes in klotho mutant mice. Neuroscience 152(4):924–941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.01.032
Abraham CR, Chen C, Cuny GD, Glicksman MA, Zeldich E (2012) Small-molecule Klotho enhancers as novel treatment of neurodegeneration. Future Med Chem 4(13):1671–1679. https://doi.org/10.4155/fmc.12.134
Slotkin TA, MacKillop EA, Ryde IT, Seidler FJ (2007) Ameliorating the developmental neurotoxicity of chlorpyrifos: a mechanisms-based approach in PC12 cells. Environ Health Perspect 115(9):1306–1313. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.10194
Li P, Ma R, Dong L, Liu L, Zhou G, Tian Z, Zhao Q, Xia T, Zhang S, Wang A (2019) Autophagy impairment contributes to PBDE-47-induced developmental neurotoxicity and its relationship with apoptosis. Theranostics 9(15):4375–4390. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.33688
Lerman J, Sikich N, Kleinman S, Yentis S (1994) The pharmacology of sevoflurane in infants and children. Anesthesiology 80(4):814–824. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000542-199404000-00014
Feng X, Liu JJ, Zhou X, Song FH, Yang XY, Chen XS, Huang WQ, Zhou LH, Ye JH (2012) Single sevoflurane exposure decreases neuronal nitric oxide synthase levels in the hippocampus of developing rats. Br J Anaesth 109(2):225–233. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/aes121
Zhang Y, Dong Y, Wu X, Lu Y, Xu Z, Knapp A, Yue Y, Xu T, Xie Z (2010) The mitochondrial pathway of anesthetic isoflurane-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 285(6):4025–4037. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.065664
Zhu X, Yao Y, Guo M, Li J, Yang P, Xu H, Lin D (2021) Sevoflurane increases intracellular calcium to induce mitochondrial injury and neuroapoptosis. Toxicol Lett 336:11–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2020.11.002
Suen DF, Norris KL, Youle RJ (2008) Mitochondrial dynamics and apoptosis. Genes Dev 22(12):1577–1590. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1658508
Abraham CR, Mullen PC, Tucker-Zhou T, Chen CD, Zeldich E (2016) Klotho is a neuroprotective and cognition-enhancing protein. Vitam Horm 101:215–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.vh.2016.02.004
Adeli S, Zahmatkesh M, Tavoosidana G, Karimian M, Hassanzadeh G (2017) Simvastatin enhances the hippocampal klotho in a rat model of streptozotocin-induced cognitive decline. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 72:87–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2016.09.009
Yamamoto M, Clark JD, Pastor JV, Gurnani P, Nandi A, Kurosu H, Miyoshi M, Ogawa Y, Castrillon DH, Rosenblatt KP, Kuro-o M (2005) Regulation of oxidative stress by the anti-aging hormone klotho. J Biol Chem 280(45):38029–38034. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M509039200
Funding
This study was supported by Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation, Guangdong Province, China (No. 2021A1515011414).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have financial relationships with biotechnology manufacturers, pharmaceutical companies, or other commercial entities with an interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscripts.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lian, WY., Lu, ZP., Zhao, W. et al. The Role of Klotho Protein Against Sevoflurane-Induced Neuronal Injury. Neurochem Res 47, 315–326 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03444-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03444-5